The convergence of artificial intelligence and the General Data Protection Regulation represents one of the most significant regulatory challenges facing organizations today. As machine learning systems become increasingly sophisticated and pervasive in processing personal data, the imperative to ensure compliance with European privacy law has never been more critical. The GDPR’s comprehensive framework for data protection creates a complex landscape that AI developers, data scientists, and organizations must navigate carefully to avoid substantial penalties while maintaining the innovative potential of artificial intelligence technologies.
Stay updated with the latest AI compliance trends to understand how regulatory frameworks are evolving alongside technological advancement. The intersection of privacy law and artificial intelligence represents a rapidly evolving domain where technical innovation must harmonize with fundamental privacy rights and regulatory requirements established by the European Union to protect individual data subjects.
Understanding GDPR Fundamentals in AI Context
The General Data Protection Regulation fundamentally transforms how organizations must approach personal data processing, particularly when artificial intelligence systems are involved. The regulation establishes stringent requirements for lawful processing, consent mechanisms, data subject rights, and accountability measures that directly impact how machine learning models can be developed, trained, and deployed. Understanding these foundational principles becomes essential for any organization seeking to leverage AI technologies while maintaining compliance with European privacy law.
The GDPR’s emphasis on transparency, purpose limitation, and data minimization creates particular challenges for AI systems that often rely on large datasets and complex algorithmic processing that may not easily align with traditional privacy frameworks. Organizations must carefully consider how their AI initiatives intersect with the regulation’s core principles, including lawfulness of processing, fairness in automated decision-making, and the fundamental requirement to respect individual privacy rights throughout the entire machine learning lifecycle.
The regulatory framework requires organizations to implement privacy by design and privacy by default principles, which means that data protection considerations must be integrated into AI systems from the earliest stages of development rather than being retrofitted as compliance afterthoughts. This proactive approach to privacy protection demands a comprehensive understanding of both the technical aspects of machine learning and the legal requirements established by the GDPR.
Lawful Bases for AI Data Processing
Establishing appropriate lawful bases for processing personal data within AI systems represents one of the most critical compliance challenges organizations face under the GDPR. The regulation provides six potential lawful bases for processing, including consent, contract performance, legal obligations, vital interests, public tasks, and legitimate interests, each carrying distinct implications for how AI systems can collect, process, and utilize personal data.
Consent as a lawful basis requires that individuals provide freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous indication of their agreement to data processing, which can prove challenging in AI contexts where the full scope of data utilization may not be predictable at the time of collection. The dynamic nature of machine learning algorithms and their potential for discovering unexpected patterns in data creates complexity in obtaining truly informed consent that accurately reflects how personal information will ultimately be processed.
Legitimate interests provide an alternative lawful basis that many organizations find more practical for AI applications, requiring a careful balancing test between organizational interests and individual privacy rights. This approach demands thorough documentation of the legitimate interest assessment, consideration of individual expectations and potential impact, and implementation of appropriate safeguards to protect personal data throughout the AI processing lifecycle.
Explore advanced AI compliance solutions with Claude for comprehensive analysis of legal requirements and technical implementation strategies. The complexity of establishing and maintaining appropriate lawful bases necessitates ongoing evaluation and adjustment as AI systems evolve and regulatory interpretations develop.
Data Subject Rights and AI Systems
The GDPR establishes comprehensive rights for data subjects that create significant technical and operational challenges for organizations deploying AI systems. These rights include access, rectification, erasure, restriction of processing, data portability, objection, and protection against automated decision-making, each requiring careful consideration of how they can be effectively implemented within machine learning environments.
The right of access requires organizations to provide individuals with detailed information about how their personal data is being processed, including the logic involved in automated decision-making systems. This transparency requirement can be particularly challenging for complex machine learning models where the decision-making process may not be easily explainable or where algorithmic logic involves proprietary techniques that organizations prefer to keep confidential.
The right to rectification and erasure presents technical challenges for AI systems where personal data may be deeply embedded within trained models or distributed across multiple processing systems. Organizations must develop technical capabilities to identify, modify, or remove specific personal data from AI systems while maintaining model integrity and performance, which often requires sophisticated data management and model governance frameworks.
The right to object to automated decision-making with legal or similarly significant effects requires organizations to implement mechanisms for human review and intervention in AI-driven processes. This requirement necessitates careful consideration of which AI applications fall within the scope of automated decision-making regulations and the implementation of appropriate human oversight mechanisms that provide meaningful review rather than mere rubber-stamping of algorithmic decisions.
