The integration of artificial intelligence into organizational workflows represents one of the most significant technological transformations in modern business history, fundamentally altering how employees interact with technology, process information, and deliver value to customers. Successfully navigating this transformation requires a comprehensive understanding of change management principles specifically tailored to the unique challenges and opportunities presented by AI implementation, ensuring that human resources remain engaged, productive, and aligned with evolving organizational objectives.
Discover the latest trends in AI implementation to understand how leading organizations are successfully managing the transition to AI-powered workflows while maintaining employee satisfaction and productivity. The complexity of AI adoption extends far beyond technical implementation, encompassing cultural shifts, skill development requirements, and fundamental changes in job roles and responsibilities that must be carefully orchestrated to achieve sustainable transformation.
Understanding the Human Element in AI Transformation
The most critical factor determining the success or failure of AI implementation initiatives lies not in the sophistication of the technology itself, but in the organization’s ability to effectively manage the human aspects of change. Employees facing AI integration often experience a complex range of emotions including excitement about new possibilities, anxiety about job security, confusion about new processes, and resistance to changing established workflows that have served them well in the past.
Successful AI change management begins with acknowledging these human concerns and developing comprehensive strategies that address both the rational and emotional aspects of transformation. Organizations must recognize that AI adoption represents not merely a technological upgrade, but a fundamental shift in how work is conceptualized, executed, and evaluated, requiring careful attention to employee psychology, organizational culture, and communication strategies that build trust and confidence in the transformation process.
The most effective change management approaches for AI implementation focus on transparency, education, and inclusive participation in the transformation process, ensuring that employees understand not only what changes are occurring, but why these changes are necessary and how they will benefit both individual career development and organizational success. This human-centered approach to AI adoption creates a foundation for sustainable change that leverages technology to enhance rather than replace human capabilities.
Developing a Comprehensive AI Adoption Framework
Creating a structured framework for AI adoption provides organizations with a roadmap for managing complexity while ensuring that all stakeholders understand their roles and responsibilities throughout the transformation process. This framework must encompass strategic planning, stakeholder engagement, technical implementation, training and development, and continuous evaluation components that work together to create a cohesive approach to organizational change.
The strategic planning component of an AI adoption framework requires clear articulation of organizational objectives, identification of key performance indicators, establishment of realistic timelines, and development of risk mitigation strategies that address potential challenges before they become obstacles to success. This planning phase must involve representatives from all organizational levels and departments to ensure that diverse perspectives are considered and that the resulting framework reflects the full complexity of the organizational environment.
Stakeholder engagement represents another critical component of the adoption framework, requiring systematic identification of all individuals and groups who will be affected by AI implementation, assessment of their current capabilities and concerns, and development of targeted communication and support strategies that address their specific needs and circumstances. This engagement process must be ongoing throughout the transformation, providing regular opportunities for feedback, adjustment, and refinement of the adoption approach.
Experience advanced AI capabilities with Claude to understand how sophisticated AI tools can be integrated into existing workflows while maintaining focus on human-centered design and usability. The technical implementation component of the framework must balance cutting-edge AI capabilities with practical considerations such as system integration, data security, user interface design, and performance optimization that ensures smooth operation within existing organizational infrastructure.
Addressing Employee Resistance and Building Buy-in
Employee resistance to AI implementation often stems from legitimate concerns about job security, increased workload during transition periods, potential skill obsolescence, and fundamental changes to familiar work processes that have provided stability and competence. Understanding the root causes of resistance is essential for developing targeted strategies that address specific concerns while building enthusiasm for the benefits that AI implementation can provide.
Communication strategies that address resistance must be honest, transparent, and specific about how AI implementation will affect individual roles and responsibilities, providing concrete examples of how technology will enhance rather than replace human capabilities. Organizations must avoid generic assurances about AI benefits and instead focus on demonstrating specific ways that AI tools will reduce tedious tasks, provide better decision-making support, and create opportunities for employees to engage in more strategic and creative work.
Building buy-in requires active participation from employees in the AI selection, customization, and implementation process, ensuring that their expertise and preferences are reflected in the final solutions. This participatory approach not only improves the quality of AI implementations by incorporating frontline insights, but also creates a sense of ownership and investment in the success of the transformation that translates into higher adoption rates and more effective utilization of AI capabilities.
