The rapid proliferation of artificial intelligence technologies across industries has created an urgent need for comprehensive governance frameworks that ensure responsible development, deployment, and management of AI systems. As organizations increasingly integrate AI into their operations, the complexity of regulatory compliance has grown exponentially, requiring sophisticated tools and methodologies to navigate the evolving landscape of AI governance requirements. These frameworks serve as critical infrastructure for maintaining ethical standards, protecting stakeholder interests, and ensuring that AI systems operate within acceptable boundaries of risk and social responsibility.
Explore the latest AI governance trends and developments to stay informed about emerging regulatory requirements and compliance standards that are shaping the future of responsible AI deployment. The establishment of robust governance frameworks represents not merely a compliance obligation but a strategic imperative for organizations seeking to build trust, mitigate risks, and unlock the full potential of artificial intelligence technologies while maintaining alignment with societal values and regulatory expectations.
The Foundation of AI Governance
Modern AI governance frameworks represent a sophisticated synthesis of technical standards, ethical principles, and regulatory requirements designed to address the multifaceted challenges associated with artificial intelligence systems. These frameworks provide structured approaches for managing AI-related risks throughout the entire lifecycle of AI systems, from initial conception and development through deployment, monitoring, and eventual decommissioning. The complexity of these frameworks reflects the inherent challenges of governing technologies that operate with varying degrees of autonomy and can impact multiple stakeholders across diverse domains.
The development of effective AI governance frameworks requires deep understanding of both technical capabilities and limitations of AI systems, as well as comprehensive awareness of regulatory landscapes that continue to evolve rapidly across different jurisdictions. Organizations must navigate a complex web of requirements that encompass data protection regulations, algorithmic transparency mandates, fairness standards, and accountability mechanisms that vary significantly depending on the specific application domain and geographical location of deployment.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance Requirements
The regulatory environment surrounding artificial intelligence has undergone dramatic transformation in recent years, with governments worldwide introducing comprehensive legislation aimed at ensuring responsible AI development and deployment. The European Union’s Artificial Intelligence Act represents one of the most comprehensive regulatory frameworks, establishing risk-based classifications for AI systems and imposing stringent requirements for high-risk applications. Similarly, jurisdictions including the United States, United Kingdom, and various Asian markets have developed their own regulatory approaches, creating a complex patchwork of compliance requirements that organizations must navigate.
These regulatory frameworks typically address fundamental concerns including algorithmic bias, data privacy, transparency, accountability, and safety considerations that are essential for maintaining public trust in AI systems. Organizations operating across multiple jurisdictions must develop sophisticated compliance strategies that account for varying regulatory requirements while maintaining operational efficiency and innovation capabilities. The challenge is further complicated by the fact that regulatory frameworks continue to evolve rapidly as lawmakers and regulators gain deeper understanding of AI technologies and their societal implications.
Leverage advanced AI compliance tools like Claude to navigate complex regulatory requirements and ensure comprehensive adherence to evolving governance standards across multiple jurisdictions. The integration of AI-powered compliance monitoring represents a significant advancement in organizations’ ability to maintain continuous compliance while adapting to changing regulatory landscapes.
Risk Assessment and Management Frameworks
Effective AI governance requires sophisticated risk assessment methodologies that can identify, evaluate, and mitigate potential risks associated with AI system deployment and operation. These frameworks encompass technical risks related to system performance and reliability, as well as broader societal risks including bias, fairness, privacy violations, and unintended consequences that may emerge from AI system behavior. The complexity of AI risk assessment stems from the dynamic nature of AI systems that can evolve and adapt over time, potentially developing behaviors that were not anticipated during initial development and testing phases.
Risk management frameworks must address both immediate operational risks and longer-term strategic risks that may emerge as AI systems scale and evolve. This includes considerations of systemic risks that could arise from widespread adoption of similar AI technologies, as well as competitive risks that may result from regulatory compliance costs or operational restrictions. Organizations must develop comprehensive risk registers that capture the full spectrum of potential AI-related risks while implementing monitoring and mitigation strategies that can adapt to changing risk profiles over time.
