The artificial intelligence investment landscape has experienced unprecedented growth and transformation over the past decade, fundamentally reshaping how venture capital firms evaluate opportunities and how startups position themselves in an increasingly competitive marketplace. The convergence of technological advancement, market demand, and investor appetite has created a dynamic ecosystem where AI-focused companies command premium valuations and attract substantial funding rounds that were previously reserved for more established technology sectors.
Explore the latest AI trends and developments to understand how emerging technologies are influencing investment decisions and market dynamics across the artificial intelligence sector. The relationship between technological innovation and financial investment has never been more intertwined, with breakthrough developments in machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision directly correlating with funding availability and investor confidence.
The Evolution of AI Investment Landscape
The artificial intelligence investment ecosystem has undergone a remarkable transformation since the early 2010s, evolving from a niche technological curiosity to one of the most hotly contested sectors in venture capital and private equity. This evolution reflects not only the maturation of AI technologies but also the growing recognition among investors that artificial intelligence represents a fundamental shift in how businesses operate, compete, and create value across virtually every industry vertical.
Early AI investments were primarily concentrated in research-heavy initiatives and academic spin-offs that required significant capital investment with uncertain commercial applications. The landscape has since shifted dramatically toward more commercially viable applications with clearer paths to market adoption and revenue generation. This transformation has been driven by several key factors including the exponential growth in computing power, the availability of vast datasets for training machine learning models, and the development of more sophisticated algorithms that can deliver tangible business value.
The democratization of AI tools and platforms has also contributed to this investment evolution, enabling startups with smaller teams and limited resources to develop sophisticated AI applications that can compete with established technology companies. This leveling of the playing field has attracted venture capital attention to early-stage companies that demonstrate innovative approaches to solving real-world problems using artificial intelligence technologies.
Venture Capital Strategies in AI Investment
Venture capital firms have developed increasingly sophisticated strategies for evaluating and investing in artificial intelligence companies, recognizing that traditional metrics and evaluation criteria may not adequately capture the potential of AI-driven businesses. The unique characteristics of AI companies, including their reliance on data assets, algorithmic intellectual property, and network effects, require specialized due diligence processes and investment frameworks that differ significantly from conventional software or hardware investments.
Leading venture capital firms have established dedicated AI investment teams with technical expertise capable of evaluating the underlying technology, assessing the quality and accessibility of training data, and understanding the competitive dynamics within specific AI application domains. These specialized teams work closely with portfolio companies to provide not only financial capital but also strategic guidance on product development, market positioning, and talent acquisition in an increasingly competitive landscape for AI expertise.
Discover advanced AI capabilities and investment opportunities that are attracting significant venture capital attention and driving innovation across multiple industry sectors. The strategic value proposition of AI investments extends beyond immediate financial returns to include portfolio synergies, cross-pollination of technologies, and positioning for future market opportunities that may emerge as AI capabilities continue to advance.
Sector-Specific AI Investment Patterns
The distribution of AI investment across different industry sectors reveals interesting patterns and trends that reflect both market maturity and investor confidence in various application domains. Healthcare AI has consistently attracted substantial investment due to the sector’s large addressable market, regulatory barriers that provide competitive moats, and the potential for AI to address critical societal challenges while generating significant returns on investment.
Financial services represents another major destination for AI investment, driven by the industry’s early adoption of algorithmic trading, fraud detection, and risk assessment technologies. The combination of abundant data, clear regulatory frameworks, and established customer relationships makes financial services an attractive sector for AI investment, with applications ranging from robo-advisors and automated underwriting to sophisticated market analysis and trading systems.
Autonomous vehicles and transportation technologies have garnered enormous investor attention and capital deployment, though the sector has also experienced significant volatility as technical challenges and regulatory complexities have proven more difficult to overcome than initially anticipated. Despite these challenges, the potential market size and transformative nature of autonomous transportation continue to attract substantial venture capital investment and corporate strategic initiatives.
Enterprise software enhanced with AI capabilities represents a rapidly growing investment category that combines the predictable revenue models of traditional software-as-a-service businesses with the competitive advantages and pricing power that AI functionality can provide. These investments often focus on vertical-specific applications that can leverage domain expertise and specialized datasets to create defensible market positions.
