The evolution of industrial manufacturing has reached a pivotal moment where artificial intelligence and robotics converge to create unprecedented levels of automation, efficiency, and precision. At the forefront of this technological revolution stand two industry giants: ABB and KUKA, each bringing distinctive approaches to AI-powered industrial robotics that are reshaping the landscape of smart manufacturing. These companies have established themselves as leaders in developing sophisticated robotic systems that integrate advanced artificial intelligence capabilities to deliver solutions that extend far beyond traditional automation.
Discover the latest trends in AI-powered manufacturing to understand how cutting-edge technologies are transforming industrial operations across global markets. The competition between ABB and KUKA represents more than just a battle for market share; it embodies the fundamental question of how artificial intelligence can be most effectively integrated into industrial robotics to maximize productivity, quality, and operational flexibility in modern manufacturing environments.
ABB’s AI-Driven Robotics Philosophy
ABB has positioned itself as a pioneer in collaborative robotics and intelligent automation systems, developing a comprehensive ecosystem of AI-powered solutions that emphasize seamless integration between human workers and robotic systems. The company’s approach to artificial intelligence in industrial robotics centers on creating adaptive systems that can learn from their environment, optimize their performance in real-time, and collaborate safely with human operators in shared workspaces.
The foundation of ABB’s AI strategy lies in their YuMi collaborative robot series and the more recent GoFa and SWIFTI robot families, which incorporate advanced machine learning algorithms that enable these systems to perform complex tasks with minimal programming requirements. These robots utilize sophisticated computer vision systems, force-feedback sensors, and predictive maintenance algorithms that allow them to adapt to changing production requirements while maintaining consistent quality standards.
ABB’s RobotStudio simulation software represents another crucial component of their AI-driven approach, providing manufacturers with powerful tools for virtual commissioning, path optimization, and predictive modeling. This software enables companies to design, test, and optimize robotic applications before physical implementation, significantly reducing deployment time and minimizing the risk of operational disruptions during system integration.
KUKA’s Intelligent Manufacturing Ecosystem
KUKA has established itself as a leader in high-performance industrial robotics with a particular focus on automotive manufacturing, aerospace applications, and heavy industry automation. The company’s approach to artificial intelligence emphasizes precision, speed, and reliability, developing robotic systems that can handle the most demanding manufacturing processes while incorporating advanced AI capabilities for continuous improvement and optimization.
The KUKA iiwa series represents the pinnacle of the company’s AI integration efforts, featuring lightweight robots with built-in intelligence that can perform sensitive assembly tasks, quality inspection operations, and complex manipulation procedures. These systems incorporate advanced force-torque sensing, machine learning algorithms for motion optimization, and sophisticated safety systems that enable safe human-robot collaboration in industrial environments.
Explore advanced AI tools like Claude for comprehensive analysis and decision-making support in industrial automation projects. KUKA’s smartPAD teaching pendant and KUKA.Sim simulation environment provide intuitive interfaces for programming and optimizing robotic operations, incorporating AI-powered features such as automatic path planning, collision avoidance, and performance optimization that reduce the expertise required for complex robotic implementations.
Technological Capabilities and Performance Comparison
The technological capabilities of ABB and KUKA robotic systems reflect fundamentally different approaches to AI integration in industrial automation. ABB’s focus on collaborative robotics has led to the development of systems that excel in applications requiring close human-robot interaction, flexible manufacturing processes, and rapid reconfiguration for different production requirements. Their robots typically feature advanced safety systems, intuitive programming interfaces, and sophisticated sensing capabilities that enable them to work effectively in dynamic manufacturing environments.
KUKA’s technological emphasis on precision and performance has resulted in robotic systems that excel in high-speed manufacturing operations, heavy payload handling, and applications requiring exceptional accuracy and repeatability. Their robots typically offer superior speed and precision characteristics, making them particularly well-suited for automotive assembly lines, aerospace manufacturing, and other applications where performance requirements are paramount.