Privacy by Design in Machine Learning
Implementing privacy by design principles within machine learning systems requires fundamental changes to how AI development projects are conceived, designed, and executed. The principle demands that privacy protection be embedded into the technological architecture of AI systems from the earliest stages rather than being added as an afterthought, requiring close collaboration between legal, technical, and business teams throughout the development lifecycle.
Privacy by design in AI contexts involves implementing technical measures such as differential privacy, federated learning, homomorphic encryption, and secure multi-party computation that enable machine learning while protecting individual privacy. These techniques require specialized expertise and may impact model performance or accuracy, necessitating careful trade-off decisions between privacy protection and analytical capabilities.
The proactive rather than reactive approach required by privacy by design means that organizations must anticipate potential privacy risks and implement preventive measures before problems arise. This forward-thinking approach requires comprehensive threat modeling, privacy impact assessments, and ongoing monitoring of AI systems to ensure that privacy protections remain effective as systems evolve and scale.
Data minimization principles require organizations to collect and process only the personal data that is adequate, relevant, and limited to what is necessary for the specific AI application. This principle challenges traditional big data approaches that assume more data invariably leads to better model performance, requiring organizations to develop more sophisticated approaches to data selection, feature engineering, and model optimization that achieve analytical objectives while minimizing privacy exposure.

A comprehensive GDPR compliance framework for AI systems requires integration of multiple regulatory requirements and technical safeguards throughout the artificial intelligence lifecycle. The framework encompasses lawful basis establishment, data subject rights implementation, privacy by design principles, transparency requirements, data minimization strategies, and robust security measures that collectively ensure regulatory compliance while enabling innovative AI applications.
Automated Decision-Making and Profiling
The GDPR’s provisions regarding automated decision-making and profiling create specific obligations for organizations deploying AI systems that make decisions with legal or similarly significant effects on individuals. These provisions require careful analysis of AI applications to determine when automated decision-making regulations apply and what safeguards must be implemented to protect individual rights.
Automated decision-making encompasses any process where decisions are made solely through automated means without human intervention, while profiling involves automated processing to evaluate, analyze, or predict aspects of individual behavior, performance, or characteristics. Many AI applications involve elements of both automated decision-making and profiling, requiring comprehensive compliance strategies that address both regulatory frameworks.
Organizations must provide meaningful information about the logic involved in automated decision-making, including the significance and envisaged consequences for individuals. This transparency requirement can be particularly challenging for complex machine learning models such as deep neural networks or ensemble methods where the decision-making logic may not be easily interpretable or explainable to non-technical individuals.
The regulation requires implementation of suitable measures to safeguard individual rights, including the right to obtain human intervention, express views, and contest automated decisions. These safeguards must provide meaningful review rather than perfunctory oversight, requiring organizations to develop processes and train personnel to effectively evaluate and potentially override automated decisions based on individual circumstances and additional information.
Enhance your privacy research capabilities with Perplexity for comprehensive analysis of regulatory developments and best practices in AI compliance. The evolving landscape of automated decision-making regulation requires ongoing monitoring of regulatory guidance and enforcement actions to ensure continued compliance.
Data Protection Impact Assessments for AI
Data Protection Impact Assessments represent a crucial compliance tool for organizations deploying AI systems that are likely to result in high risk to individual rights and freedoms. The systematic assessment process requires organizations to identify, evaluate, and mitigate privacy risks associated with AI processing activities before implementation, providing a structured framework for ensuring GDPR compliance.
The GDPR specifically requires DPIAs for automated decision-making with legal or similarly significant effects, systematic monitoring of publicly accessible areas, and processing of special categories of personal data on a large scale. Many AI applications involve one or more of these high-risk processing activities, making DPIA completion a regulatory requirement rather than merely a best practice recommendation.
Effective DPIAs for AI systems must address the complex technical and social implications of machine learning technologies, including potential biases in algorithmic decision-making, accuracy and reliability of automated processing, security vulnerabilities in AI systems, and the broader societal impact of deploying artificial intelligence in specific contexts. This comprehensive analysis requires multidisciplinary expertise spanning legal, technical, ethical, and business domains.
The DPIA process must include consultation with data subjects or their representatives when appropriate, consideration of alternative processing methods that might reduce privacy risks, and identification of measures to address identified risks including technical safeguards, organizational procedures, and ongoing monitoring mechanisms. The assessment must be documented and regularly reviewed as AI systems evolve and new risks emerge.
