The landscape of three-dimensional modeling and digital content creation has experienced a revolutionary transformation with the integration of artificial intelligence technologies. Two prominent platforms have emerged as leaders in this evolution: NVIDIA Omniverse, a comprehensive collaboration and simulation platform, and Blender, the open-source 3D creation suite enhanced with cutting-edge AI capabilities. The convergence of artificial intelligence with traditional 3D modeling workflows has fundamentally altered how artists, designers, and developers approach digital content creation, offering unprecedented levels of automation, intelligence, and creative possibility.
Explore the latest AI trends in creative technology to understand how artificial intelligence is reshaping industries beyond traditional software development. The integration of AI into 3D modeling represents a paradigm shift that extends far beyond simple automation, encompassing intelligent content generation, procedural creation techniques, and collaborative workflows that bridge the gap between human creativity and machine learning capabilities.
The Evolution of AI-Powered 3D Creation
The traditional approach to 3D modeling has historically required extensive technical expertise, time-intensive manual processes, and deep understanding of complex software interfaces. The introduction of AI-powered tools has democratized access to sophisticated 3D creation capabilities while simultaneously enhancing the productivity and creative potential of experienced professionals. This transformation represents more than technological advancement; it signifies a fundamental reimagining of how digital content is conceived, created, and refined in modern creative workflows.
NVIDIA Omniverse and Blender represent two distinct approaches to AI integration in 3D modeling, each offering unique advantages and targeting different aspects of the creative pipeline. Omniverse leverages NVIDIA’s extensive expertise in GPU computing, real-time ray tracing, and collaborative technologies to create a comprehensive platform that facilitates seamless collaboration between multiple software applications and creative teams. Blender, conversely, has embraced AI through community-driven development and open-source innovation, integrating machine learning capabilities directly into its core modeling, rendering, and animation systems.
NVIDIA Omniverse: Enterprise-Grade AI Collaboration
NVIDIA Omniverse represents a revolutionary approach to collaborative 3D content creation, built upon the foundation of Universal Scene Description (USD) and powered by advanced AI technologies. The platform serves as a comprehensive ecosystem that enables real-time collaboration between artists using different software applications, while leveraging artificial intelligence to enhance various aspects of the creative process. Omniverse’s AI capabilities extend across multiple domains, including automated scene optimization, intelligent asset management, and advanced rendering techniques that utilize machine learning for enhanced visual quality and performance.
The platform’s AI-driven features include sophisticated denoising algorithms that accelerate rendering times while maintaining visual fidelity, intelligent upscaling techniques that enhance texture quality, and automated optimization systems that streamline complex scenes for real-time collaboration. Omniverse’s integration with NVIDIA’s broader AI ecosystem, including technologies like DLSS and RTX, creates a comprehensive environment where artificial intelligence enhances every aspect of the 3D creation pipeline from initial concept to final rendering.
Experience advanced AI capabilities with Claude for complex problem-solving and creative assistance that complements technical 3D modeling workflows. The synergy between AI assistants and specialized 3D creation tools creates unprecedented opportunities for innovation and creative expression in digital content development.
Blender’s Open-Source AI Revolution
Blender’s approach to AI integration represents the power of community-driven innovation and open-source development in advancing creative technologies. The platform has incorporated machine learning capabilities through various addons, built-in features, and community contributions that enhance traditional 3D modeling workflows with intelligent automation and creative assistance. Blender’s AI tools span multiple disciplines, including procedural generation, texture synthesis, animation enhancement, and rendering optimization, all integrated seamlessly into the familiar Blender interface.
The open-source nature of Blender has facilitated rapid innovation in AI integration, with developers worldwide contributing specialized tools that address specific creative challenges. These contributions include AI-powered geometry nodes that enable procedural modeling based on machine learning algorithms, texture generation systems that create realistic materials from minimal input, and animation tools that utilize artificial intelligence to enhance character movement and environmental dynamics. The accessibility and flexibility of Blender’s architecture have made it an ideal platform for experimenting with cutting-edge AI techniques in 3D creation.