Geographic Distribution and Global Investment Flows
The geographic distribution of AI investment reveals significant concentrations in established technology hubs while also highlighting the emergence of new centers of AI innovation and entrepreneurship. Silicon Valley continues to dominate AI investment volumes, benefiting from its established venture capital ecosystem, concentration of technical talent, and proximity to major technology companies that serve as both customers and potential acquirers for AI startups.
China has emerged as a formidable competitor in AI investment, with government support, abundant data resources, and a large domestic market creating favorable conditions for AI startups to develop and scale their technologies. The unique regulatory environment and market dynamics in China have enabled the development of AI applications that differ significantly from their Western counterparts, particularly in areas such as facial recognition, social credit systems, and smart city infrastructure.
European AI investment has grown substantially, driven by strong academic research institutions, supportive government policies, and increasing recognition of the strategic importance of artificial intelligence for economic competitiveness. Countries such as the United Kingdom, Germany, and France have implemented national AI strategies that include significant public and private investment commitments to support the development of domestic AI capabilities and startups.
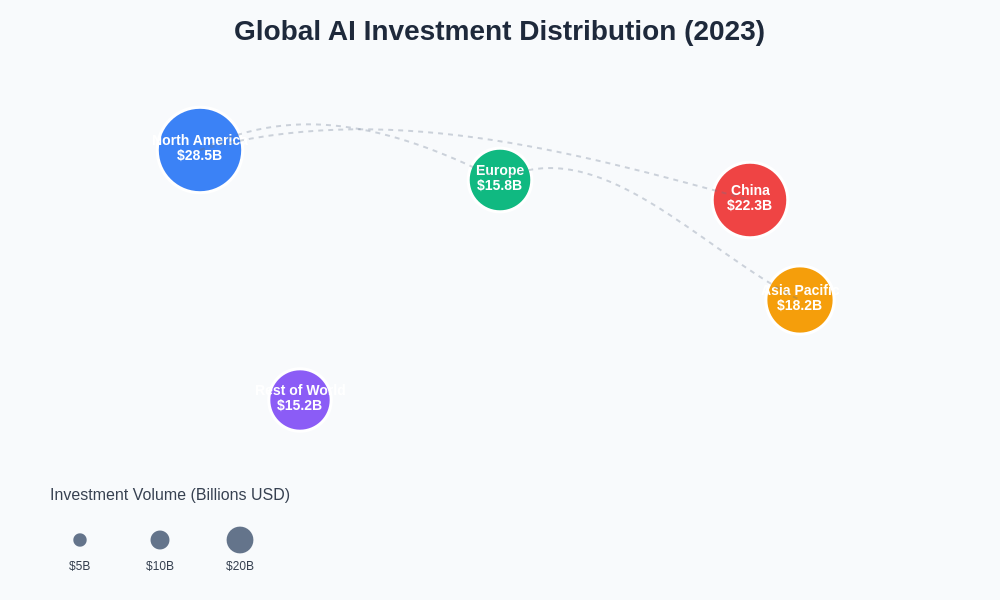
The international flow of AI investment capital reflects both the global nature of artificial intelligence development and the strategic importance that different regions place on maintaining competitive positions in this critical technology sector. Cross-border investment patterns also reveal how venture capital firms are diversifying their geographic exposure while seeking access to unique talent pools, datasets, and market opportunities that may not be available in their home markets. North America continues to lead in absolute investment volume, while China maintains strong growth in domestic AI development and Asia Pacific emerges as a significant destination for AI investment capital.
Investment Stage Analysis and Funding Dynamics
The distribution of AI investment across different funding stages reveals important insights into market maturity, investor confidence, and the capital requirements of AI companies at various stages of their development. Seed and early-stage AI investments have increased dramatically as the barriers to entry for AI development have decreased and more entrepreneurs have gained access to the tools and knowledge necessary to build AI-powered products and services.
Series A and B funding rounds in the AI sector have grown both in frequency and average size, reflecting the substantial capital requirements for data acquisition, talent recruitment, and infrastructure development that characterize many AI companies. These larger funding rounds also indicate increasing investor confidence in the commercial viability of AI technologies and the ability of startups to achieve significant scale and market penetration.