Cross-Border Data Transfers and AI
International data transfers represent a particularly complex aspect of GDPR compliance for AI systems, especially given the global nature of cloud computing infrastructure and the international collaboration often involved in AI development and deployment. Organizations must ensure that personal data transferred outside the European Economic Area receives adequate protection through appropriate transfer mechanisms.
The invalidation of Privacy Shield and subsequent developments in international transfer regulations have created uncertainty for organizations relying on cloud-based AI services or international AI development partnerships. Organizations must carefully evaluate the adequacy decisions, standard contractual clauses, and other transfer mechanisms available for their specific AI use cases while considering the potential impact of surveillance laws in destination countries.
Many AI applications involve processing personal data across multiple jurisdictions through cloud infrastructure, distributed computing systems, or international partnerships, requiring comprehensive mapping of data flows and implementation of appropriate safeguards for each transfer. This complexity necessitates close collaboration between legal and technical teams to ensure that AI architectures comply with transfer restrictions while maintaining operational effectiveness.
The emergence of data localization requirements and restrictions on international transfers of personal data used in AI systems creates additional compliance challenges that organizations must navigate carefully. These requirements may necessitate architectural changes to AI systems, implementation of data residency controls, or development of localized AI capabilities that can operate within specific jurisdictional boundaries.
Technical Privacy Protection Measures
Implementing effective technical privacy protection measures represents a critical component of GDPR compliance for AI systems, requiring organizations to deploy sophisticated privacy-enhancing technologies that enable machine learning while protecting individual privacy. These technical measures must be integrated into AI architectures from the design stage rather than being retrofitted after system development.
Differential privacy provides mathematical guarantees about privacy protection by adding carefully calibrated noise to datasets or model outputs, enabling organizations to extract useful insights from personal data while limiting the ability to identify specific individuals. Implementation of differential privacy in AI systems requires careful parameter tuning to balance privacy protection with analytical utility, often requiring specialized expertise in privacy-preserving machine learning techniques.
Federated learning enables training of machine learning models across distributed data sources without centralizing personal data, allowing organizations to benefit from collaborative AI development while minimizing privacy exposure. This approach can be particularly valuable for healthcare, financial services, and other sectors where data sharing is limited by privacy concerns or regulatory restrictions, though it requires sophisticated technical infrastructure and coordination mechanisms.
Homomorphic encryption and secure multi-party computation enable computation on encrypted data, allowing AI processing while maintaining data confidentiality throughout the computational process. These advanced cryptographic techniques show promise for privacy-preserving AI applications but currently impose significant computational overhead and complexity that may limit their practical applicability in many real-world scenarios.
Data anonymization and pseudonymization techniques can reduce privacy risks associated with AI processing, though organizations must carefully evaluate the effectiveness of these measures given the potential for re-identification through sophisticated analytical techniques. The dynamic nature of AI systems and their ability to discover unexpected patterns in data creates ongoing challenges for maintaining effective anonymization over time.
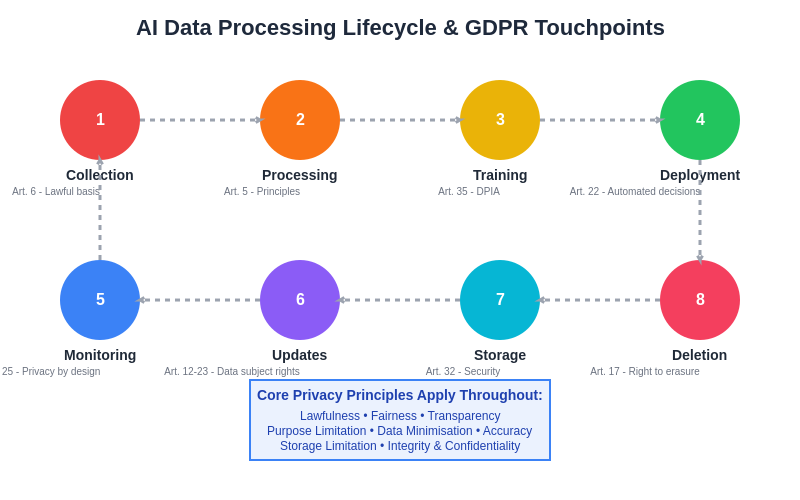
The AI data processing lifecycle demonstrates how GDPR requirements intersect with every stage of artificial intelligence development and deployment. From initial data collection through model training, deployment, monitoring, and eventual deletion, each phase must incorporate specific privacy protections and regulatory compliance measures that ensure personal data processing remains lawful, fair, and transparent throughout the entire AI system lifecycle.