Technical Standards and Certification Processes
The development of technical standards for AI systems represents a critical component of comprehensive governance frameworks, providing measurable criteria for evaluating AI system performance, safety, and compliance with regulatory requirements. These standards encompass various aspects of AI system development including data quality, model validation, testing procedures, documentation requirements, and ongoing monitoring protocols that ensure continued compliance throughout the system lifecycle. International standards organizations including ISO, IEEE, and NIST have developed comprehensive frameworks that provide guidance for implementing robust technical governance practices.
Certification processes built upon these technical standards offer organizations mechanisms for demonstrating compliance with regulatory requirements while providing external validation of their governance practices. These certification programs typically involve rigorous auditing processes that evaluate both technical implementations and organizational processes related to AI governance. The emergence of third-party certification bodies specializing in AI governance has created new opportunities for organizations to demonstrate their commitment to responsible AI practices while building stakeholder confidence in their AI systems.
Data Governance and Privacy Protection
Data governance represents a fundamental pillar of AI governance frameworks, addressing the complex challenges associated with data collection, processing, storage, and utilization in AI systems. Comprehensive data governance frameworks must address regulatory requirements including GDPR, CCPA, and other privacy regulations while ensuring that data practices support effective AI system development and operation. This includes implementing robust data quality assurance processes, establishing clear data lineage tracking, and maintaining comprehensive documentation of data processing activities throughout the AI system lifecycle.
Privacy protection in AI systems requires sophisticated approaches that go beyond traditional data protection measures to address unique challenges associated with AI processing including inference risks, model inversion attacks, and privacy leakage through model outputs. Organizations must implement privacy-enhancing technologies including differential privacy, federated learning, and secure multi-party computation to protect individual privacy while enabling effective AI system operation. These technical privacy protections must be integrated with organizational privacy governance processes that ensure consistent application of privacy principles across all AI initiatives.

The architectural complexity of modern AI governance frameworks requires systematic organization of multiple interconnected components that address technical, legal, ethical, and operational considerations. This comprehensive structure ensures that all aspects of AI system governance are properly addressed while maintaining operational efficiency and innovation capabilities.
Algorithmic Transparency and Explainability
Regulatory requirements for algorithmic transparency and explainability have created significant challenges for organizations deploying AI systems, particularly those utilizing complex machine learning models that may be difficult to interpret or explain. Governance frameworks must address these requirements through comprehensive approaches that balance transparency obligations with intellectual property protection and competitive considerations. This includes developing standardized documentation practices, implementing explainable AI technologies, and establishing processes for responding to transparency requests from regulators and stakeholders.
The implementation of explainability requirements varies significantly depending on the specific AI application domain and regulatory context. High-risk applications such as healthcare, financial services, and criminal justice systems typically face more stringent explainability requirements compared to lower-risk applications. Organizations must develop risk-based approaches to explainability that provide appropriate levels of transparency while maintaining system effectiveness and protecting sensitive information.
Enhance your AI governance capabilities with Perplexity’s research tools to stay informed about evolving transparency requirements and best practices for implementing explainable AI systems across different regulatory contexts. The integration of advanced research capabilities enables organizations to maintain current awareness of rapidly evolving explainability standards and regulatory expectations.
Compliance Monitoring and Auditing Tools
The complexity of AI governance frameworks necessitates sophisticated monitoring and auditing tools that can provide continuous oversight of AI system compliance with regulatory requirements and organizational policies. These tools must address both technical compliance monitoring that evaluates system performance against predefined standards and process compliance monitoring that ensures adherence to governance procedures and documentation requirements. Advanced monitoring systems utilize automated analysis capabilities to detect potential compliance violations while providing comprehensive reporting and alerting mechanisms.
Auditing tools for AI governance must provide capabilities for comprehensive evaluation of AI systems across multiple dimensions including technical performance, regulatory compliance, ethical considerations, and risk management effectiveness. These tools typically incorporate standardized assessment frameworks that enable consistent evaluation across different AI systems while providing detailed documentation of audit findings and recommendations. The development of specialized AI auditing methodologies has created new professional disciplines focused specifically on AI system evaluation and compliance verification.
Organizational Governance Structures
Effective AI governance requires establishment of clear organizational structures that define roles, responsibilities, and accountability mechanisms for AI-related decisions and activities. These structures typically include AI governance committees, ethics boards, and specialized roles such as AI risk officers and compliance managers who are responsible for overseeing different aspects of AI governance implementation. The design of these organizational structures must balance the need for specialized expertise with requirements for cross-functional collaboration and efficient decision-making processes.