Later-stage AI investments and growth equity funding have attracted attention from traditional private equity firms and strategic corporate investors who recognize the strategic value of AI capabilities for their existing businesses and investment portfolios. These larger funding rounds often focus on companies that have demonstrated clear product-market fit and are seeking capital to accelerate growth, expand into new markets, or develop additional AI capabilities.
Access comprehensive investment research and analysis tools to evaluate AI investment opportunities and market trends that are shaping the future of artificial intelligence funding and development. The complexity of AI investment evaluation requires sophisticated analytical capabilities and access to comprehensive market data that can inform investment decisions and risk assessment.
Valuation Methodologies and Market Dynamics
The valuation of AI companies presents unique challenges that have forced investors to develop new methodologies and frameworks for assessing the worth of businesses built around artificial intelligence technologies. Traditional valuation approaches based on revenue multiples or discounted cash flows may not adequately capture the value of AI companies’ data assets, algorithmic intellectual property, or potential for network effects and market disruption.
Data assets represent a particularly complex valuation challenge, as the value of data depends not only on its quantity and quality but also on its uniqueness, accessibility, and the company’s ability to extract insights and create competitive advantages from that data. The proprietary nature of many AI datasets and the difficulty of replicating them create potential competitive moats that may justify premium valuations but are challenging to quantify using conventional financial metrics.
The talent premium associated with AI companies also influences valuation dynamics, as the scarcity of experienced AI engineers, data scientists, and machine learning researchers drives up compensation costs while also creating valuable human capital assets that contribute to company valuation. The ability to attract and retain top AI talent has become a critical factor in investment decisions and company valuations.
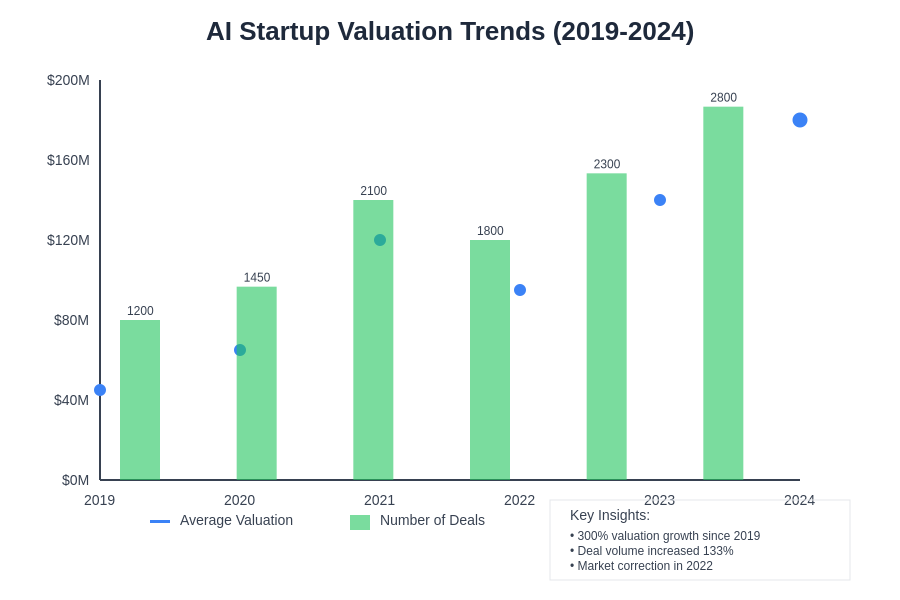
Market timing and competitive positioning play crucial roles in AI company valuations, with companies that achieve early market leadership or develop breakthrough technologies commanding significant premiums over competitors. The winner-take-all dynamics that characterize many AI markets can result in substantial valuation differences between market leaders and followers, even when the underlying technology capabilities may be relatively similar. The chart demonstrates the significant growth trajectory in AI startup valuations, with average valuations quadrupling since 2019 despite the market correction experienced in 2022.
Corporate Strategic Investment and Partnerships
Corporate strategic investment in AI startups has become increasingly prevalent as established companies recognize the need to access external innovation and maintain competitive positions in an AI-driven business environment. These strategic investments often provide more than just capital, offering startups access to customer bases, distribution channels, data resources, and operational expertise that can accelerate growth and market penetration.
