The artificial intelligence landscape has witnessed an unprecedented transformation with the emergence of sophisticated AI assistants that are reshaping how we approach search, productivity, and information processing. At the forefront of this revolution stand two technological giants: Google Bard and Microsoft Copilot, each representing distinct philosophies and approaches to AI-powered assistance. These platforms have fundamentally altered the paradigm of human-computer interaction, moving beyond simple query-response mechanisms to offer comprehensive, contextually aware assistance that adapts to individual needs and preferences.
Explore the latest AI developments and trends to understand how these platforms are continuously evolving and introducing new capabilities that push the boundaries of what artificial intelligence can accomplish in practical applications. The competition between these two AI powerhouses has accelerated innovation across the entire industry, resulting in more capable, accessible, and user-friendly AI tools that are transforming both personal productivity and professional workflows.
Understanding the Competitive Landscape
The rivalry between Google Bard and Microsoft Copilot represents more than just a technological competition; it embodies fundamentally different approaches to artificial intelligence integration and user experience design. Google Bard leverages the company’s extensive experience in search technologies and vast data repositories to provide comprehensive, research-oriented responses that excel in information retrieval and synthesis. Microsoft Copilot, conversely, focuses on deep integration with productivity applications and enterprise workflows, emphasizing practical utility and seamless incorporation into existing business processes.
This philosophical divergence has resulted in two distinct AI ecosystems, each with unique strengths and specialized use cases. Google Bard excels in scenarios requiring extensive research, creative content generation, and comprehensive analysis of complex topics, drawing upon Google’s unparalleled access to web-based information and advanced natural language processing capabilities. Microsoft Copilot demonstrates superior performance in structured productivity tasks, document creation, data analysis, and collaborative work environments, leveraging Microsoft’s deep understanding of enterprise software and business processes.
Search Capabilities and Information Retrieval
The fundamental approach to search and information retrieval represents one of the most significant differentiators between these two AI platforms. Google Bard harnesses the power of Google’s search infrastructure, providing real-time access to current information across the web while maintaining sophisticated understanding of query intent and context. This integration enables Bard to deliver comprehensive responses that synthesize information from multiple sources, identify trending topics, and provide up-to-date insights on rapidly evolving subjects.
Microsoft Copilot approaches search through a more structured lens, integrating with Microsoft’s ecosystem to provide contextually relevant information that aligns with user workflows and productivity objectives. Rather than focusing solely on comprehensive information retrieval, Copilot emphasizes actionable insights and practical applications of searched information, making it particularly effective for business intelligence, market research, and professional decision-making processes.
Experience advanced AI capabilities with Claude for sophisticated reasoning and analysis tasks that complement both Bard and Copilot’s capabilities. The emergence of multiple AI platforms has created an ecosystem where different tools excel in different scenarios, allowing users to select the most appropriate AI assistant based on their specific requirements and use cases.
Productivity Integration and Workflow Enhancement
The integration of artificial intelligence into productivity workflows represents a crucial battleground where Microsoft Copilot demonstrates significant advantages due to its native integration with Microsoft Office applications and enterprise software solutions. Copilot seamlessly incorporates into Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Outlook, and Teams, providing contextual assistance that understands document structure, data relationships, and collaborative requirements. This deep integration enables users to generate content, analyze data, create presentations, and manage communications without leaving their familiar work environment.
Google Bard approaches productivity through a more conversational and flexible interface, excelling in creative ideation, content brainstorming, and comprehensive research tasks that inform productivity workflows. While Bard may not offer the same level of direct application integration as Copilot, it provides superior capabilities for generating diverse content types, exploring creative alternatives, and conducting thorough analysis that can be exported and utilized across various productivity platforms and applications.