The artificial intelligence implementations in both companies’ systems demonstrate distinct philosophical approaches to machine learning and automation. ABB’s AI systems prioritize adaptability and ease of use, incorporating machine learning algorithms that can quickly adapt to new tasks and environmental conditions with minimal human intervention. KUKA’s AI implementations focus on optimization and performance enhancement, utilizing sophisticated algorithms to maximize throughput, minimize cycle times, and ensure consistent quality in high-volume manufacturing operations.
Smart Manufacturing Integration Strategies
The integration of ABB and KUKA robotic systems into smart manufacturing environments reveals significant differences in their approaches to Industry 4.0 implementation. ABB has developed a comprehensive digital ecosystem that emphasizes connectivity, data analytics, and cloud-based services to enable manufacturers to achieve maximum value from their robotic investments. Their ABB Ability platform provides advanced analytics, predictive maintenance capabilities, and performance optimization tools that help manufacturers reduce downtime, improve efficiency, and enhance overall equipment effectiveness.
KUKA’s smart manufacturing strategy focuses on creating highly integrated production systems that combine robotics, automation technology, and digital services to deliver complete manufacturing solutions. Their KUKA Connect platform provides real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and remote service capabilities that enable manufacturers to optimize their operations and minimize unplanned downtime.
The artificial intelligence capabilities integrated into both companies’ manufacturing platforms enable sophisticated analysis of production data, identification of optimization opportunities, and predictive maintenance scheduling that can significantly improve overall manufacturing performance. These AI-powered insights help manufacturers make informed decisions about production scheduling, quality control, and equipment maintenance that can have substantial impacts on operational efficiency and profitability.
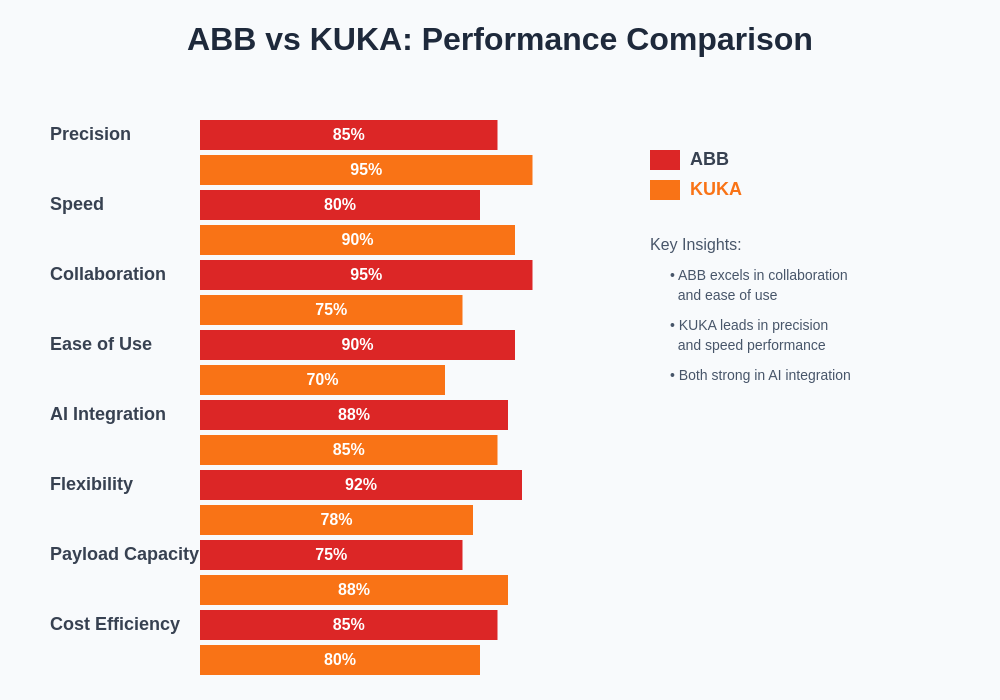
The performance characteristics and capabilities of ABB and KUKA robotic systems demonstrate complementary strengths that make each company’s solutions particularly well-suited for different types of manufacturing applications. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for manufacturers seeking to optimize their automation investments and achieve maximum return on their technology investments.