Governance structures must also address the challenge of managing AI initiatives across different business units and geographical locations while maintaining consistent application of governance principles and requirements. This includes establishing clear escalation procedures, defining decision-making authorities, and implementing communication mechanisms that ensure effective coordination of AI governance activities across the organization. The evolution of AI governance organizations reflects the growing recognition that effective AI governance requires dedicated resources and specialized expertise.
Implementation Challenges and Best Practices
Organizations implementing AI governance frameworks face numerous challenges including resource constraints, technical complexity, regulatory uncertainty, and cultural resistance to governance requirements. Successful implementation requires comprehensive change management strategies that address both technical and organizational aspects of governance adoption. This includes providing appropriate training and education, establishing clear incentives for governance compliance, and developing communication strategies that highlight the business value of effective AI governance.
Best practices for AI governance implementation emphasize the importance of starting with pilot projects that demonstrate governance value while building organizational capabilities and experience. Organizations should focus on developing scalable governance processes that can adapt to changing requirements and growing AI portfolios while maintaining operational efficiency. The integration of governance requirements into existing development and operational processes helps ensure that governance becomes an integral part of AI system lifecycle management rather than an external compliance burden.
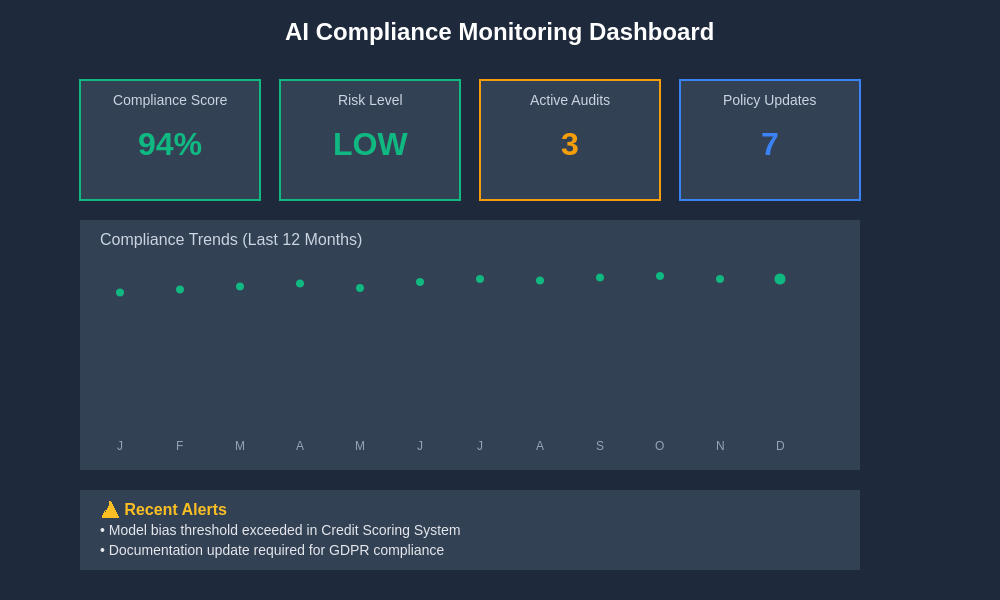
Modern compliance monitoring systems provide comprehensive visibility into AI system performance and regulatory adherence through sophisticated dashboard interfaces that enable real-time tracking of key governance metrics and compliance indicators across organizational AI portfolios.
Technology Solutions and Vendor Ecosystem
The growing demand for AI governance capabilities has spawned a diverse ecosystem of technology vendors offering specialized solutions for different aspects of AI governance including risk assessment, compliance monitoring, explainability, and auditing. These solutions range from comprehensive governance platforms that address multiple governance requirements to specialized tools that focus on specific aspects such as bias detection, model validation, or privacy protection. Organizations must carefully evaluate vendor solutions against their specific governance requirements while considering factors such as integration capabilities, scalability, and long-term viability.
The vendor ecosystem continues to evolve rapidly as new governance requirements emerge and existing solutions mature. Organizations should develop vendor evaluation frameworks that assess both current capabilities and roadmap alignment with anticipated future requirements. The integration of multiple vendor solutions requires careful attention to data interoperability, security considerations, and overall system architecture to ensure effective governance implementation.