Comparative Analysis of AI Capabilities
The fundamental differences between NVIDIA Omniverse and Blender’s AI implementations reflect their distinct philosophical approaches to creative technology. Omniverse prioritizes enterprise-grade collaboration, seamless software integration, and performance optimization through dedicated hardware acceleration. The platform’s AI capabilities are deeply integrated with NVIDIA’s GPU architecture, enabling real-time ray tracing, advanced denoising, and collaborative rendering that scales across multiple workstations and cloud environments.
Blender’s AI integration emphasizes accessibility, community innovation, and creative experimentation within a comprehensive open-source framework. The platform’s machine learning capabilities focus on enhancing individual artist productivity through intelligent automation, procedural generation, and creative assistance tools that integrate naturally with existing workflows. While Blender may not match Omniverse’s enterprise collaboration features, its open-source nature enables rapid prototyping and implementation of experimental AI techniques that push the boundaries of creative possibility.
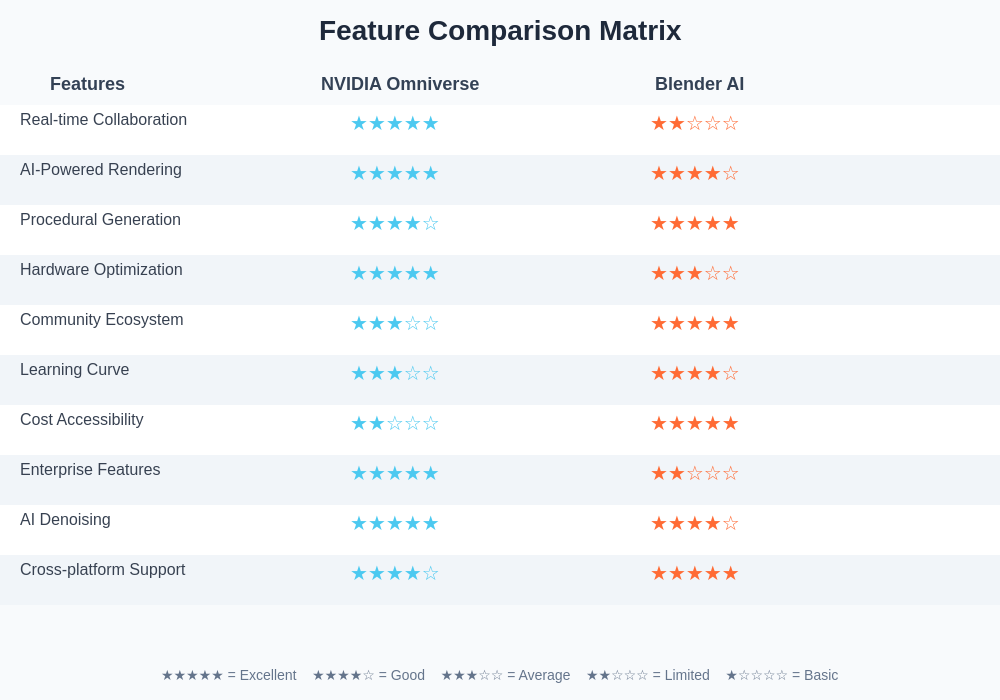
The detailed analysis of features across both platforms demonstrates their distinct positioning within the 3D creation market, with each excelling in different areas that align with their core design philosophies and target audiences.
Real-Time Collaboration and AI Enhancement
One of the most significant advantages of NVIDIA Omniverse lies in its revolutionary approach to real-time collaboration in 3D environments. The platform enables multiple artists to work simultaneously on the same project using different software applications, with AI systems managing synchronization, conflict resolution, and performance optimization across distributed teams. This capability transforms traditional 3D production pipelines by eliminating the bottlenecks associated with file sharing, version control, and software compatibility issues that have historically plagued collaborative creative projects.