The most successful buy-in strategies also include recognition and reward systems that celebrate early adopters, acknowledge the effort required to learn new skills, and provide tangible benefits for employees who contribute to successful AI implementation. These recognition programs must be carefully designed to avoid creating division between early adopters and those who require more time to adapt, instead fostering a culture of mutual support and collective success.
Designing Effective Training and Development Programs
The success of AI adoption depends heavily on the quality and comprehensiveness of training programs that help employees develop the skills, knowledge, and confidence necessary to work effectively with AI tools and systems. These training programs must address not only the technical aspects of using AI tools, but also the conceptual understanding of how AI works, its limitations and capabilities, and best practices for integrating AI into existing work processes.
Effective AI training programs recognize that different employees have varying levels of technical expertise, learning preferences, and comfort with new technologies, requiring diverse training approaches that can accommodate these differences while ensuring that everyone achieves the necessary competency levels. This might include hands-on workshops, self-paced online learning modules, mentoring programs, and peer-to-peer learning opportunities that provide multiple pathways for skill development.
The content of training programs must evolve continuously as AI technologies advance and organizational needs change, requiring ongoing assessment of training effectiveness, identification of skill gaps, and development of advanced training modules that help employees grow their capabilities over time. This continuous learning approach ensures that AI adoption remains dynamic and responsive to changing technological capabilities and business requirements.
Training programs must also address the ethical and responsible use of AI tools, helping employees understand issues such as data privacy, algorithmic bias, decision transparency, and the appropriate boundaries for AI-assisted decision-making. This ethical component of training ensures that AI adoption supports organizational values and maintains compliance with relevant regulations and standards.
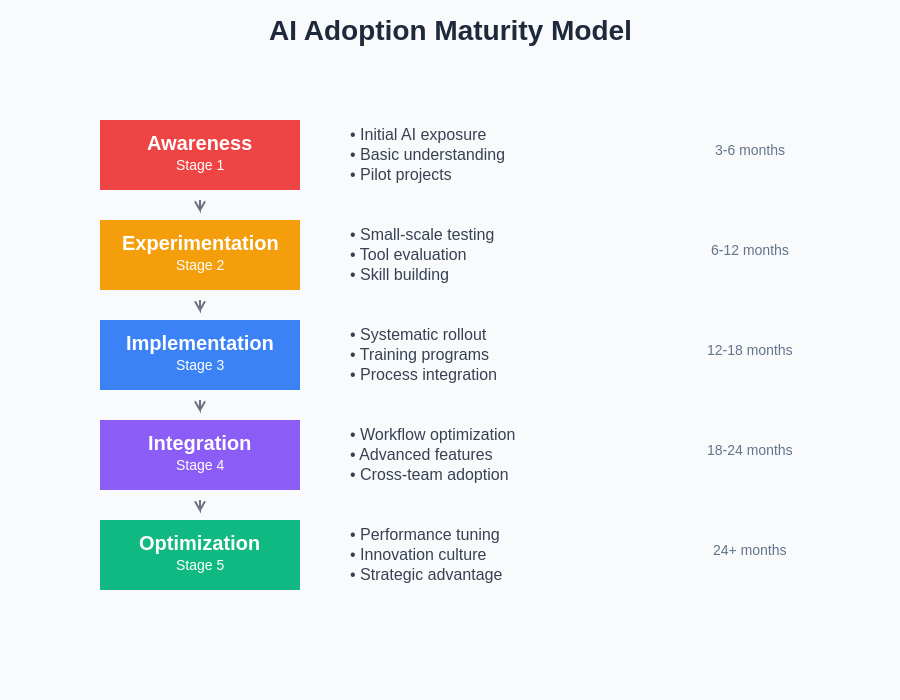
Organizations progress through distinct stages of AI maturity, each requiring different change management approaches and employee development strategies. Understanding these stages helps leaders tailor their adoption strategies to current organizational capabilities while building toward more advanced AI integration.
Creating Support Systems and Resources
Successful AI adoption requires robust support systems that provide employees with ongoing assistance, troubleshooting resources, and opportunities for continuous learning and development. These support systems must be accessible, responsive, and comprehensive enough to address the diverse needs of employees at different stages of the adoption journey.