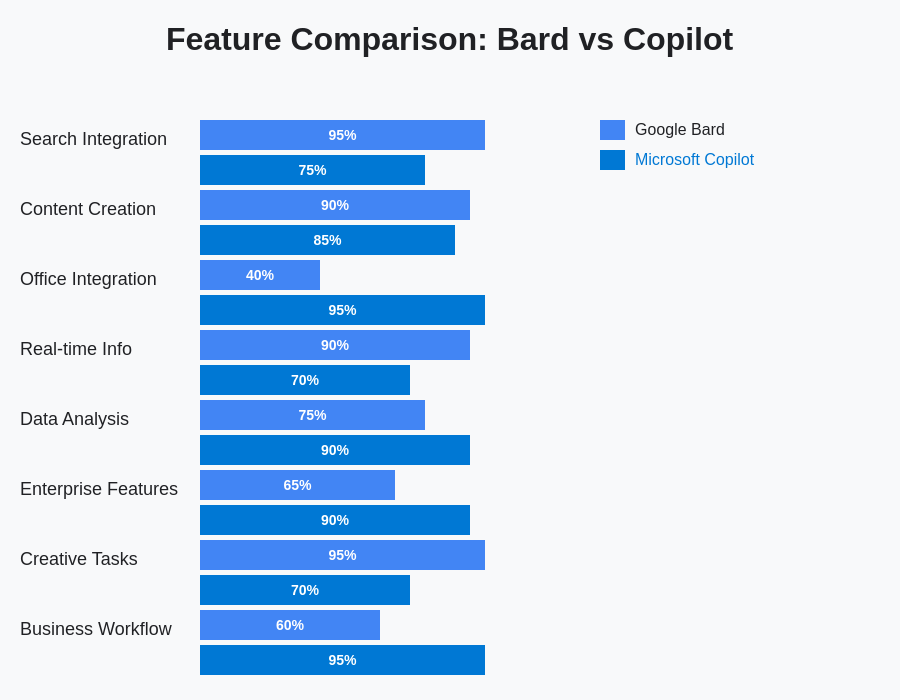
The comparative analysis of features reveals distinct strengths and specializations that make each platform uniquely valuable for different user types and use cases. Understanding these differences enables users to make informed decisions about which AI assistant best aligns with their specific requirements and workflow preferences.
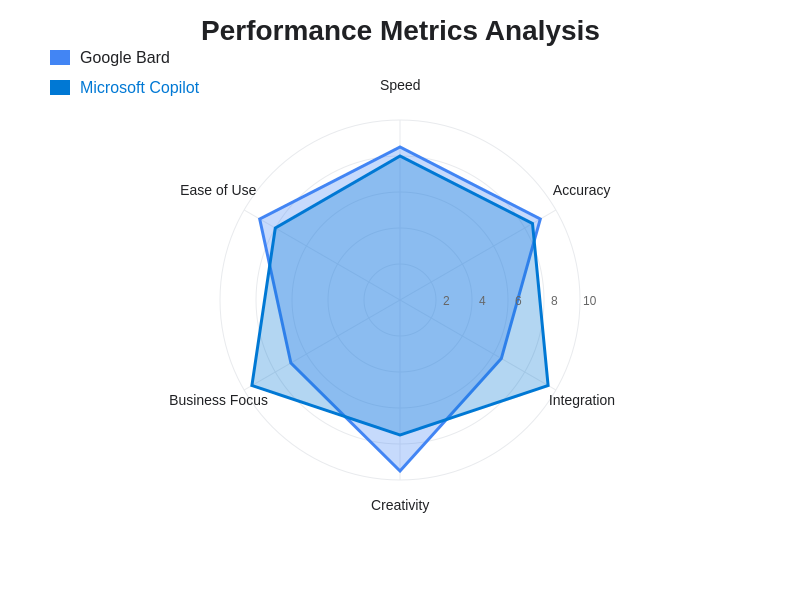
Content Generation and Creative Capabilities
Content creation represents an area where both platforms demonstrate remarkable capabilities, yet with distinctly different strengths and approaches. Google Bard excels in generating diverse, creative content that spans multiple formats, styles, and subject areas, drawing upon its extensive training data and sophisticated language modeling to produce engaging, informative, and contextually appropriate content. The platform demonstrates particular strength in long-form content creation, creative writing, educational materials, and comprehensive analysis pieces that require synthesis of information from multiple perspectives.
Microsoft Copilot focuses on business-oriented content generation that aligns with professional requirements and enterprise standards. The platform excels in creating structured documents, professional communications, data-driven reports, and presentation materials that adhere to corporate formatting and style guidelines. Copilot’s strength lies in generating content that integrates seamlessly with existing business processes and maintains consistency with organizational branding and communication standards.
The creative capabilities of both platforms extend beyond simple text generation to include assistance with ideation, brainstorming, problem-solving, and strategic planning. Google Bard approaches creativity through exploration and experimentation, encouraging users to explore multiple perspectives and unconventional approaches to challenges. Microsoft Copilot emphasizes practical creativity that drives business outcomes and supports organizational objectives through structured, goal-oriented content generation.
Data Analysis and Business Intelligence
The approach to data analysis and business intelligence showcases another significant differentiation between these AI platforms. Microsoft Copilot leverages its integration with Excel, Power BI, and other Microsoft analytics tools to provide sophisticated data analysis capabilities that include statistical analysis, trend identification, predictive modeling, and comprehensive reporting. The platform can interpret complex datasets, generate visualizations, and provide actionable insights that inform business decision-making processes.
