The educational landscape has been transformed by the emergence of artificial intelligence-powered chatbots that serve as virtual teaching assistants, student support systems, and learning companions. Among the most prominent and successful implementations in this domain are Jill Watson, developed by Georgia Institute of Technology, and Ada Student Support, created to enhance student engagement and academic success across various educational institutions. These sophisticated AI systems represent the cutting edge of educational technology, demonstrating how artificial intelligence can be seamlessly integrated into academic environments to provide personalized, accessible, and effective learning support.
Explore the latest developments in AI education technology to understand how these innovative systems are reshaping the educational experience for students and educators worldwide. The comparison between these two pioneering platforms reveals fundamental differences in design philosophy, implementation strategies, and educational objectives that define the current state and future direction of AI-powered educational assistance.
The Genesis of Educational AI Assistants
The development of educational chatbots emerged from the recognition that traditional educational support systems often fail to provide immediate, personalized, and consistently available assistance to students. Educational institutions worldwide face challenges related to student-to-faculty ratios, limited office hours, and the need for scalable support mechanisms that can accommodate diverse learning styles and schedules. The introduction of AI-powered educational assistants represents a revolutionary approach to addressing these persistent challenges while enhancing the overall quality of educational experiences.
Jill Watson, named after IBM’s Watson cognitive computing platform, was conceived as an experiment in augmenting traditional teaching methods with artificial intelligence capabilities. The system was designed to handle routine student inquiries, provide immediate responses to frequently asked questions, and serve as a bridge between students and human instructors. Similarly, Ada Student Support was developed with the mission of creating a comprehensive student engagement platform that could provide academic guidance, emotional support, and administrative assistance through sophisticated conversational interfaces.
The evolution of these systems reflects broader trends in educational technology adoption, where institutions seek to leverage artificial intelligence not as a replacement for human educators but as a powerful complement that enhances the teaching and learning experience. Both platforms demonstrate how thoughtful implementation of AI technology can address specific educational challenges while maintaining the human elements that remain essential for effective education.
Jill Watson: The Academic Teaching Assistant Revolution
Jill Watson represents one of the most successful implementations of AI technology in higher education, serving as a virtual teaching assistant in online courses at Georgia Institute of Technology. The system was initially deployed in graduate-level courses where it seamlessly integrated with existing learning management systems to provide students with immediate access to course-related information, assignment clarifications, and academic guidance. The remarkable aspect of Jill Watson’s implementation was that students remained unaware they were interacting with an AI system for several months, demonstrating the sophisticated level of natural language processing and contextual understanding achieved by the platform.
The technical architecture underlying Jill Watson combines advanced natural language processing algorithms with comprehensive knowledge bases derived from course materials, previous student interactions, and instructor guidance. The system continuously learns from student inquiries and instructor feedback, refining its responses and expanding its knowledge base to provide increasingly accurate and helpful assistance. This adaptive learning capability ensures that Jill Watson becomes more effective over time, developing a deeper understanding of course-specific terminology, common student challenges, and optimal response strategies.
Experience advanced AI capabilities with Claude for educational applications that require sophisticated reasoning and contextual understanding. The success of Jill Watson demonstrates the potential for AI systems to handle complex educational interactions while maintaining the quality and accuracy expected in academic environments.
Ada Student Support: Comprehensive Student Engagement Platform
Ada Student Support takes a broader approach to educational AI assistance, focusing on comprehensive student engagement and support across multiple dimensions of the educational experience. Unlike systems that primarily focus on academic content delivery, Ada is designed to address the holistic needs of students, including academic guidance, emotional support, administrative assistance, and career development advice. This comprehensive approach reflects an understanding that student success depends not only on academic achievement but also on overall engagement, well-being, and institutional connection.
The platform incorporates sophisticated sentiment analysis capabilities that enable it to recognize when students are experiencing stress, confusion, or frustration, allowing for appropriate escalation to human counselors or support staff when necessary. Ada’s conversational design emphasizes empathy and emotional intelligence, creating interactions that feel supportive and understanding rather than purely transactional. This emotional awareness component distinguishes Ada from more academically focused chatbots and reflects the growing recognition that effective educational support must address both cognitive and emotional aspects of learning.
Ada’s integration capabilities extend beyond traditional learning management systems to encompass student information systems, library resources, campus services, and external support networks. This comprehensive integration allows the platform to provide students with unified access to all aspects of their educational experience, from course registration and academic planning to mental health resources and career guidance services.
