The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence technologies has precipitated an urgent need for comprehensive governance frameworks that can effectively balance innovation with safety, security, and ethical considerations. As AI systems become increasingly sophisticated and pervasive across all sectors of society, governments, international organizations, and industry leaders are grappling with the complex challenge of establishing regulatory structures that can adapt to the dynamic nature of technological progress while protecting fundamental human rights and societal values.
Stay informed about the latest developments in AI policy and governance as regulatory landscapes continue to evolve at an unprecedented pace. The establishment of effective AI governance models represents one of the most critical challenges of our time, requiring unprecedented levels of international cooperation and multistakeholder collaboration to ensure that artificial intelligence serves the collective benefit of humanity.
The Imperative for AI Governance
The exponential growth of AI capabilities has outpaced traditional regulatory mechanisms, creating a governance gap that poses significant risks to individuals, organizations, and society as a whole. Current AI systems demonstrate capabilities in areas ranging from automated decision-making in healthcare and criminal justice to autonomous vehicle operation and financial trading, each carrying profound implications for human welfare and societal stability. The absence of adequate governance frameworks has already resulted in documented cases of algorithmic bias, privacy violations, and unintended consequences that underscore the urgent need for comprehensive regulatory approaches.
The complexity of AI governance stems from the technology’s dual nature as both a transformative tool for solving global challenges and a potential source of unprecedented risks. Unlike traditional technologies that operate within well-defined parameters, AI systems exhibit emergent behaviors that can be difficult to predict or control, particularly as they scale in complexity and capability. This inherent unpredictability necessitates governance approaches that are both robust enough to address current risks and flexible enough to adapt to future technological developments.
Furthermore, the global nature of AI development and deployment requires international coordination to prevent regulatory arbitrage, where organizations migrate their operations to jurisdictions with more permissive regulatory environments. The interconnected nature of modern AI systems means that inadequate governance in one region can have cascading effects across international boundaries, making effective global coordination essential for maintaining collective security and stability.
Emerging Global Regulatory Frameworks
The European Union has emerged as a pioneer in comprehensive AI regulation through the development of the AI Act, which represents the world’s first comprehensive legal framework specifically designed to govern artificial intelligence systems. This landmark legislation establishes a risk-based approach that categorizes AI applications according to their potential for harm, implementing progressively stringent requirements for higher-risk systems. The framework distinguishes between prohibited AI practices, high-risk applications requiring strict compliance measures, and lower-risk systems subject to transparency and disclosure requirements.
The United States has adopted a more fragmented approach to AI governance, relying on a combination of executive orders, agency guidance, and sectoral regulations to address AI-related risks. The Biden administration’s Executive Order on Safe, Secure, and Trustworthy AI establishes principles for federal AI use while directing agencies to develop sector-specific guidance for AI deployment in critical areas such as healthcare, finance, and national security. This approach reflects the American preference for industry self-regulation combined with targeted government intervention in areas of particular concern.
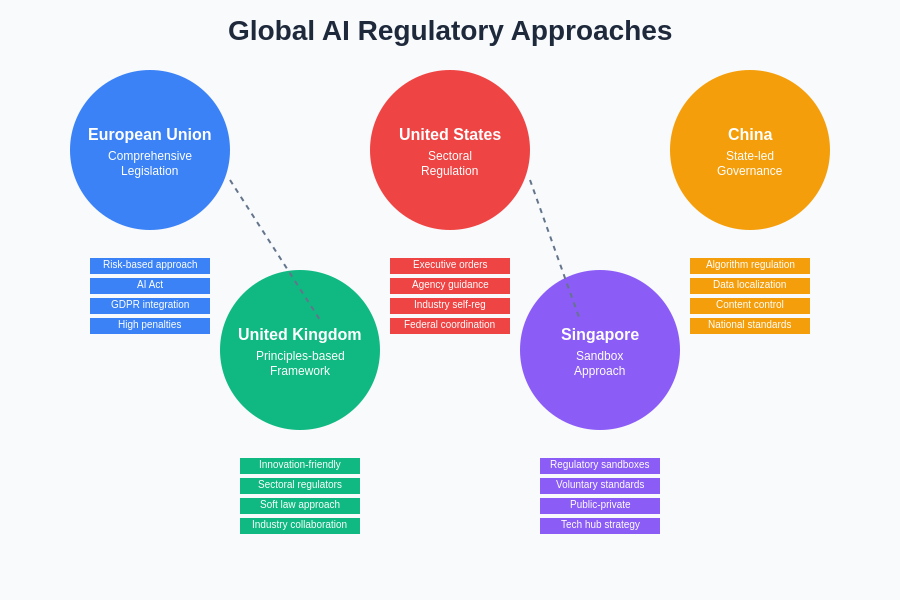
The diversity of regulatory approaches across major jurisdictions reflects fundamentally different philosophical perspectives on the role of government, technology innovation, and individual rights. Each region’s approach is shaped by its unique political systems, economic priorities, and cultural values, creating a complex patchwork of governance frameworks that organizations must navigate when deploying AI systems globally.