Organizational Compliance Framework
Establishing comprehensive organizational frameworks for AI GDPR compliance requires integration of privacy considerations into all aspects of AI governance, from strategic planning and risk management to operational procedures and incident response. This holistic approach ensures that privacy protection becomes embedded in organizational culture rather than being treated as a purely technical or legal requirement.
Data governance frameworks must be enhanced to address the specific challenges of AI processing, including data lineage tracking, model governance, algorithmic auditing, and ongoing monitoring of AI systems for privacy compliance. These frameworks require clear roles and responsibilities, documented procedures, and regular training to ensure that all personnel involved in AI development and deployment understand their privacy protection obligations.
Privacy management programs must evolve to address the unique characteristics of AI systems, including their dynamic nature, potential for unexpected outcomes, and complex interactions between different system components. This evolution requires investment in specialized expertise, privacy-enhancing technologies, and ongoing monitoring systems that can detect and respond to emerging privacy risks.
Incident response procedures must be adapted to address AI-specific privacy breaches, including situations where algorithmic processing may have violated individual rights, unauthorized access to AI training data, or model outputs that reveal sensitive personal information. These procedures require rapid response capabilities, technical expertise in AI systems, and clear communication protocols with regulators and affected individuals.
Regulatory Enforcement and Penalties
The enforcement landscape for AI GDPR compliance continues to evolve as regulators gain experience with artificial intelligence technologies and their privacy implications. Early enforcement actions have focused on fundamental compliance failures such as lack of lawful basis, inadequate data subject rights implementation, and failure to conduct required impact assessments, providing important guidance for organizations developing AI compliance strategies.
Maximum penalties under the GDPR can reach four percent of global annual turnover or twenty million euros, whichever is higher, creating significant financial incentives for robust compliance programs. The calculation of penalties considers factors including the nature and severity of violations, intentionality, cooperation with authorities, and measures taken to mitigate harm, emphasizing the importance of proactive compliance rather than reactive remediation.
Regulatory guidance on AI applications continues to develop through enforcement actions, formal guidance documents, and collaborative initiatives between privacy authorities. Organizations must monitor these developments closely to ensure their AI systems remain compliant with evolving regulatory expectations and enforcement priorities.
The increasing sophistication of regulatory technical expertise in AI technologies means that compliance efforts must go beyond superficial measures to demonstrate genuine privacy protection. Regulators are developing capabilities to evaluate the effectiveness of privacy-enhancing technologies, assess the adequacy of algorithmic transparency measures, and identify situations where organizations claim compliance while failing to provide meaningful privacy protection.
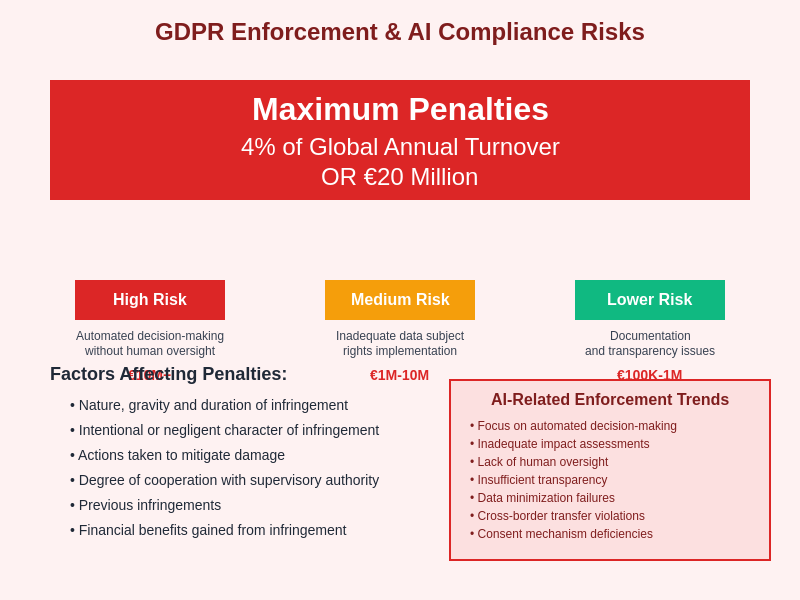
GDPR enforcement for AI systems carries substantial financial and reputational risks, with maximum penalties reaching four percent of global annual turnover or twenty million euros. Organizations deploying AI systems face particular scrutiny in areas of automated decision-making, data subject rights implementation, and documentation requirements, with enforcement factors including the nature and duration of infringement, degree of cooperation with authorities, and actions taken to mitigate potential harm to data subjects.