Comparative Analysis: Technical Architecture and Capabilities
The technical foundations of Jill Watson and Ada Student Support reveal fundamental differences in their architectural approaches and technological priorities. Jill Watson’s architecture emphasizes deep integration with specific course content and learning objectives, utilizing sophisticated natural language processing algorithms optimized for academic discourse and subject-specific terminology. The system’s knowledge representation framework is designed to handle complex academic concepts, multi-layered course structures, and the nuanced relationships between different educational components.
Ada Student Support employs a more distributed architecture that prioritizes flexibility and scalability across diverse institutional contexts and student populations. The platform’s technical design emphasizes modular components that can be customized and configured for different educational environments, student demographics, and institutional priorities. This architectural approach enables Ada to serve as a comprehensive student engagement platform rather than being limited to specific courses or academic subjects.
Both systems utilize advanced machine learning algorithms for continuous improvement and adaptation, but their learning strategies differ significantly in scope and focus. Jill Watson’s learning algorithms are optimized for deep understanding of specific academic domains, enabling highly accurate responses to course-related inquiries and sophisticated handling of subject-specific questions. Ada’s learning algorithms prioritize broader pattern recognition across diverse student interactions, emotional states, and support needs, enabling the system to provide more comprehensive but potentially less specialized assistance.
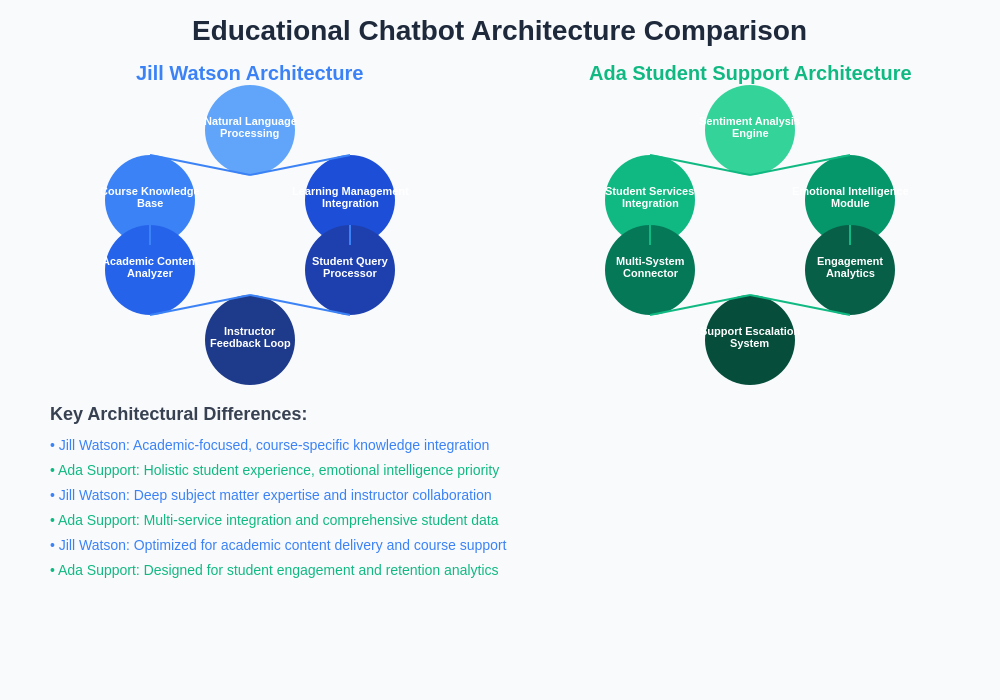
The architectural differences between these systems reflect their distinct educational philosophies and implementation strategies, with Jill Watson focusing on academic excellence and Ada emphasizing comprehensive student support and engagement.
Implementation Strategies and Institutional Integration
The deployment strategies employed by Jill Watson and Ada Student Support demonstrate different approaches to institutional integration and change management in educational environments. Jill Watson’s implementation strategy emphasizes gradual integration with existing course structures, beginning with pilot programs in specific courses before expanding to broader institutional adoption. This cautious approach allows for careful monitoring of system performance, student satisfaction, and educational outcomes while minimizing disruption to established teaching practices.
The system’s integration with learning management platforms such as Canvas and Blackboard ensures seamless incorporation into existing workflows for both students and instructors. Jill Watson’s deployment process includes comprehensive training for faculty members, detailed analytics and reporting capabilities, and systematic evaluation mechanisms that enable continuous improvement and optimization of the system’s performance within specific educational contexts.
Ada Student Support employs a more comprehensive institutional transformation approach that requires significant changes to existing student support infrastructures and service delivery models. The platform’s implementation involves coordination across multiple departments, including academic affairs, student services, information technology, and counseling services. This holistic approach necessitates substantial institutional commitment and change management processes but offers the potential for more transformative improvements in overall student experience and outcomes.