Technical support systems should include help desk services, user documentation, tutorial resources, and troubleshooting guides that help employees resolve common issues quickly and independently. However, effective support goes beyond technical assistance to include emotional and psychological support that helps employees navigate the stress and uncertainty that often accompany significant organizational change.
Peer support networks and communities of practice can be particularly valuable for AI adoption, creating opportunities for employees to share experiences, exchange tips and best practices, and provide mutual encouragement and assistance. These informal support networks often prove more valuable than formal training programs because they provide real-time, contextual assistance from colleagues who understand specific organizational challenges and constraints.
Enhance your research capabilities with Perplexity to access comprehensive information resources that support ongoing learning and development in AI technologies and change management practices. The availability of high-quality information and research resources enables employees to continue developing their understanding of AI capabilities and applications beyond formal training programs.
Measuring Success and Continuous Improvement
Effective change management for AI adoption requires systematic measurement of progress, identification of areas for improvement, and continuous refinement of adoption strategies based on real-world experience and feedback. This measurement process must encompass both quantitative metrics such as usage rates, productivity improvements, and error reduction, as well as qualitative measures such as employee satisfaction, confidence levels, and perceived value of AI tools.
Key performance indicators for AI adoption should align with overall organizational objectives while providing specific insights into the effectiveness of change management strategies. These might include metrics such as time-to-competency for new AI tools, employee engagement scores during transition periods, retention rates of key personnel, and the frequency of AI tool utilization across different departments and functions.
Regular assessment of adoption progress provides opportunities to identify and address emerging challenges before they become significant obstacles to success. This might involve conducting surveys, focus groups, interviews, and observational studies that provide insights into employee experiences and perceptions of the AI adoption process.
The continuous improvement approach to AI change management recognizes that adoption is an ongoing process rather than a one-time event, requiring sustained attention to employee needs, technological developments, and organizational evolution. This long-term perspective ensures that AI implementations remain effective and valuable as both technology and organizational requirements continue to evolve.
Leadership’s Role in AI Transformation
Leadership plays a crucial role in determining the success of AI adoption initiatives, serving as champions for change, role models for desired behaviors, and architects of organizational culture that supports innovation and continuous learning. Effective leadership during AI transformation requires a combination of strategic vision, emotional intelligence, communication skills, and technical understanding that enables leaders to guide their organizations through complex change processes.
Leaders must demonstrate genuine commitment to AI adoption through their actions, decisions, and resource allocation, showing employees that the transformation is a strategic priority that deserves serious attention and investment. This commitment must be visible and consistent across all levels of leadership, from executive sponsors to front-line supervisors who directly manage employees affected by AI implementation.
Communication from leadership must be frequent, honest, and specific about both the opportunities and challenges associated with AI adoption, helping employees understand the rationale for change while acknowledging the difficulties involved in transformation processes. Leaders must be prepared to address concerns, answer questions, and provide reassurance during periods of uncertainty and stress.
The most effective leaders during AI transformation also serve as continuous learners themselves, demonstrating curiosity about new technologies, willingness to experiment with AI tools, and openness to feedback from employees who may have greater technical expertise in specific areas. This learning orientation from leadership creates a culture where continuous development and adaptation are valued and supported.
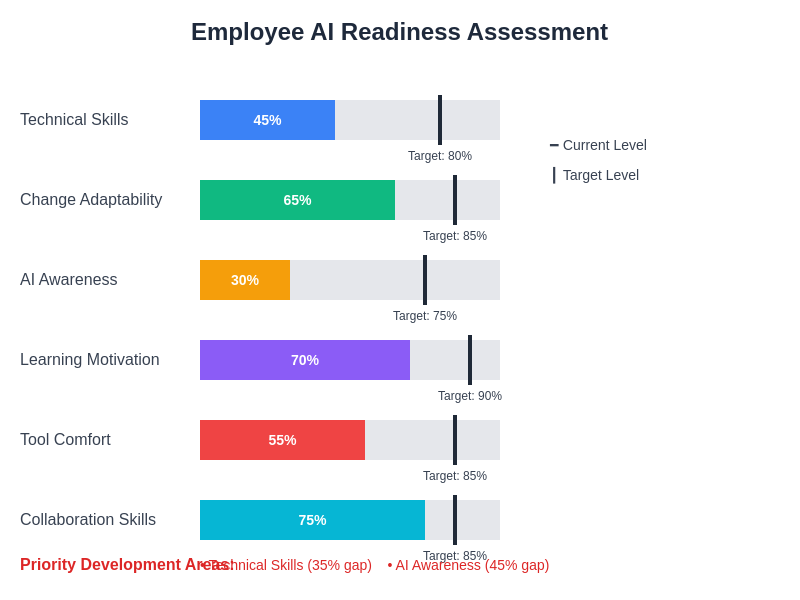
Understanding employee readiness levels across different dimensions enables organizations to develop targeted support strategies and allocate resources effectively during AI adoption initiatives.