Technology giants such as Google, Microsoft, Amazon, and Facebook have established corporate venture capital arms specifically focused on AI investments, seeking to identify emerging technologies and talented teams that could enhance their existing AI capabilities or create new business opportunities. These investments serve dual purposes of generating financial returns while also providing strategic intelligence about emerging trends and potential competitive threats.
Traditional industries have also increased their strategic AI investments as they seek to digitally transform their operations and maintain competitiveness against AI-native startups that may disrupt their markets. Automotive companies investing in autonomous vehicle technologies, financial institutions backing fintech AI startups, and healthcare organizations supporting medical AI development represent examples of defensive strategic investment strategies.
The partnership dynamics between corporate strategic investors and AI startups often extend beyond pure financial relationships to include joint development agreements, licensing arrangements, and potential acquisition pathways that provide multiple value creation opportunities for both parties. These strategic relationships can significantly enhance startup valuations while providing corporations with optionality on emerging technologies and market opportunities.
Regulatory Impact and Policy Considerations
The evolving regulatory landscape surrounding artificial intelligence has significant implications for investment decisions and market dynamics, as investors must consider not only the technical and commercial viability of AI startups but also the potential regulatory risks and compliance requirements that may affect future operations and profitability. The increasing focus on AI ethics, data privacy, and algorithmic transparency has created new compliance costs and operational complexities that investors must factor into their investment decisions.
International regulatory differences present additional challenges for AI investors, particularly those seeking to build portfolio companies that operate across multiple jurisdictions with varying regulatory frameworks and compliance requirements. The European Union’s proposed AI Act, China’s AI governance initiatives, and various national AI strategies create a complex regulatory environment that requires sophisticated legal and policy expertise to navigate effectively.
Data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation in Europe and various state-level privacy laws in the United States have direct implications for AI companies that rely on personal data for training and operating their machine learning systems. These regulatory requirements may limit certain types of AI applications while creating opportunities for companies that can develop privacy-preserving AI technologies or help other organizations achieve regulatory compliance.
The potential for future regulatory changes presents both risks and opportunities for AI investors, as new regulations could either constrain certain AI applications or create new markets for compliance-related AI technologies. Investors must therefore develop expertise in regulatory forecasting and policy analysis to make informed investment decisions in this rapidly evolving landscape.
Talent Acquisition and Human Capital Challenges
The competition for AI talent represents one of the most significant challenges facing AI startups and their investors, as the limited pool of experienced AI professionals has created a hypercompetitive hiring environment with rapidly escalating compensation levels. This talent scarcity affects not only the operational costs of AI companies but also their ability to execute on their business plans and achieve the growth targets that justify their valuations.
Venture capital firms have responded to this challenge by developing specialized recruiting networks, establishing relationships with academic institutions, and creating programs to help portfolio companies attract and retain top AI talent. Some investors have also increased their focus on founding teams with strong technical credentials and track records in AI development, recognizing that talent quality is often the most critical factor in AI startup success.
The global nature of the AI talent pool has created opportunities for investors to access high-quality technical teams in regions with lower labor costs, potentially improving the capital efficiency of AI investments. However, this geographic distribution of talent also creates challenges related to team coordination, intellectual property protection, and cultural integration that investors must carefully consider.
The increasing importance of AI talent has also influenced investment strategies, with some venture capital firms focusing on backing serial entrepreneurs and technical leaders who have demonstrated the ability to build and scale AI teams effectively. The track record of founding teams in attracting and developing AI talent has become a key factor in investment decisions and due diligence processes.
Market Consolidation and Exit Strategies
The AI investment landscape is experiencing increasing consolidation as larger technology companies acquire promising startups to enhance their AI capabilities, eliminate potential competitors, or gain access to specialized talent and intellectual property. This consolidation trend has created attractive exit opportunities for early investors while also concentrating AI capabilities within a relatively small number of large technology platforms.
Strategic acquisitions represent the primary exit pathway for many AI startups, as the technical complexity and capital requirements of scaling AI technologies often make independent growth challenging. The acquirer pool has expanded beyond traditional technology companies to include financial institutions, healthcare organizations, automotive manufacturers, and other industry leaders seeking to integrate AI capabilities into their operations.
