The intersection of artificial intelligence and legal frameworks has created an unprecedented challenge for organizations seeking to harness the power of machine learning while maintaining regulatory compliance and mitigating legal risks. As AI systems become increasingly sophisticated and integrated into critical business operations, the complexity of contract negotiation for ML services has evolved far beyond traditional software licensing agreements, demanding a nuanced understanding of emerging legal doctrines, liability structures, and regulatory requirements that continue to evolve at a rapid pace.
Stay updated with the latest AI legal developments as regulatory frameworks and industry standards continue to evolve in response to technological advancement. The legal landscape surrounding artificial intelligence represents one of the most dynamic areas of contemporary law, where traditional contractual frameworks must adapt to accommodate the unique characteristics and risks associated with machine learning systems and their deployment across diverse industries and jurisdictions.
The Evolution of AI Contract Law
The emergence of artificial intelligence as a transformative business tool has necessitated a fundamental reconceptualization of how legal agreements are structured, negotiated, and enforced in the context of machine learning services. Traditional software contracts, which typically focused on defined functionalities and predictable outcomes, prove inadequate when dealing with AI systems that learn, adapt, and evolve over time, creating novel legal challenges that require innovative contractual solutions and risk allocation mechanisms.
The dynamic nature of machine learning systems introduces unprecedented complexities in contract drafting, as parties must account for the probabilistic nature of AI outputs, the potential for algorithmic bias, and the continuous evolution of model performance over time. Legal practitioners and business stakeholders must navigate a landscape where traditional concepts of warranty, performance guarantees, and liability allocation require careful reconsideration in light of the inherent uncertainties and emergent behaviors characteristic of sophisticated AI systems.
Liability Frameworks and Risk Allocation
One of the most critical aspects of AI contract negotiation involves the establishment of comprehensive liability frameworks that adequately address the unique risks associated with machine learning deployments. Unlike traditional software applications that operate within predictable parameters, AI systems can produce unexpected outcomes, exhibit biased behavior, or fail in ways that are difficult to anticipate or prevent, creating complex questions about responsibility and accountability that must be addressed through carefully crafted contractual provisions.
The allocation of liability in AI contracts requires sophisticated understanding of the various stakeholders involved in the machine learning lifecycle, from data providers and model developers to deployment platforms and end-users. Each party in this ecosystem contributes to the overall risk profile of the AI system, and contracts must establish clear boundaries of responsibility while providing mechanisms for addressing situations where multiple parties may share accountability for adverse outcomes or system failures.
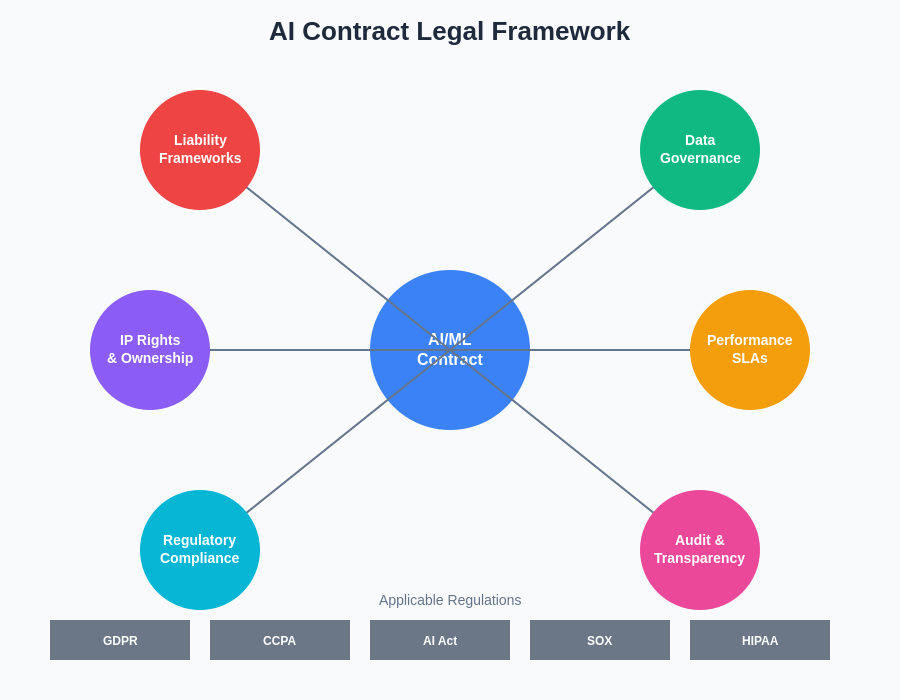
The comprehensive legal framework for AI contracts encompasses multiple interconnected domains that must be carefully balanced to ensure effective risk management while enabling innovation and operational efficiency. Each component of this framework represents a critical area of negotiation that requires specialized expertise and careful consideration of both current and emerging legal requirements.