Application-Specific Performance Analysis
The real-world performance of ABB and KUKA robotic systems varies significantly across different manufacturing applications, reflecting the companies’ distinct design philosophies and target markets. In automotive manufacturing, KUKA’s systems have traditionally dominated high-speed assembly operations, welding applications, and heavy payload handling tasks where precision and speed are critical success factors. Their robots consistently demonstrate superior performance in applications requiring rapid cycle times, high precision, and reliable operation under demanding conditions.
ABB’s robotic systems excel in applications requiring flexibility, adaptability, and close human-robot collaboration. Their collaborative robots have found particular success in electronics assembly, small parts manufacturing, and applications where production requirements change frequently. The AI-powered adaptive capabilities of ABB systems enable them to quickly adjust to new products, modified processes, and changing quality requirements without extensive reprogramming or system reconfiguration.
Enhance your research capabilities with Perplexity for comprehensive analysis of industrial automation trends and technology comparisons. The artificial intelligence implementations in both companies’ systems provide manufacturers with sophisticated tools for optimizing their operations, but the specific benefits and capabilities vary significantly depending on the application requirements and operational environment.
Economic Considerations and Return on Investment
The economic implications of choosing between ABB and KUKA robotic systems extend far beyond initial acquisition costs, encompassing factors such as implementation complexity, ongoing maintenance requirements, operational flexibility, and long-term scalability. ABB’s collaborative robotics approach often results in lower implementation costs due to simplified safety requirements, reduced infrastructure modifications, and shorter deployment timelines. The AI-powered ease of use features in ABB systems can also reduce the training requirements for operators and maintenance personnel, potentially lowering total cost of ownership over the system lifecycle.
KUKA’s focus on high-performance applications often justifies higher initial investments through superior productivity gains, reduced cycle times, and enhanced product quality. The precision and speed capabilities of KUKA systems can enable manufacturers to achieve production volumes and quality levels that would be difficult or impossible with alternative automation solutions. The artificial intelligence features integrated into KUKA systems provide ongoing optimization benefits that can compound over time, potentially delivering substantial long-term value.
The return on investment calculations for both companies’ systems must consider factors such as production volume requirements, quality specifications, flexibility needs, and integration complexity. Manufacturers with high-volume, standardized production requirements may find KUKA systems provide superior economic benefits, while companies with diverse product lines, changing requirements, or limited automation expertise may achieve better results with ABB solutions.
Safety and Compliance Standards
Safety considerations represent a critical differentiator between ABB and KUKA robotic systems, particularly in applications involving human-robot collaboration or operation in environments with strict safety requirements. ABB’s collaborative robotics focus has led to the development of sophisticated safety systems that enable safe operation in shared workspaces without traditional safety barriers. Their robots incorporate advanced force limiting, collision detection, and emergency stopping capabilities that meet or exceed international safety standards for collaborative applications.
KUKA’s safety implementations emphasize comprehensive protection systems that ensure safe operation in traditional industrial environments while providing options for collaborative applications where appropriate. Their safety systems typically include advanced monitoring capabilities, redundant safety circuits, and sophisticated risk assessment algorithms that help manufacturers achieve compliance with applicable safety standards while maintaining optimal performance.
The artificial intelligence features integrated into both companies’ safety systems provide enhanced protection through predictive hazard identification, adaptive safety responses, and continuous monitoring of operational conditions. These AI-powered safety enhancements represent significant advances over traditional safety systems and help manufacturers achieve higher levels of protection while maintaining operational efficiency.