The AI systems within Omniverse continuously monitor collaborative sessions, automatically optimizing scene complexity based on network conditions and hardware capabilities while maintaining visual fidelity across all connected clients. Machine learning algorithms analyze usage patterns and predict optimal resource allocation, ensuring smooth collaboration regardless of team size or geographic distribution. This intelligent collaboration framework represents a fundamental advancement in how creative teams approach complex 3D projects, enabling unprecedented levels of real-time creative interaction and iterative refinement.
Procedural Generation and Creative AI
Both platforms have embraced procedural generation as a key application of artificial intelligence in 3D modeling, though their implementations reflect their respective design philosophies. NVIDIA Omniverse leverages AI-driven procedural techniques primarily for optimization and automation within collaborative workflows, utilizing machine learning to generate efficient level-of-detail models, optimize texture streaming, and manage complex scene hierarchies automatically. These systems operate transparently, enhancing performance and workflow efficiency without requiring extensive user intervention or technical expertise.
Blender’s approach to procedural AI generation emphasizes creative empowerment and artistic exploration through accessible tools that enable artists to experiment with machine learning-driven content creation. The platform’s geometry nodes system incorporates AI algorithms that can generate complex organic forms, architectural structures, and natural phenomena based on minimal user input and creative guidance. This creative-focused approach to procedural generation democratizes access to sophisticated content creation techniques while maintaining the artistic control and creative flexibility that define Blender’s design philosophy.
Enhance your research and development with Perplexity for comprehensive information gathering about emerging AI techniques and 3D modeling innovations. The rapid evolution of AI in creative applications requires continuous learning and adaptation to stay current with technological advancements.
Rendering and Performance Optimization
The rendering capabilities of both platforms showcase distinct approaches to AI-enhanced visual computation. NVIDIA Omniverse leverages the company’s extensive expertise in GPU acceleration and real-time ray tracing to deliver cutting-edge rendering performance enhanced by AI denoising, upscaling, and optimization algorithms. The platform’s integration with RTX technology enables real-time global illumination, accurate reflections, and sophisticated material rendering that would be impossible without AI acceleration. These capabilities transform the creative process by providing immediate visual feedback during modeling and design phases, eliminating the traditional wait times associated with high-quality rendering.
Blender’s rendering improvements through AI focus on accessibility and creative flexibility rather than pure performance optimization. The platform incorporates machine learning-enhanced denoising algorithms, intelligent sampling techniques, and AI-driven material generation that improve rendering quality while remaining accessible to users without specialized hardware. Blender’s open-source nature has enabled the integration of community-developed AI rendering techniques that push creative boundaries while maintaining compatibility with diverse hardware configurations and budget constraints.
Workflow Integration and Learning Curves
The integration of AI capabilities into existing 3D modeling workflows presents different challenges and opportunities for each platform. NVIDIA Omniverse is designed to integrate seamlessly with established production pipelines, supporting popular 3D applications like Maya, 3ds Max, and Substance Designer while adding AI-enhanced collaboration and optimization capabilities. This approach minimizes disruption to existing workflows while providing immediate benefits through intelligent automation and enhanced performance. The platform’s enterprise focus means that AI features are implemented with production stability and reliability as primary considerations.
Blender’s AI integration follows a more experimental and creative approach, often requiring users to actively explore and implement AI-enhanced workflows through addons, custom nodes, and community-developed tools. While this approach demands greater technical engagement from users, it also provides unprecedented flexibility for creative experimentation and custom workflow development. The learning curve for Blender’s AI features varies significantly depending on the specific tools and techniques employed, ranging from intuitive visual interfaces to advanced scripting and node-based systems that require technical expertise.

The structural differences in workflow implementation demonstrate how each platform’s design philosophy influences the practical application of AI technologies in creative production environments.