Leverage advanced AI research capabilities with Perplexity to explore implementation strategies and best practices for educational technology integration. The success of both platforms demonstrates the importance of thoughtful implementation planning and institutional alignment in achieving positive educational outcomes through AI technology.
Student Interaction Patterns and User Experience Design
The user experience design philosophies underlying Jill Watson and Ada Student Support reflect their different priorities and target outcomes in educational settings. Jill Watson’s interaction design emphasizes efficiency and accuracy in academic information delivery, with conversational flows optimized for quick resolution of course-related inquiries and seamless integration with learning activities. The system’s interface prioritizes clarity and directness, enabling students to obtain needed information without unnecessary complexity or confusion.
Student interaction patterns with Jill Watson typically involve specific, goal-oriented queries related to course content, assignment requirements, deadlines, and academic procedures. The system’s response patterns are designed to provide comprehensive yet concise information that enables students to continue with their learning activities without significant interruption or delay. This focused approach to interaction design has resulted in high student satisfaction rates and measurable improvements in course engagement and completion rates.
Ada Student Support’s user experience design takes a more conversational and relationship-building approach, emphasizing the development of ongoing supportive relationships between students and the AI system. The platform’s interaction patterns encourage exploration and discovery, with conversational flows designed to help students identify resources, opportunities, and support services they might not have otherwise discovered. This approach reflects an understanding that effective student support often involves helping students articulate and address needs they may not have initially recognized.
The emotional intelligence components integrated into Ada’s interaction design enable the system to adapt its communication style based on student emotional states, stress levels, and engagement patterns. This adaptive approach to conversation management creates more personalized and supportive interactions that can evolve over time as the system learns more about individual student needs and preferences.
Learning Outcomes and Educational Effectiveness
The measurement of educational effectiveness and learning outcomes represents a critical area where Jill Watson and Ada Student Support demonstrate their distinct approaches to educational improvement. Jill Watson’s impact on learning outcomes is primarily measured through traditional academic metrics such as course completion rates, assignment submission patterns, student engagement levels, and overall course satisfaction scores. Research conducted at Georgia Institute of Technology has demonstrated significant improvements in these areas following Jill Watson’s implementation, with students reporting higher levels of satisfaction with course support and more efficient resolution of academic questions.
The system’s effectiveness in reducing instructor workload while maintaining high-quality student support has been particularly noteworthy, enabling faculty members to focus more time and attention on complex educational activities such as research guidance, critical thinking development, and personalized mentoring. This redistribution of educational effort has resulted in improved overall course quality and enhanced student-faculty relationships despite reduced direct interaction time.
Ada Student Support’s effectiveness is measured through broader student success indicators including retention rates, academic progress, utilization of support services, and overall student well-being metrics. The platform’s comprehensive approach to student engagement has shown positive impacts on students’ sense of belonging, institutional connection, and persistence through challenging academic periods. These outcomes reflect Ada’s focus on addressing the multifaceted nature of student success rather than focusing exclusively on academic performance metrics.
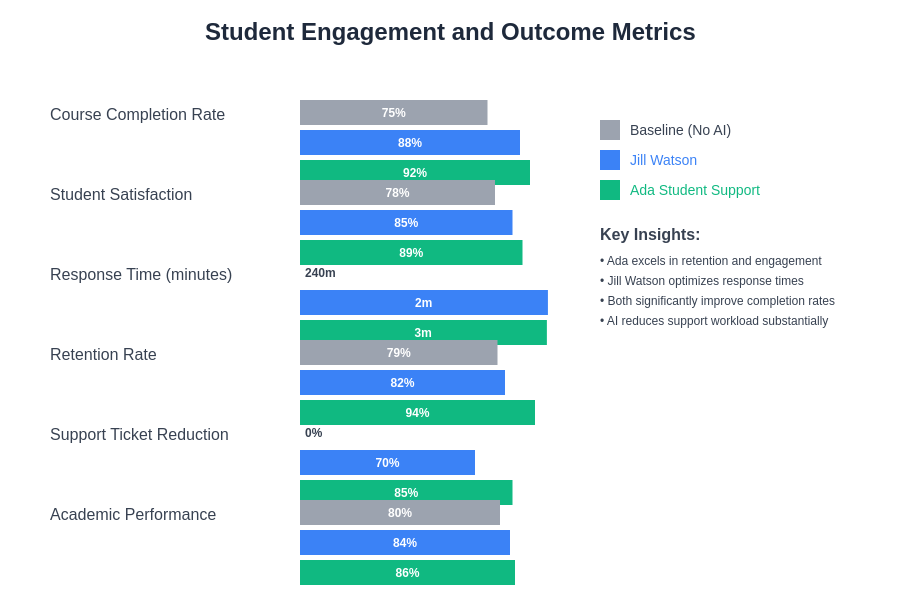
The comparative analysis of learning outcomes demonstrates that both platforms achieve their intended objectives within their respective domains, with Jill Watson excelling in academic support efficiency and Ada Student Support demonstrating superior performance in comprehensive student engagement and retention.