Google Bard approaches data analysis through a more conversational and exploratory framework, excelling in explaining complex analytical concepts, interpreting research findings, and providing comprehensive context for data-driven insights. While Bard may not offer the same level of direct integration with business intelligence tools as Copilot, it provides superior capabilities for understanding and explaining analytical methodologies, interpreting statistical results, and generating comprehensive reports that synthesize quantitative and qualitative information.
Enhance your research capabilities with Perplexity for comprehensive information gathering that complements the analytical capabilities of both Bard and Copilot. The combination of multiple AI tools creates a powerful research and analysis ecosystem that addresses diverse information needs and analytical requirements.
User Experience and Interface Design
The user experience design philosophy of each platform reflects their respective approaches to AI assistance and user interaction. Google Bard emphasizes simplicity and conversational flow, providing a clean, intuitive interface that encourages exploration and experimentation. The platform’s design philosophy centers on making AI assistance feel natural and accessible, with minimal barriers between users and the AI’s capabilities. This approach particularly appeals to users who prefer flexible, open-ended interactions and appreciate the ability to explore topics deeply through extended conversations.
Microsoft Copilot integrates seamlessly into familiar Microsoft applications, maintaining consistency with established user interface patterns while introducing AI capabilities in contextually appropriate ways. The platform’s design philosophy prioritizes productivity and efficiency, ensuring that AI assistance enhances rather than disrupts existing workflows. This approach appeals particularly to business users and professionals who value integration with existing tools and processes over exploratory AI interaction.
The learning curve and accessibility of each platform vary significantly based on user background and requirements. Google Bard offers immediate accessibility with minimal setup requirements, making it attractive to casual users and those seeking quick AI assistance for diverse tasks. Microsoft Copilot requires familiarity with Microsoft applications but provides more powerful capabilities for users already embedded in the Microsoft ecosystem.
Performance Benchmarks and Comparative Analysis
Evaluating the performance of these AI platforms requires consideration of multiple factors including response accuracy, processing speed, context retention, and task completion effectiveness. Google Bard demonstrates superior performance in creative tasks, comprehensive research, and open-ended problem solving, leveraging its extensive training data and sophisticated language modeling to generate nuanced, contextually appropriate responses. The platform excels in scenarios requiring synthesis of information from multiple sources and generation of comprehensive, well-structured content.
Microsoft Copilot shows superior performance in structured business tasks, data manipulation, and productivity-focused activities, benefiting from its deep integration with Microsoft applications and understanding of business processes. The platform demonstrates particular strength in scenarios requiring precise formatting, data analysis, and integration with existing business workflows and documentation standards.

The quantitative analysis of performance metrics reveals complementary strengths that make both platforms valuable for different use cases and user requirements. Understanding these performance characteristics enables users to select the most appropriate AI assistant based on their specific objectives and workflow requirements.
Enterprise Integration and Security Considerations
Enterprise adoption considerations reveal significant differences in how these platforms approach organizational needs and security requirements. Microsoft Copilot offers comprehensive enterprise features including data governance, compliance monitoring, administrative controls, and integration with existing Microsoft security infrastructure. The platform provides detailed audit trails, user access management, and data protection mechanisms that align with enterprise security policies and regulatory requirements.
Google Bard approaches enterprise needs through its integration with Google Workspace and cloud infrastructure, providing scalable solutions that emphasize accessibility and collaboration. The platform offers robust privacy controls and data protection mechanisms, though with a somewhat different approach to enterprise integration compared to Microsoft’s more structured organizational framework.
Security and privacy considerations play crucial roles in platform selection, particularly for organizations handling sensitive information or operating in regulated industries. Both platforms implement comprehensive security measures, but with different approaches to data handling, storage, and user privacy protection that may influence adoption decisions based on specific organizational requirements and regulatory compliance needs.
Cost Structure and Value Proposition
The economic considerations surrounding these AI platforms reflect their different target markets and value propositions. Google Bard offers competitive pricing structures that emphasize accessibility and scalability, making advanced AI capabilities available to diverse user types including individuals, small businesses, and large organizations. The platform’s pricing model typically focuses on usage-based billing that scales with actual utilization rather than requiring significant upfront commitments.
Microsoft Copilot integrates into existing Microsoft licensing structures, often providing AI capabilities as part of broader productivity suite subscriptions. This approach can offer significant value for organizations already invested in Microsoft ecosystems, as it leverages existing infrastructure and user familiarity while adding advanced AI capabilities without requiring separate platform adoption or user training.
The total cost of ownership considerations extend beyond direct licensing fees to include training, integration, maintenance, and ongoing support requirements. Organizations must evaluate not only the direct costs of AI platform adoption but also the indirect costs associated with workflow modification, user training, and system integration requirements.