Hardware Requirements and Scalability
The hardware demands of AI-enhanced 3D modeling vary significantly between NVIDIA Omniverse and Blender, reflecting their different target audiences and technical approaches. Omniverse is optimized for NVIDIA’s GPU ecosystem, particularly RTX series graphics cards that provide dedicated AI acceleration hardware. This optimization enables exceptional performance for AI-enhanced rendering, real-time collaboration, and complex scene management, but requires significant hardware investment for optimal results. The platform’s enterprise focus justifies these requirements through enhanced productivity, collaboration capabilities, and rendering performance that scales effectively across professional production environments.
Blender’s AI capabilities are designed to be more hardware-agnostic, supporting diverse GPU configurations and CPU-based processing for users without access to specialized AI acceleration hardware. While Blender can leverage NVIDIA’s CUDA and OptiX technologies when available, the platform’s open-source nature ensures compatibility with AMD graphics cards, integrated graphics solutions, and CPU-only configurations. This accessibility makes AI-enhanced 3D modeling available to a broader audience, though performance may vary significantly based on hardware capabilities and specific AI feature utilization.
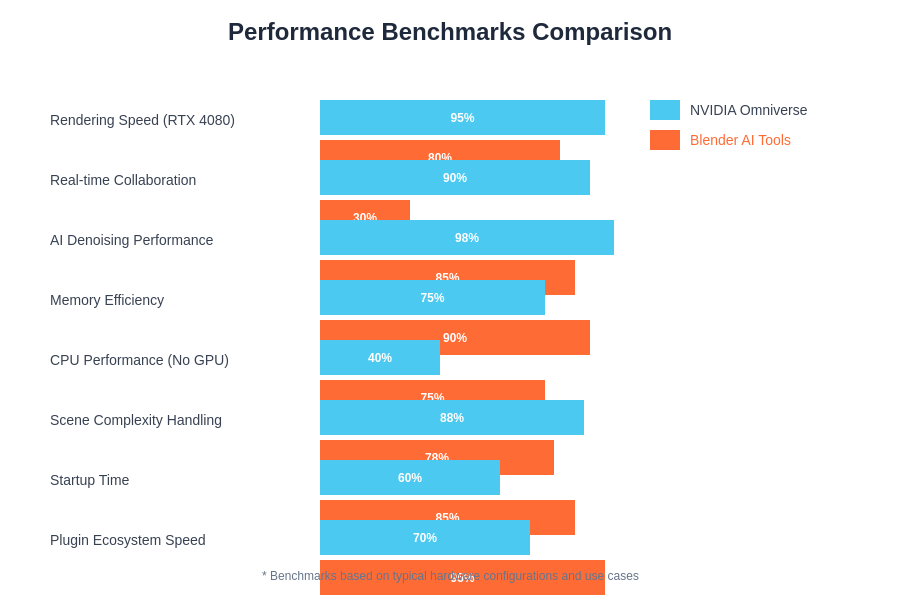
The quantitative analysis of performance across different hardware configurations and use cases reveals significant variations in how each platform leverages available computational resources, with distinct advantages emerging based on specific workflow requirements and hardware availability.
Community and Ecosystem Development
The development ecosystems surrounding NVIDIA Omniverse and Blender represent fundamentally different approaches to innovation and community engagement in AI-enhanced 3D modeling. Omniverse benefits from NVIDIA’s substantial corporate resources, extensive research and development capabilities, and partnerships with major software vendors and content creation studios. This corporate backing enables rapid development of cutting-edge AI technologies, comprehensive technical support, and integration with industry-standard production pipelines. The platform’s ecosystem development follows a structured approach that prioritizes stability, compatibility, and enterprise-grade features.
Blender’s community-driven development model has fostered an extraordinarily vibrant and innovative ecosystem of AI-enhanced tools, addons, and creative techniques. The open-source nature of the platform enables rapid experimentation with emerging AI technologies, community-driven problem-solving, and diverse perspectives on creative AI implementation. This approach has resulted in a rich ecosystem of specialized tools that address niche creative challenges while pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with AI in 3D modeling. The community’s collaborative spirit has accelerated innovation in areas that might not receive immediate attention from corporate development teams.