Scalability and Institutional Adoption Challenges
The scalability characteristics of educational AI chatbots present significant considerations for institutional decision-making and long-term strategic planning. Jill Watson’s scalability model focuses on horizontal expansion across courses and academic departments within institutions, with the system’s architecture designed to accommodate increasing numbers of courses and students without proportional increases in computational resources or maintenance requirements. This scalability approach has enabled successful implementation across multiple courses at Georgia Institute of Technology and has attracted interest from other educational institutions seeking similar academic support capabilities.
The technical scalability of Jill Watson is enhanced by its integration with existing educational technology infrastructures, minimizing the need for additional hardware investments or complex system modifications. However, the system’s scalability is somewhat limited by its dependence on course-specific knowledge bases and the need for ongoing instructor involvement in system training and oversight.
Ada Student Support’s scalability model emphasizes vertical integration across different aspects of student experience and horizontal expansion across diverse institutional contexts and student populations. The platform’s modular architecture enables institutions to implement selected components based on their specific needs and resources while maintaining the option to expand functionality over time. This flexible approach to scalability has facilitated adoption across different types of educational institutions, from small colleges to large university systems.
The comprehensive nature of Ada’s functionality creates both opportunities and challenges for scalability, as the system’s effectiveness depends on successful integration with multiple institutional systems and processes. While this integration complexity can present implementation challenges, the resulting comprehensive student support capabilities offer significant value for institutions committed to transformative improvements in student experience and outcomes.
Privacy, Security, and Ethical Considerations
The implementation of AI-powered educational chatbots raises important considerations related to student privacy, data security, and ethical use of artificial intelligence in educational contexts. Both Jill Watson and Ada Student Support have developed comprehensive approaches to addressing these critical concerns while maintaining the functionality and effectiveness that makes them valuable educational tools.
Jill Watson’s privacy and security framework emphasizes the protection of student academic information and course-related data through encryption, access controls, and compliance with educational privacy regulations such as FERPA. The system’s data collection practices are limited to information necessary for providing academic support, with clear policies governing data retention, usage, and sharing. The transparency of Jill Watson’s AI nature, once revealed to students, has generally been well-received and has contributed to trust in the system’s ethical implementation.
Ada Student Support’s privacy considerations are more complex due to the broader scope of student information handled by the platform, including emotional state data, personal circumstances, and comprehensive educational records. The system implements sophisticated privacy protection mechanisms including differential privacy techniques, anonymization processes, and strict access controls that ensure student information is used only for providing support services and improving system effectiveness.
Both platforms address ethical considerations related to AI bias, fairness, and transparency through regular auditing processes, diverse training data sets, and ongoing monitoring of system responses for potential bias or inappropriate content. The commitment to ethical AI implementation reflects the educational community’s recognition that trust and transparency are essential for successful adoption of AI technology in educational settings.
Future Development Trends and Innovation Directions
The future evolution of educational AI chatbots is likely to be influenced by advances in artificial intelligence technology, changing educational needs, and emerging pedagogical approaches that emphasize personalized and adaptive learning experiences. Both Jill Watson and Ada Student Support are positioned to benefit from ongoing developments in natural language processing, machine learning, and educational technology integration.
Future enhancements to Jill Watson may include more sophisticated understanding of complex academic concepts, improved ability to provide personalized learning recommendations, and enhanced integration with emerging educational technologies such as virtual and augmented reality learning environments. The system’s evolution will likely focus on deepening its academic support capabilities while maintaining its efficiency and reliability advantages.
Ada Student Support’s future development trajectory may emphasize enhanced emotional intelligence capabilities, improved predictive analytics for identifying at-risk students, and expanded integration with emerging student support technologies and services. The platform’s comprehensive approach to student engagement positions it well for incorporation of new technologies that address evolving student needs and institutional priorities.
The convergence of educational AI technologies suggests that future systems may combine the academic focus of platforms like Jill Watson with the comprehensive support capabilities of systems like Ada, creating next-generation educational AI assistants that provide both deep academic support and holistic student engagement capabilities.
Implementation Best Practices and Recommendations
The successful implementation of educational AI chatbots requires careful consideration of institutional context, student needs, technical infrastructure, and change management processes. Based on the experiences of Jill Watson and Ada Student Support, several best practices emerge for institutions considering adoption of similar technologies.