Future Development and Innovation Trajectories
The roadmap for future development reveals exciting possibilities for both platforms as they continue to evolve and expand their capabilities. Google Bard’s development trajectory emphasizes enhanced integration with Google’s broader AI research initiatives, including advances in multimodal AI, improved reasoning capabilities, and expanded knowledge integration. The platform continues to benefit from Google’s extensive research investments and access to cutting-edge AI technologies that promise to deliver increasingly sophisticated and capable AI assistance.
Microsoft Copilot’s future development focuses on deeper integration with Microsoft’s productivity ecosystem, enhanced enterprise features, and expanded support for specialized business workflows. The platform’s development roadmap includes improved data analysis capabilities, enhanced collaboration features, and more sophisticated automation tools that promise to transform how organizations approach productivity and efficiency.
Both platforms are investing heavily in personalization capabilities, contextual understanding, and adaptive learning mechanisms that will enable more tailored and effective AI assistance. The convergence of these development efforts promises to deliver increasingly powerful and user-friendly AI tools that will continue to reshape how we approach information processing, content creation, and productivity optimization.
Making the Strategic Choice
Selecting between Google Bard and Microsoft Copilot requires careful consideration of specific use cases, organizational requirements, existing technology investments, and strategic objectives. Google Bard represents the optimal choice for organizations and individuals prioritizing creative content generation, comprehensive research capabilities, and flexible AI interaction patterns. The platform particularly excels in scenarios requiring exploration, experimentation, and synthesis of diverse information sources.
Microsoft Copilot emerges as the superior choice for organizations deeply embedded in Microsoft ecosystems, with strong requirements for business process integration, structured productivity workflows, and enterprise-grade security and compliance features. The platform offers unmatched value for users who require seamless integration with existing Microsoft applications and business processes.
The decision ultimately depends on aligning platform capabilities with specific requirements, workflow preferences, and strategic objectives. Many organizations may benefit from adopting both platforms for different use cases, leveraging the unique strengths of each to create a comprehensive AI assistance ecosystem that addresses diverse needs and requirements.
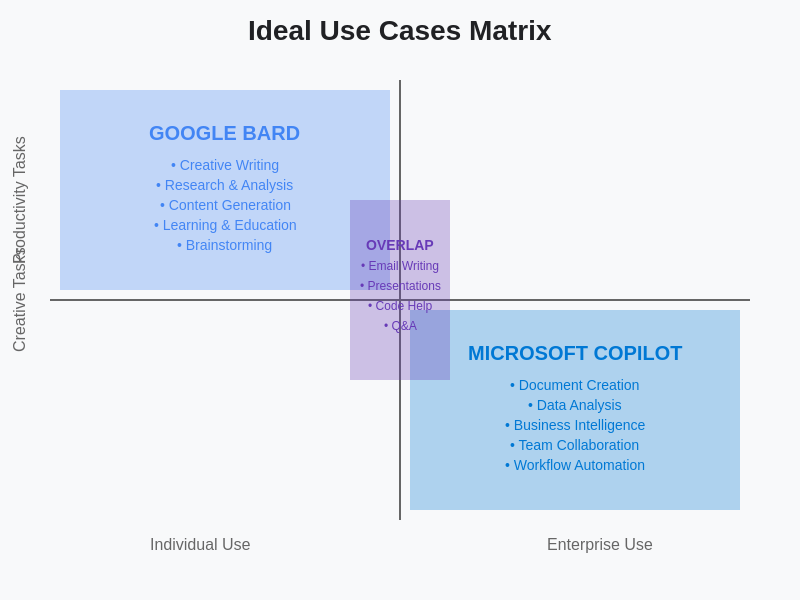
The strategic positioning of each platform becomes clear when analyzing their optimal use cases and target scenarios. This matrix visualization helps organizations and individuals identify which platform aligns best with their specific needs and operational requirements.
The evolution of artificial intelligence continues to accelerate, promising even more sophisticated and capable AI assistants that will further transform how we approach information processing, content creation, and productivity optimization. Both Google Bard and Microsoft Copilot represent significant steps forward in making advanced AI capabilities accessible and practical for everyday use, contributing to a future where human creativity and artificial intelligence collaborate to achieve unprecedented levels of productivity and innovation.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional advice. The views expressed are based on current understanding of AI technologies and their applications. Readers should conduct their own research and consider their specific requirements when selecting AI platforms. The effectiveness and suitability of these platforms may vary depending on individual use cases, organizational needs, and technical requirements. All product names, trademarks, and registered trademarks are property of their respective owners.