Explore advanced AI tools like Claude to understand the technical complexities that inform legal risk assessment in machine learning deployments. The technical sophistication of modern AI systems demands that legal professionals develop deep understanding of underlying technologies to craft effective contractual protections and risk mitigation strategies.
Data Governance and Privacy Compliance
The foundation of any machine learning system lies in its training data, making data governance and privacy compliance central considerations in AI contract negotiation. Organizations must navigate complex regulatory environments that include the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation, the California Consumer Privacy Act, and numerous sector-specific regulations that impose strict requirements on data collection, processing, and retention practices that directly impact how AI systems can be developed, deployed, and maintained.
Contracts for AI services must establish comprehensive frameworks for data handling that address not only initial training data requirements but also ongoing data collection, model retraining protocols, and data retention policies that align with evolving privacy regulations. The global nature of many AI deployments adds additional complexity, as organizations must ensure compliance with data localization requirements, cross-border transfer restrictions, and varying privacy standards across different jurisdictions where their AI systems operate.
The challenge of maintaining privacy compliance in AI systems is further complicated by the inherent difficulty of anonymizing training data, the potential for models to inadvertently memorize sensitive information, and the emerging recognition that machine learning models themselves may constitute personal data under certain regulatory frameworks, requiring novel approaches to consent management, data subject rights, and breach notification procedures.
Intellectual Property Rights and Model Ownership
The question of intellectual property ownership in AI systems presents complex legal challenges that must be carefully addressed in machine learning service contracts. Traditional software licensing models prove inadequate when dealing with AI systems that may be trained on vast datasets containing copyrighted materials, generate novel outputs that may qualify for intellectual property protection, or incorporate pre-trained models with unclear ownership lineages that complicate the establishment of clear title and usage rights.
Organizations entering into AI service agreements must negotiate clear frameworks for intellectual property ownership that address not only the underlying algorithms and model architectures but also the training data, derived models, and generated outputs that result from AI system operation. The collaborative nature of many AI development projects, where multiple parties contribute data, expertise, and computational resources, requires sophisticated licensing structures that protect each party’s contributions while enabling effective system deployment and operation.
The emergence of foundation models and large language models has introduced additional complexity to intellectual property negotiations, as organizations must consider the implications of using models that may have been trained on copyrighted content, the potential for model outputs to infringe existing intellectual property rights, and the evolving legal landscape surrounding fair use and transformative applications in the context of machine learning systems.
Performance Standards and Service Level Agreements
Establishing meaningful performance standards and service level agreements for AI systems presents unique challenges that distinguish machine learning contracts from traditional software agreements. The probabilistic nature of AI outputs means that traditional metrics of software performance, such as uptime and response times, must be supplemented with sophisticated measures of accuracy, bias, fairness, and robustness that reflect the unique characteristics and limitations of machine learning systems.
Contract negotiations must address the inherent trade-offs in AI system performance, acknowledging that improvements in one metric may come at the cost of degradation in others, and that the optimal configuration of an AI system may vary depending on specific use cases, data distributions, and business requirements that evolve over time. Service level agreements must account for the continuous learning nature of many AI systems, establishing protocols for model updates, performance monitoring, and remediation procedures when systems fail to meet established benchmarks.
The challenge of defining appropriate performance metrics is further complicated by the need to address potential biases and fairness concerns that may not be apparent through traditional accuracy measures, requiring the development of comprehensive evaluation frameworks that consider the impact of AI decisions on different demographic groups, the potential for discriminatory outcomes, and the broader societal implications of automated decision-making systems.
Leverage research capabilities like Perplexity to stay current with evolving performance measurement standards and fairness metrics that inform contemporary AI contract negotiations. The rapid advancement of evaluation methodologies and fairness frameworks requires continuous learning and adaptation to ensure contracts reflect current best practices and regulatory expectations.
Regulatory Compliance and Evolving Standards
The regulatory landscape governing artificial intelligence continues to evolve rapidly, with new legislation, regulatory guidance, and industry standards emerging regularly across multiple jurisdictions, creating significant challenges for organizations seeking to establish long-term AI service agreements that remain compliant with changing legal requirements. Contract negotiations must anticipate future regulatory developments while establishing flexible frameworks that can adapt to new compliance obligations without requiring complete renegotiation of existing agreements.
The European Union’s proposed Artificial Intelligence Act represents the most comprehensive attempt to regulate AI systems to date, establishing risk-based classifications that impose varying levels of compliance obligations depending on the intended use and potential impact of AI applications. Organizations operating in multiple jurisdictions must navigate the complexity of ensuring compliance with divergent regulatory approaches while maintaining operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness in their AI deployments.