China has implemented a comprehensive regulatory framework that emphasizes algorithm transparency, data protection, and content moderation, reflecting the country’s broader approach to technology governance that prioritizes social stability and government oversight. The algorithmic recommendation regulation and draft measures for deep synthesis provisions demonstrate China’s commitment to maintaining control over AI systems that could influence public opinion or social behavior. This regulatory approach reflects distinct cultural and political values that prioritize collective welfare and government authority over individual privacy and corporate autonomy.
Explore comprehensive AI governance resources with Claude to understand the nuances of different regulatory approaches and their implications for global AI development. The diversity of regulatory approaches across major jurisdictions reflects fundamentally different philosophical perspectives on the role of government, individual rights, and technological innovation in society.
International Standards and Coordination Mechanisms
The development of international standards for AI governance has become a critical priority for ensuring interoperability, safety, and ethical deployment of AI systems across borders. The International Organization for Standardization has initiated multiple working groups focused on developing technical standards for AI systems, including frameworks for risk management, testing and validation, and ethical considerations. These standards aim to provide common technical baselines that can inform national regulatory approaches while facilitating international trade and cooperation in AI technologies.
The Global Partnership on AI represents a significant multilateral initiative designed to foster international cooperation on AI governance issues. This partnership brings together leading AI-developing nations to share best practices, coordinate research efforts, and develop common approaches to AI safety and ethics. The partnership’s working groups focus on critical areas including responsible AI, data governance, and the future of work, demonstrating the broad scope of challenges that require international coordination.
The United Nations has established multiple initiatives focused on AI governance, including the High-Level Panel on Digital Cooperation and various specialized agencies working on AI applications in their respective domains. These efforts aim to ensure that AI development aligns with international human rights standards and sustainable development goals while providing platforms for developing nations to participate in global AI governance discussions. The UN’s approach emphasizes the need for inclusive governance frameworks that consider the perspectives and needs of all nations, regardless of their current level of AI development capability.
Risk Assessment and Management Frameworks
Contemporary AI governance models increasingly rely on sophisticated risk assessment methodologies that attempt to quantify and categorize the potential harms associated with different AI applications. These frameworks typically consider factors such as the scope of deployment, the potential for automated decision-making to impact individuals, the reversibility of decisions, and the availability of human oversight and intervention mechanisms. The development of standardized risk assessment tools represents a critical component of effective AI governance, enabling consistent evaluation of AI systems across different contexts and jurisdictions.
The implementation of risk management frameworks requires organizations to establish comprehensive governance structures that include technical safeguards, organizational controls, and ongoing monitoring mechanisms. These structures must address the entire AI lifecycle, from initial development and training through deployment, operation, and eventual decommissioning. The dynamic nature of AI systems necessitates continuous risk assessment and management processes that can adapt to changing system behaviors and evolving threat landscapes.