Cultural Transformation and Organizational Alignment
AI adoption often requires fundamental changes to organizational culture, including shifts in how decisions are made, how performance is evaluated, how risks are managed, and how innovation is encouraged and supported. These cultural changes can be more challenging to implement than technical changes, requiring sustained effort and attention from all levels of the organization.
Creating a culture that supports AI adoption requires emphasis on values such as continuous learning, experimentation, data-driven decision-making, and collaboration between humans and technology. These cultural values must be reinforced through organizational policies, procedures, reward systems, and daily management practices that demonstrate their importance and relevance.
The alignment between AI implementation and existing organizational values and practices must be carefully managed to avoid conflicts and contradictions that can undermine adoption efforts. This might require modification of existing processes, policies, and practices to ensure consistency with new AI-enabled workflows and decision-making processes.
Cultural transformation also requires attention to diversity, equity, and inclusion considerations, ensuring that AI adoption does not inadvertently create or exacerbate existing inequalities within the organization. This includes careful consideration of how AI tools are designed, implemented, and used to ensure that they support fair and equitable treatment of all employees.
Risk Management and Mitigation Strategies
AI adoption involves various risks including technical failures, security vulnerabilities, regulatory compliance issues, employee burnout, productivity disruptions, and potential negative impacts on customer relationships. Effective change management requires systematic identification, assessment, and mitigation of these risks throughout the adoption process.
Technical risks can be addressed through careful vendor selection, thorough testing procedures, phased implementation approaches, and robust backup and recovery systems that ensure business continuity even when AI systems encounter problems. However, change management must also address human and organizational risks that can be equally damaging to adoption success.
Employee burnout during AI adoption can result from excessive workload during transition periods, stress related to learning new skills, anxiety about job security, and frustration with technical difficulties. Mitigation strategies for these risks include realistic timeline planning, adequate resource allocation, stress management support, and clear communication about long-term career development opportunities.
Productivity disruptions during AI adoption are inevitable but can be minimized through careful planning, phased implementation approaches, and provision of adequate training and support resources that help employees maintain effectiveness while adapting to new tools and processes. These mitigation strategies must balance the need for rapid adoption with recognition of the time required for employees to achieve competency with new systems.
Integration with Existing Systems and Processes
Successful AI adoption requires careful integration with existing organizational systems, processes, and workflows to ensure that new capabilities enhance rather than disrupt current operations. This integration challenge extends beyond technical compatibility to include process alignment, role clarification, and workflow optimization that leverages AI capabilities while maintaining operational effectiveness.
The integration process must begin with comprehensive assessment of current systems and processes to identify opportunities for AI enhancement, potential conflicts or redundancies, and requirements for system modification or replacement. This assessment should involve employees who have deep knowledge of existing workflows and can provide insights into practical integration challenges and opportunities.
Process redesign during AI integration should focus on optimizing the combination of human and artificial intelligence capabilities, ensuring that each contributes its unique strengths to overall organizational effectiveness. This might involve eliminating redundant steps, automating routine tasks, and creating new roles that leverage AI insights for strategic decision-making.
Change management during system integration must address the complexity and potential confusion that can result from operating both old and new systems simultaneously during transition periods. Clear communication, comprehensive training, and robust support systems are essential for helping employees navigate these complex transition periods successfully.