Industry Applications and Use Cases
The practical applications of AI-enhanced 3D modeling through both platforms span diverse industries and creative disciplines, each leveraging the unique strengths of their respective AI implementations. NVIDIA Omniverse has found significant adoption in architectural visualization, automotive design, film production, and enterprise collaboration scenarios where real-time collaboration and high-performance rendering are critical requirements. The platform’s AI capabilities enhance these applications through intelligent scene optimization, collaborative workflow management, and rendering performance that enables real-time creative iteration across distributed teams.
Blender’s AI tools have empowered independent artists, small studios, educational institutions, and creative experimenters to explore sophisticated 3D modeling techniques that were previously accessible only to well-funded production teams. The platform’s applications include procedural game asset creation, architectural visualization, scientific visualization, and artistic exploration of AI-generated content. Blender’s accessibility has democratized access to AI-enhanced 3D creation, enabling innovative applications in fields ranging from academic research to independent film production.
Cost Analysis and Accessibility
The financial implications of adopting AI-enhanced 3D modeling tools represent a crucial consideration for individuals and organizations evaluating these platforms. NVIDIA Omniverse follows a freemium model with basic collaboration features available at no cost, while advanced enterprise features, cloud services, and specialized AI capabilities require subscription fees that can represent significant ongoing expenses for professional teams. The platform’s hardware requirements for optimal performance add substantial upfront costs, particularly for teams requiring multiple high-end workstations with RTX graphics cards.
Blender’s open-source nature eliminates software licensing costs entirely, making AI-enhanced 3D modeling accessible to users regardless of budget constraints. The platform’s community-driven development model means that many AI tools and addons are available freely, though some specialized commercial addons may require modest fees. The primary costs associated with Blender adoption relate to hardware, training, and potential productivity differences compared to specialized commercial alternatives. This cost structure has made Blender an attractive option for educational institutions, independent creators, and organizations seeking to minimize software licensing expenses.
Future Development Trajectories
The future evolution of AI in 3D modeling promises continued innovation and convergence between these platforms’ distinctive approaches. NVIDIA Omniverse is likely to expand its AI capabilities through deeper integration with emerging technologies like neural rendering, AI-driven content generation, and enhanced collaboration features that leverage machine learning for intelligent project management and creative assistance. The platform’s corporate backing and hardware optimization provide substantial resources for developing cutting-edge AI applications that push the boundaries of real-time 3D creation and collaboration.
Blender’s future AI development will likely continue following community-driven innovation patterns, with increasing integration of machine learning capabilities into core modeling, animation, and rendering systems. The platform’s open-source nature positions it well for rapid adoption of emerging AI techniques, experimental feature development, and creative applications that explore the artistic potential of machine learning in 3D creation. The continued growth of Blender’s community and ecosystem suggests accelerating innovation in AI-enhanced creative tools and techniques.
The convergence of AI technologies with traditional 3D modeling represents just the beginning of a broader transformation in digital content creation. Both NVIDIA Omniverse and Blender are positioned to play significant roles in this evolution, each contributing unique perspectives and capabilities that will shape the future of AI-enhanced creative workflows. The ultimate impact of these developments will depend on continued innovation, community adoption, and the creative vision of artists and developers who push these technologies toward new applications and artistic possibilities.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional advice. The information presented is based on current understanding of AI technologies and 3D modeling platforms as of the publication date. Readers should conduct their own research and evaluate their specific requirements when selecting 3D modeling tools and AI-enhanced workflows. Performance characteristics, feature availability, and pricing models may vary based on specific use cases, hardware configurations, and software versions. The effectiveness of AI tools depends on individual expertise, project requirements, and technical environment considerations.