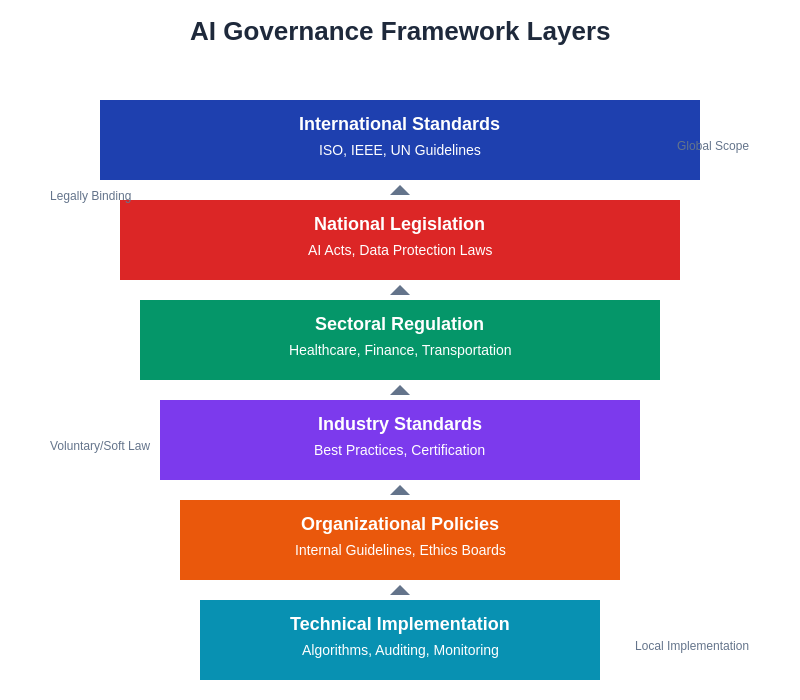
Effective AI governance requires coordination across multiple layers of oversight, from international standards and national legislation down to technical implementation and organizational policies. This multi-layered approach ensures comprehensive coverage while allowing for appropriate flexibility and specialization at each level of the governance hierarchy.
Algorithmic impact assessments have emerged as a key tool for evaluating the potential societal effects of AI systems before deployment. These assessments require organizations to systematically analyze how their AI systems might affect different demographic groups, considering factors such as fairness, transparency, and potential for discriminatory outcomes. The development of standardized impact assessment methodologies represents an important step toward ensuring that AI deployment decisions are made with full consideration of their broader societal implications.
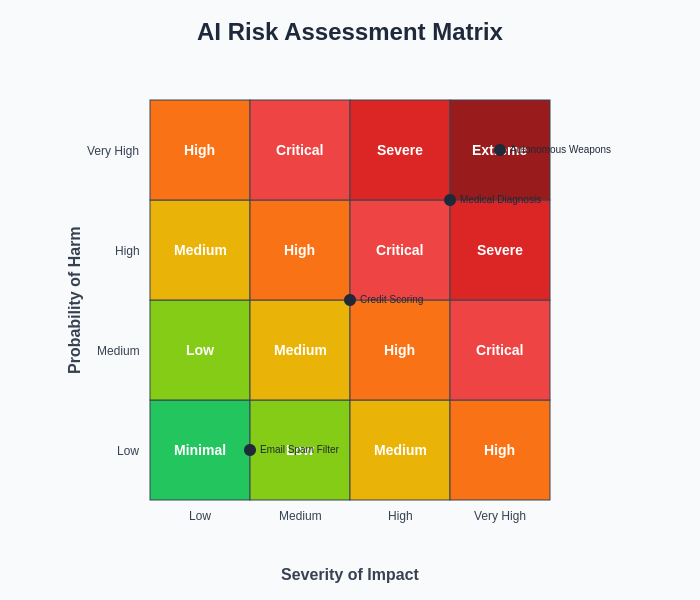
Risk assessment matrices provide a systematic approach to evaluating AI applications based on both the probability and severity of potential harm. This framework enables organizations and regulators to prioritize governance efforts and allocate resources effectively while ensuring that high-risk applications receive appropriate oversight and control measures.
Sectoral Governance Approaches
Healthcare represents one of the most heavily regulated sectors for AI applications, reflecting the critical importance of patient safety and the potential for AI errors to cause significant harm. Regulatory frameworks for medical AI typically require extensive clinical validation, ongoing safety monitoring, and clear delineation of physician oversight responsibilities. The FDA’s approach to AI medical devices exemplifies the challenges of regulating technologies that continue to learn and evolve after deployment, requiring new paradigms for ensuring continued safety and efficacy.
Financial services regulation of AI focuses primarily on ensuring fairness in automated decision-making, particularly in areas such as credit scoring and insurance underwriting where discriminatory outcomes could violate civil rights laws. Regulatory frameworks in this sector emphasize explainability and transparency requirements that enable individuals to understand and challenge automated decisions that affect their financial well-being. The integration of AI into high-frequency trading and risk management systems also raises concerns about systemic risk and market stability that require specialized regulatory approaches.