Initial public offerings of AI companies have been relatively limited compared to other technology sectors, partly due to the early stage of market development and the preference of many AI companies to be acquired by strategic buyers rather than pursuing independent public market strategies. However, successful AI IPOs have generally commanded premium valuations and strong investor interest, suggesting potential for increased public market activity as the sector matures.
The exit environment for AI investments continues to evolve as the market matures and more companies achieve the scale and profitability necessary to support independent operations or public market listings. Investors are increasingly focused on building companies that can achieve sustainable competitive advantages and defensible market positions rather than relying solely on acquisition exits.
Future Investment Outlook and Emerging Opportunities
The future of AI investment is likely to be characterized by increasing specialization and sophistication as the market matures and investors develop deeper expertise in evaluating AI technologies and business models. The shift toward more applied AI solutions and industry-specific applications is expected to create new investment opportunities while potentially reducing the premium valuations associated with general-purpose AI technologies.
Emerging areas such as AI infrastructure, edge computing for AI applications, and AI-powered automation represent potential growth areas for future investment as the market moves beyond basic AI capabilities toward more sophisticated and specialized applications. The increasing importance of AI governance, explainability, and ethical considerations may also create new investment opportunities in companies that address these emerging market needs.
The democratization of AI development through improved tools, platforms, and educational resources is expected to lower barriers to entry and increase the number of AI startups seeking investment, potentially creating more competitive dynamics while also expanding the overall market opportunity. This trend may favor investors who can provide more than just capital, including technical expertise, market access, and operational support.
International expansion and cross-border investment flows are likely to increase as AI technologies become more globally applicable and investors seek to diversify their geographic exposure while accessing unique market opportunities and talent pools in different regions. The continued evolution of regulatory frameworks and international trade policies will play important roles in shaping these global investment patterns.
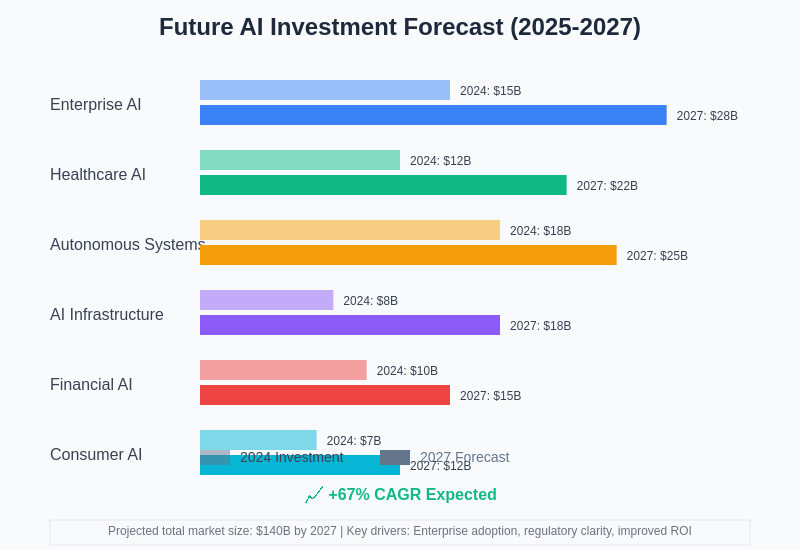
The integration of AI capabilities into existing industries and business models represents a significant long-term investment opportunity as traditional companies seek to transform their operations and maintain competitiveness in an increasingly AI-driven economy. This transformation creates opportunities for both direct AI investments and investments in companies that successfully integrate AI technologies to enhance their existing business models and market positions. The forecast indicates that enterprise AI and autonomous systems will continue to attract the largest investment volumes, while AI infrastructure represents the highest growth potential as the market matures and requires more sophisticated supporting technologies.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute investment advice or recommendations. The analysis presented is based on publicly available information and general market observations and should not be relied upon for making investment decisions. Readers should conduct their own research and consult with qualified financial advisors before making any investment decisions. The AI investment landscape is highly dynamic and subject to significant risks including technological, regulatory, and market uncertainties that could materially affect investment outcomes.