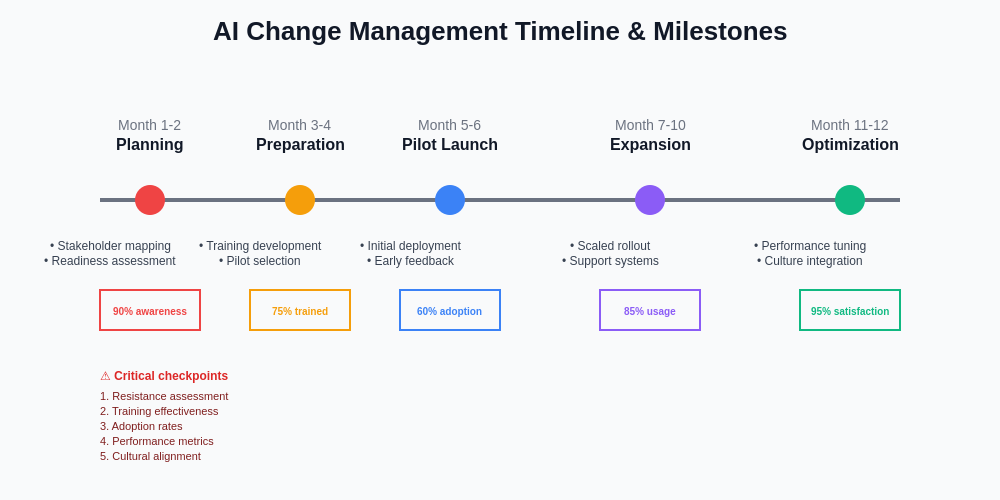
A structured timeline with clear milestones helps organizations manage the complexity of AI adoption while maintaining momentum and accountability throughout the transformation process.
Future-Proofing AI Adoption Strategies
The rapid pace of AI development means that adoption strategies must be designed to accommodate continuous evolution of capabilities, requirements, and best practices. Future-proofing requires building flexibility and adaptability into adoption approaches while maintaining focus on fundamental principles of effective change management.
Organizations must develop capabilities for continuous technology assessment, allowing them to identify and evaluate new AI developments that might enhance their current implementations or require modifications to existing systems and processes. This ongoing assessment capability ensures that AI investments remain current and valuable as technology continues to advance.
Future-proofing also requires development of employee capabilities that transcend specific AI tools or technologies, focusing on skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, creativity, and emotional intelligence that remain valuable regardless of technological changes. These foundational capabilities enable employees to adapt to new AI tools and applications as they become available.
The organizational learning and adaptation capabilities developed during initial AI adoption provide a foundation for managing future technological changes more effectively. This includes development of change management expertise, employee resilience, and organizational agility that facilitate adoption of future innovations and improvements.
Successful future-proofing also requires attention to ethical and regulatory considerations that may evolve as AI technologies become more sophisticated and widespread. Organizations must build capabilities for monitoring and responding to changing ethical standards, regulatory requirements, and societal expectations regarding AI use in business contexts.
Conclusion and Long-term Sustainability
The successful adoption of AI technologies requires a comprehensive approach to change management that addresses not only technical implementation but also the human, cultural, and organizational factors that determine long-term success. This holistic approach recognizes that AI adoption is fundamentally about enabling people to work more effectively rather than simply implementing new technology.
Sustainable AI adoption requires ongoing attention to employee development, organizational learning, and continuous improvement that ensures AI capabilities remain aligned with evolving business needs and employee capabilities. This long-term perspective prevents AI implementations from becoming obsolete or underutilized as circumstances change.
The change management strategies and capabilities developed during AI adoption provide valuable foundations for managing future technological and organizational changes, creating resilient organizations that can adapt effectively to an increasingly dynamic and technology-driven business environment. These capabilities represent lasting value that extends far beyond any specific AI implementation.
Organizations that successfully manage AI adoption through comprehensive change management approaches position themselves for sustained competitive advantage, enhanced employee satisfaction, and improved organizational effectiveness that benefits all stakeholders over the long term.
Disclaimer
This article provides general guidance on change management for AI adoption and should not be considered as professional consulting advice. The effectiveness of change management strategies may vary based on organizational context, industry requirements, regulatory considerations, and specific technological implementations. Organizations should conduct thorough assessment of their unique circumstances and may benefit from professional change management and AI implementation consulting services to ensure successful adoption outcomes.