Access cutting-edge research and analysis with Perplexity to stay current with the latest developments in sector-specific AI regulation and its implications for industry practices. The diversity of sectoral approaches reflects the varying risk profiles and existing regulatory structures across different industries, highlighting the need for tailored governance frameworks that address sector-specific challenges while maintaining consistency in fundamental principles.
Transportation and autonomous vehicle regulation represents a particularly complex governance challenge due to the safety-critical nature of these applications and the need for extensive coordination between multiple regulatory agencies. The development of regulatory frameworks for autonomous vehicles requires addressing questions of liability, insurance, infrastructure requirements, and public acceptance while ensuring that safety standards keep pace with rapidly evolving technology capabilities.
Ethical Frameworks and Human Rights Considerations
The integration of human rights principles into AI governance frameworks represents a fundamental shift toward recognizing AI systems as having profound implications for human dignity, autonomy, and equality. International human rights law provides a foundational framework for AI governance, establishing principles such as non-discrimination, privacy, freedom of expression, and due process that must be preserved and protected in AI-enabled systems. The challenge lies in translating these abstract principles into concrete technical and operational requirements that can be implemented and verified in complex AI systems.
Algorithmic fairness has emerged as a central concern in AI governance, requiring organizations to address potential biases in training data, model architecture, and deployment contexts that could result in discriminatory outcomes. The development of technical methods for measuring and mitigating bias represents an active area of research, though significant challenges remain in defining fairness in ways that are both mathematically rigorous and socially meaningful. Different conceptions of fairness often conflict with one another, requiring governance frameworks to make explicit value judgments about which fairness criteria should take precedence in different contexts.
Transparency and explainability requirements represent another critical component of ethical AI governance, enabling individuals to understand how AI systems make decisions that affect them and providing accountability mechanisms for addressing errors or unfair outcomes. However, the implementation of explainability requirements must balance the need for transparency against legitimate concerns about intellectual property protection and system security. The development of standardized approaches to AI explainability represents an ongoing challenge that requires collaboration between technologists, policymakers, and affected communities.
Enforcement Mechanisms and Compliance Strategies
The effectiveness of AI governance frameworks ultimately depends on robust enforcement mechanisms that can detect violations, impose meaningful penalties, and incentivize compliance across diverse organizational contexts. Traditional regulatory enforcement approaches may be inadequate for addressing the unique characteristics of AI systems, including their opacity, complexity, and capacity for continuous learning and adaptation. New enforcement paradigms must incorporate technical auditing capabilities, ongoing monitoring requirements, and collaborative approaches that leverage both regulatory authority and industry expertise.
Algorithmic auditing has emerged as a critical tool for ensuring AI system compliance with governance requirements, though significant technical and methodological challenges remain in developing standardized auditing approaches. Effective auditing requires access to training data, model architecture, and deployment statistics that organizations may be reluctant to share due to competitive concerns or technical complexity. The development of privacy-preserving auditing techniques and standardized audit methodologies represents an important area for continued innovation and collaboration.
The global nature of AI development and deployment creates particular challenges for enforcement, as organizations may develop AI systems in one jurisdiction for deployment in another, potentially circumventing local governance requirements. International cooperation mechanisms, including information sharing agreements and mutual recognition of regulatory standards, will be essential for ensuring effective enforcement across borders. The development of technical standards for AI system documentation and traceability can also support enforcement efforts by enabling regulators to understand and evaluate AI systems regardless of where they were developed.
Industry Self-Regulation and Multi-Stakeholder Initiatives
Industry self-regulation plays a crucial complementary role to government regulation in AI governance, particularly in rapidly evolving technical domains where formal regulation may struggle to keep pace with innovation. Leading AI companies have established internal ethics boards, developed responsible AI principles, and implemented voluntary standards that often exceed current regulatory requirements. These self-regulatory efforts can serve as testing grounds for emerging governance approaches and provide valuable insights for policymakers developing formal regulatory frameworks.
Multi-stakeholder initiatives bring together diverse perspectives from industry, academia, civil society, and government to develop consensus approaches to AI governance challenges. Organizations such as the Partnership on AI and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers have facilitated collaborative development of ethical guidelines, technical standards, and best practices that can inform both industry self-regulation and government policymaking. These initiatives demonstrate the value of inclusive approaches to governance that incorporate diverse perspectives and expertise.