International Harmonization and Standards Development
The global nature of AI deployment has created strong incentives for international harmonization of AI governance standards and regulatory approaches. Various international organizations including the OECD, ISO, and IEEE are working to develop common frameworks and standards that can facilitate cross-border AI deployment while maintaining appropriate governance oversight. These harmonization efforts face significant challenges due to different regulatory philosophies, cultural values, and economic priorities across different jurisdictions.
The development of international standards represents a critical component of the broader AI governance ecosystem, providing common reference points for regulatory development and organizational implementation. Organizations operating globally benefit significantly from the emergence of internationally recognized standards that can reduce compliance complexity while providing clear guidance for governance implementation. The ongoing evolution of international AI governance standards continues to shape the development of both regulatory frameworks and organizational governance practices.
Future Directions and Emerging Trends
The future of AI governance frameworks will be shaped by several key trends including the increasing sophistication of AI technologies, evolving regulatory requirements, growing stakeholder expectations, and advances in governance technology solutions. Organizations must prepare for more stringent governance requirements as AI systems become more capable and widely deployed across critical applications. This includes developing adaptive governance capabilities that can evolve with changing technology and regulatory landscapes.
Emerging trends in AI governance include the integration of sustainability considerations, expanded focus on algorithmic justice and fairness, increased emphasis on stakeholder engagement, and the development of governance frameworks specifically designed for emerging AI technologies such as generative AI and autonomous systems. Organizations that proactively adapt their governance frameworks to address these emerging trends will be better positioned to navigate future regulatory requirements while maintaining competitive advantages in AI deployment.
The evolution of AI governance represents a fundamental shift in how organizations approach technology deployment and risk management, requiring new capabilities, processes, and organizational structures that can effectively balance innovation with responsibility. As AI technologies continue to advance and regulatory frameworks mature, the importance of robust governance frameworks will only continue to grow, making governance capabilities a critical competitive differentiator for organizations seeking to maximize the value of their AI investments while maintaining stakeholder trust and regulatory compliance.
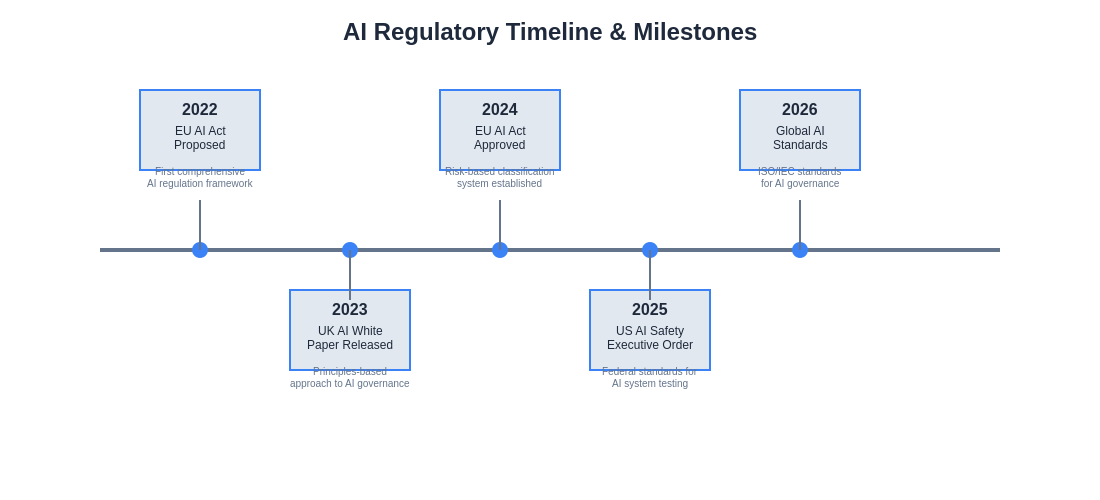
The rapid evolution of AI regulatory frameworks across global jurisdictions creates complex compliance timelines that organizations must navigate while maintaining operational flexibility and innovation capabilities in an increasingly regulated environment.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal or professional advice. The views expressed are based on current understanding of AI governance frameworks and regulatory requirements, which continue to evolve rapidly. Readers should consult with qualified legal and compliance professionals when developing AI governance strategies and should conduct thorough research to ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations in their specific jurisdictions. The effectiveness of governance frameworks may vary depending on organizational context, technology implementations, and regulatory environments.