Future Developments in AI Privacy Regulation
The regulatory landscape for AI privacy continues to evolve rapidly as policymakers grapple with the implications of increasingly sophisticated artificial intelligence technologies. Proposed AI-specific regulations such as the EU AI Act will create additional compliance obligations that intersect with GDPR requirements, necessitating integrated compliance strategies that address both privacy and AI-specific regulatory frameworks.
International coordination on AI governance and privacy protection is increasing through multilateral initiatives, standard-setting organizations, and bilateral cooperation agreements that may influence how organizations approach compliance across different jurisdictions. These developments create opportunities for harmonized approaches to AI privacy protection while also creating complexity as different regulatory frameworks evolve at different paces.
The emergence of sector-specific AI regulations in areas such as healthcare, financial services, and transportation will create additional compliance requirements that must be integrated with GDPR obligations. Organizations operating in regulated sectors must develop comprehensive compliance strategies that address the intersection of AI technologies, privacy protection, and sector-specific regulatory requirements.
Technological developments in privacy-preserving AI continue to advance rapidly, creating new opportunities for compliance while also raising questions about the adequacy of current regulatory frameworks. Organizations must balance adoption of emerging privacy technologies with the need to maintain compliance with existing regulatory requirements while preparing for potential future regulatory developments.
Building Sustainable AI Privacy Programs
Sustainable AI privacy programs require long-term commitment to privacy protection that goes beyond minimum compliance requirements to embrace privacy as a competitive advantage and organizational value. This strategic approach requires investment in privacy-enhancing technologies, specialized expertise, and organizational culture change that positions privacy protection as an enabler of AI innovation rather than a constraint.
Cross-functional collaboration between legal, technical, business, and ethics teams becomes essential for effective AI privacy programs that can address the multifaceted challenges of deploying artificial intelligence technologies in compliance with privacy regulations. This collaboration requires shared understanding of both technical and legal requirements, regular communication channels, and integrated decision-making processes.
Continuous monitoring and improvement of AI privacy programs ensures that organizations can adapt to technological changes, regulatory developments, and evolving privacy risks while maintaining effective protection of personal data. This ongoing improvement requires measurement systems, feedback mechanisms, and regular assessment of program effectiveness against both regulatory requirements and organizational objectives.
The integration of ethical considerations into AI privacy programs addresses broader societal concerns about artificial intelligence while supporting regulatory compliance and organizational reputation. This ethical dimension requires consideration of fairness, transparency, accountability, and societal impact that extends beyond minimum legal requirements to address the broader implications of AI deployment in society.
Conclusion
The intersection of artificial intelligence and GDPR compliance represents one of the defining challenges of the digital age, requiring organizations to navigate complex technical and legal requirements while preserving the innovative potential of AI technologies. Success in this domain requires comprehensive understanding of both privacy law principles and AI technical characteristics, integrated compliance strategies that address the full AI lifecycle, and ongoing adaptation to regulatory and technological developments.
Organizations that invest in robust AI privacy programs will be better positioned to leverage artificial intelligence technologies while maintaining trust with customers, regulators, and society more broadly. This investment requires short-term costs but creates long-term competitive advantages through enhanced customer trust, regulatory compliance, and operational resilience in an increasingly regulated environment.
The future of AI development will be shaped significantly by how well organizations can balance innovation with privacy protection, creating artificial intelligence systems that deliver valuable capabilities while respecting fundamental privacy rights and regulatory requirements. This balance requires ongoing commitment to privacy by design principles, investment in privacy-enhancing technologies, and organizational cultures that prioritize both innovation and privacy protection.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal advice. The views expressed are based on current understanding of GDPR requirements and AI technologies as of the publication date. Organizations should consult qualified legal counsel for specific compliance advice tailored to their particular circumstances and AI applications. Regulatory requirements and enforcement approaches may evolve, requiring ongoing monitoring and adaptation of compliance strategies.