Industry-specific regulations add another layer of complexity to AI contract negotiations, as organizations in healthcare, financial services, transportation, and other regulated sectors must ensure that their AI systems comply with sector-specific requirements that may impose additional constraints on data handling, decision-making processes, and audit trails that must be reflected in service agreements and operational protocols.
Audit Rights and Transparency Obligations
The increasing demand for transparency and explainability in AI systems has created new contractual obligations around audit rights, documentation requirements, and ongoing monitoring that extend far beyond traditional software audit provisions. Organizations must negotiate agreements that provide appropriate access to model performance data, training methodologies, and decision-making processes while protecting proprietary information and maintaining operational security.
Contract negotiations must balance the legitimate need for transparency with practical constraints around trade secret protection, competitive advantage, and operational security that may limit the extent to which AI service providers can fully disclose their methodologies and data sources. The challenge is particularly acute in regulated industries where compliance requirements may mandate extensive documentation and audit capabilities that conflict with providers’ desires to protect intellectual property and maintain competitive positioning.
The emergence of algorithmic auditing as a distinct professional practice has created new service categories and contractual relationships that must be carefully structured to ensure independence, objectivity, and effectiveness while providing clear boundaries around scope, methodology, and reporting obligations that serve the interests of all stakeholders in the AI ecosystem.
Cross-Border Data Transfers and Jurisdictional Issues
The global nature of many AI applications creates complex jurisdictional challenges that must be addressed through carefully crafted contract provisions governing data transfers, dispute resolution, and regulatory compliance across multiple legal systems. Organizations must navigate the intricacies of data localization requirements, restrictions on cross-border data transfers, and varying national security considerations that may impact where AI systems can be deployed and how they can access and process data.
The extraterritorial application of various privacy and security regulations means that organizations may be subject to multiple, potentially conflicting legal obligations that must be reconciled through sophisticated contract structures and operational procedures. The challenge is particularly acute for AI systems that operate across multiple jurisdictions, where different regulatory frameworks may impose incompatible requirements on data handling, algorithmic transparency, and user consent mechanisms.
Contract negotiations must establish clear frameworks for addressing conflicts of law, determining applicable jurisdiction for dispute resolution, and managing the practical challenges of compliance with multiple regulatory regimes while maintaining operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness in global AI deployments.
Termination and Data Retention Considerations
The termination of AI service agreements presents unique challenges that extend beyond traditional software contract termination provisions, particularly regarding the handling of trained models, learned parameters, and derived insights that may have been generated during the course of the service relationship. Organizations must negotiate clear protocols for model deletion, data destruction, and intellectual property transfer that address the technical realities of machine learning systems while protecting legitimate business interests and ensuring regulatory compliance.
The challenge is complicated by the technical difficulty of completely removing specific data influences from trained models, the potential value of learned insights that transcend individual data points, and the practical considerations around backup systems, disaster recovery procedures, and archived data that may retain AI-generated information long after formal service termination.
Contract provisions must address the handling of ongoing model performance data, user interaction logs, and feedback information that may be essential for system operation but also represent potential privacy and security risks if not properly managed during the termination process, requiring sophisticated understanding of both technical and legal constraints that govern data lifecycle management in AI systems.
Insurance and Indemnification Strategies
The unique risk profile of AI systems has created new considerations for insurance coverage and indemnification provisions that must account for the potential for widespread harm, algorithmic bias claims, privacy violations, and intellectual property infringement that may result from AI system operation. Traditional software liability insurance may prove inadequate for addressing the scale and nature of potential AI-related claims, requiring specialized coverage and risk assessment methodologies.
Contract negotiations must address the allocation of insurance obligations between different parties in the AI ecosystem, establishing clear frameworks for coverage requirements, deductible responsibilities, and claim handling procedures that account for the complex causation chains that may be involved in AI-related incidents. The challenge is particularly acute given the limited availability of AI-specific insurance products and the difficulty of accurately assessing and pricing AI-related risks.
Indemnification provisions must be carefully crafted to address the unique characteristics of AI systems, including the potential for emergent behaviors, the difficulty of predicting failure modes, and the possibility that multiple parties may bear responsibility for adverse outcomes through their contributions to training data, model development, or deployment decisions that collectively influence system behavior.