Successful implementation begins with clear definition of objectives and success metrics that align with institutional priorities and student needs. Institutions should carefully assess whether their primary goals involve improving academic support efficiency, enhancing comprehensive student engagement, or achieving specific learning outcomes that can be addressed through AI assistance. This assessment should inform the selection between platforms with different strengths and capabilities.
Technical infrastructure preparation represents another critical success factor, with institutions needing to ensure adequate computational resources, data management capabilities, and integration platforms that can support the chosen AI system. The complexity of integration requirements varies significantly between different types of educational AI platforms, necessitating careful technical planning and resource allocation.
Change management processes should address both faculty and student preparation for AI integration, including training programs, communication strategies, and ongoing support mechanisms that facilitate smooth adoption and effective utilization of AI capabilities. The success of both Jill Watson and Ada Student Support has been enhanced by comprehensive change management approaches that address concerns, build confidence, and demonstrate value to all stakeholders.
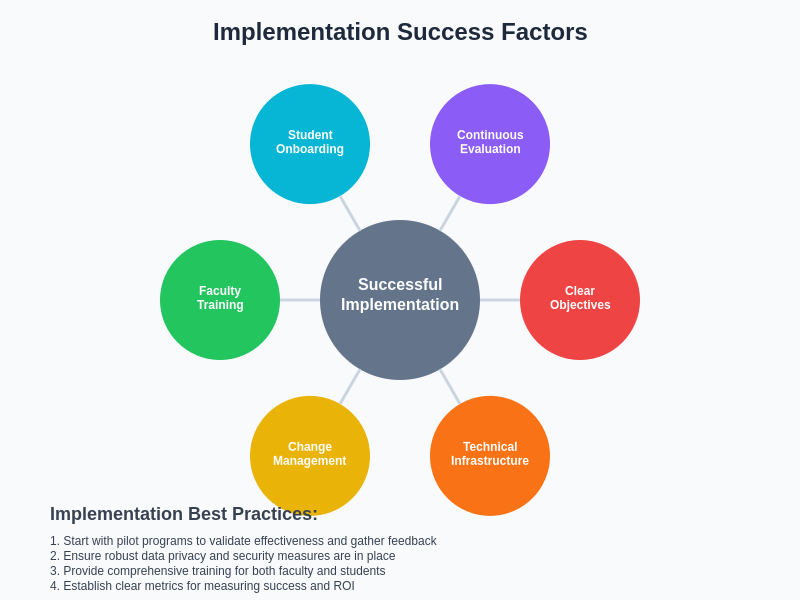
The comparative analysis of these leading educational AI platforms provides valuable insights for institutions, educators, and technology developers working to harness the transformative potential of artificial intelligence in educational settings.
Conclusion and Strategic Implications
The comparison between Jill Watson and Ada Student Support illuminates the diverse approaches and significant potential of AI-powered educational chatbots in transforming teaching, learning, and student support processes. These platforms demonstrate that successful educational AI implementation requires careful alignment between technological capabilities, institutional objectives, and student needs rather than adoption of AI technology for its own sake.
The specialized academic focus of Jill Watson offers compelling advantages for institutions seeking to enhance course-specific support and improve educational efficiency while maintaining high academic standards. The platform’s success in seamlessly integrating with existing educational workflows and providing immediate, accurate academic assistance demonstrates the potential for AI to augment traditional teaching methods without disrupting effective educational practices.
Ada Student Support’s comprehensive approach to student engagement provides a model for institutions seeking transformative improvements in overall student experience and success outcomes. The platform’s emphasis on holistic support, emotional intelligence, and institutional integration reflects an understanding that student success depends on addressing multiple dimensions of the educational experience simultaneously.
The future of educational AI lies not in choosing between these different approaches but in understanding how different AI capabilities can be strategically deployed to address specific educational challenges and opportunities. The continued evolution of both academic-focused and comprehensive student support AI platforms will provide educators and institutions with increasingly sophisticated tools for enhancing educational effectiveness and student success.
The transformative potential of educational AI chatbots extends beyond individual platforms to encompass broader changes in educational delivery models, student expectations, and institutional capabilities that will shape the future of teaching and learning in the digital age.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional advice regarding educational technology selection or implementation. The views expressed are based on publicly available information about educational AI platforms and their reported performance characteristics. Educational institutions should conduct thorough evaluations of their specific needs, technical capabilities, and regulatory requirements before implementing AI-powered educational technologies. The effectiveness of educational AI platforms may vary depending on institutional context, student populations, and implementation approaches.