The effectiveness of self-regulatory approaches depends critically on meaningful accountability mechanisms, including transparent reporting on AI system impacts, independent oversight, and consequences for non-compliance with voluntary standards. Industry initiatives must also address the competitive dynamics that may discourage individual organizations from adopting costly governance measures unless their competitors are subject to similar requirements. The development of industry-wide standards and certification programs can help address these collective action problems while maintaining incentives for innovation.
Challenges in Cross-Border AI Governance
The inherently global nature of AI technology creates significant challenges for effective governance, as AI systems developed in one jurisdiction may be deployed worldwide, potentially circumventing local regulatory requirements. The lack of consistent international standards creates opportunities for regulatory arbitrage, where organizations relocate their AI development or deployment activities to jurisdictions with more permissive regulatory environments. This dynamic can undermine the effectiveness of individual national regulatory frameworks and create a race-to-the-bottom in AI governance standards.
Data localization requirements and restrictions on cross-border data transfers further complicate international AI governance by potentially fragmenting global AI systems and reducing their effectiveness. Many AI applications depend on access to diverse, large-scale datasets that may be distributed across multiple jurisdictions, making compliance with varying data governance requirements a significant operational challenge. The development of international frameworks for data sharing and AI system interoperability represents a critical need for enabling both effective governance and continued innovation.
Trade policy considerations also play an important role in international AI governance, as restrictions on AI technology exports or requirements for technology transfer can significantly impact global AI development and deployment patterns. The intersection of AI governance with national security concerns has led some countries to restrict certain AI technologies or applications, creating additional complexity for organizations operating across multiple jurisdictions. Balancing legitimate security concerns with the benefits of international cooperation and technology sharing represents an ongoing challenge for policymakers worldwide.
Future Directions and Emerging Trends
The evolution of AI governance is likely to be shaped by several emerging trends, including the development of more sophisticated technical tools for governance implementation, increased emphasis on participatory governance approaches that include affected communities in decision-making processes, and growing recognition of the need for adaptive regulatory frameworks that can evolve with advancing technology. The integration of AI systems into critical infrastructure and essential services will likely drive demand for more stringent governance requirements and specialized regulatory expertise.
Artificial general intelligence and more advanced AI capabilities pose particularly significant governance challenges that may require fundamentally new approaches to risk assessment, safety assurance, and international coordination. The potential for AI systems to exceed human capabilities in critical domains raises questions about maintaining meaningful human control and oversight that current governance frameworks may be inadequate to address. Research into AI alignment, safety, and control represents a critical priority for ensuring that governance frameworks can evolve to address these emerging challenges.
The democratization of AI development tools and the proliferation of smaller organizations developing and deploying AI systems will require governance frameworks that can scale to address a much larger and more diverse ecosystem of AI developers. Traditional regulatory approaches that focus on large organizations with substantial compliance resources may be inadequate for addressing the risks posed by the long tail of smaller AI developers. The development of automated compliance tools, simplified governance frameworks for lower-risk applications, and support mechanisms for smaller organizations represents an important area for continued innovation.
The increasing integration of AI systems with other emerging technologies, including blockchain, quantum computing, and biotechnology, will create new governance challenges that require interdisciplinary expertise and coordinated regulatory approaches. The convergence of these technologies may enable capabilities that exceed the scope of current governance frameworks, requiring proactive development of new regulatory paradigms and international coordination mechanisms.
As AI governance frameworks continue to mature and evolve, their effectiveness will ultimately be measured by their ability to maximize the beneficial applications of AI technology while minimizing potential harms and ensuring that the benefits of AI development are distributed equitably across society. This requires governance approaches that are both technically sophisticated and democratically legitimate, incorporating diverse perspectives and values while maintaining the flexibility to adapt to technological change and emerging challenges.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal, policy, or professional advice. The views expressed are based on current understanding of AI governance developments and regulatory frameworks as of the publication date. Readers should consult with qualified legal and policy experts when making decisions related to AI governance compliance. Regulatory landscapes are rapidly evolving, and specific requirements may vary significantly across jurisdictions and applications.