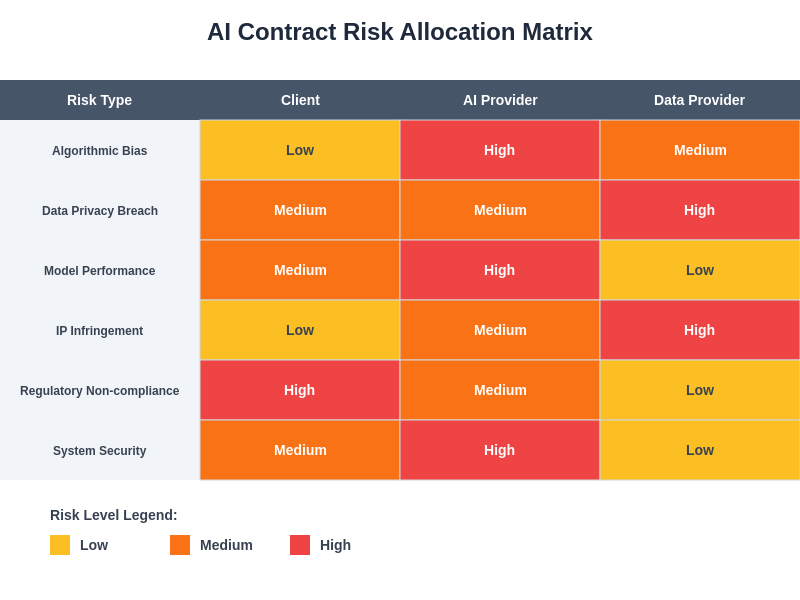
The systematic allocation of risks across different stakeholders in AI projects requires careful analysis of each party’s role, expertise, and ability to control specific risk factors. This matrix approach enables more precise contract negotiations by clearly defining responsibility boundaries and establishing appropriate insurance and indemnification requirements for each category of potential liability.
Future-Proofing AI Contracts
The rapid pace of technological advancement in artificial intelligence creates significant challenges for organizations seeking to establish long-term service agreements that remain relevant and effective as AI capabilities continue to evolve. Contract negotiations must anticipate future developments in AI technology, regulatory frameworks, and industry standards while establishing flexible mechanisms for adapting existing agreements to accommodate new requirements and capabilities.
The challenge of future-proofing AI contracts requires careful consideration of emerging technologies such as federated learning, differential privacy, and advanced explainability techniques that may fundamentally alter how AI systems are developed, deployed, and regulated. Organizations must establish contractual frameworks that can accommodate these technological developments while maintaining clear boundaries around performance obligations, liability allocation, and intellectual property rights.
The increasing integration of AI systems with other emerging technologies, including blockchain, quantum computing, and edge computing platforms, creates additional complexity for contract negotiations as organizations must consider the implications of technological convergence for their existing agreements and future development strategies, requiring sophisticated understanding of both current capabilities and anticipated technological trajectories.
The evolution of AI governance frameworks and industry standards will continue to influence contract negotiations as organizations seek to align their agreements with best practices and regulatory expectations while maintaining operational flexibility and competitive advantage in rapidly evolving markets. The key to successful AI contract negotiation lies in balancing the need for comprehensive risk management with the practical requirements of innovation and business development in an environment of continuous technological and regulatory change.
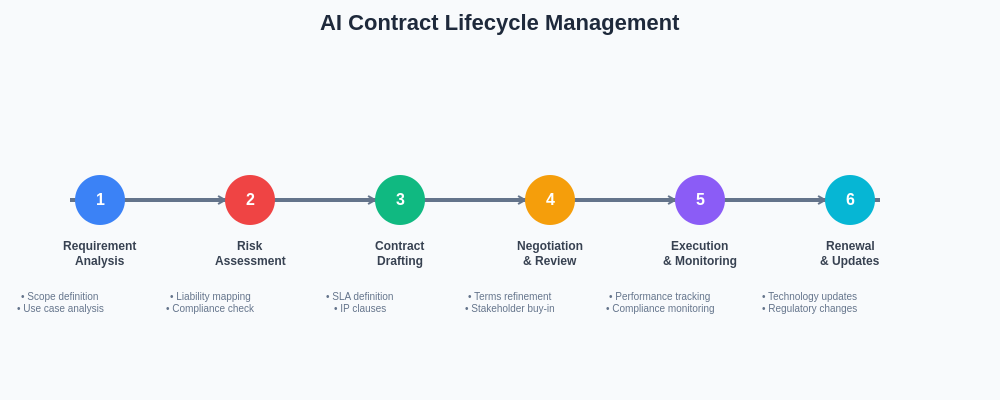
Effective AI contract management requires a structured approach to the entire contract lifecycle, from initial requirement analysis through ongoing monitoring and renewal processes. Each stage of this lifecycle presents unique challenges and opportunities that must be carefully managed to ensure long-term success and compliance in AI deployments.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal advice. The legal landscape surrounding artificial intelligence and machine learning is rapidly evolving, and specific requirements may vary significantly based on jurisdiction, industry, and use case. Organizations should consult with qualified legal professionals who specialize in technology law and AI governance when negotiating machine learning service agreements. The effectiveness of contractual provisions may depend on specific circumstances, regulatory requirements, and evolving legal interpretations of AI-related obligations and liabilities.