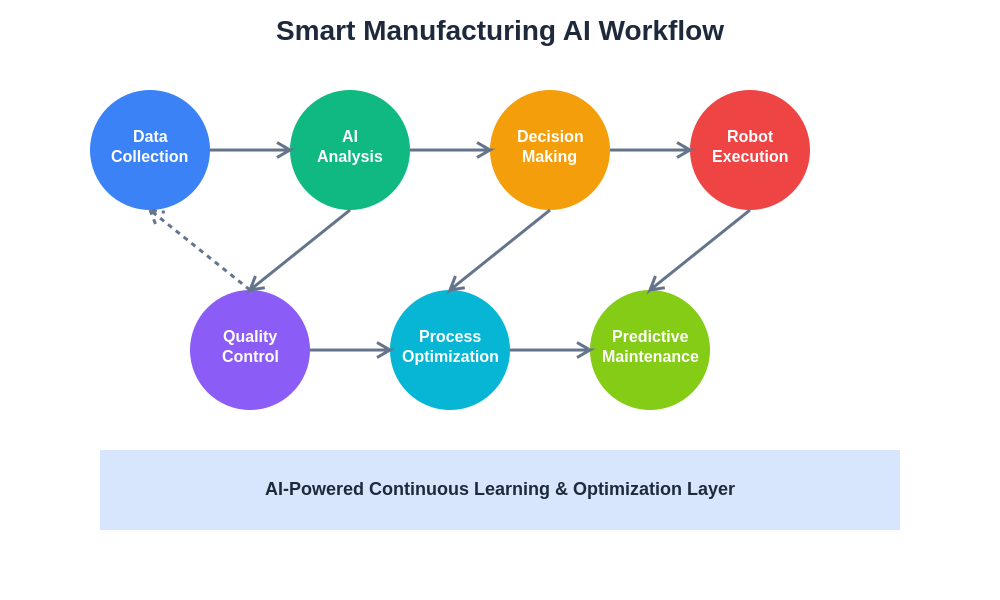
The integration of AI-powered safety systems into modern manufacturing operations creates new opportunities for achieving higher levels of protection while maintaining or improving operational efficiency. These advanced safety capabilities represent a fundamental shift from reactive to predictive safety management that can significantly reduce the risk of incidents and improve overall workplace safety.
Future Technology Roadmaps and Innovation Directions
The future development trajectories of ABB and KUKA robotic systems reflect their distinct strategic visions for the evolution of industrial automation and artificial intelligence integration. ABB’s roadmap emphasizes continued advancement in collaborative robotics, enhanced AI-powered adaptability, and deeper integration with digital manufacturing ecosystems. Their research and development efforts focus on creating more intuitive human-machine interfaces, advanced learning algorithms, and enhanced connectivity features that will enable even greater flexibility and ease of use in future generations of robotic systems.
KUKA’s innovation strategy centers on pushing the boundaries of performance, precision, and intelligence in industrial robotics applications. Their development efforts focus on advanced motion control algorithms, enhanced sensor integration, and sophisticated AI-powered optimization capabilities that will enable even higher levels of productivity and quality in demanding manufacturing environments.
Both companies are investing heavily in artificial intelligence research, machine learning algorithm development, and advanced sensor technologies that will enable future robotic systems to achieve unprecedented levels of autonomy, adaptability, and intelligence. The convergence of these technological advances promises to deliver robotic systems that can handle increasingly complex tasks with minimal human intervention while maintaining the flexibility to adapt to changing requirements and operational conditions.
Market Position and Competitive Landscape
The competitive positioning of ABB and KUKA in the industrial robotics market reflects their distinct approaches to addressing customer needs and market opportunities. ABB’s focus on collaborative robotics and ease of use has enabled them to capture significant market share in applications where traditional industrial robots were previously impractical or uneconomical. Their success in small and medium-sized manufacturing operations, electronics assembly, and flexible manufacturing applications demonstrates the market appeal of their collaborative approach.
KUKA’s strength in high-performance applications has maintained their position as a preferred supplier for demanding manufacturing operations, particularly in automotive, aerospace, and heavy industry applications. Their reputation for precision, reliability, and performance has enabled them to maintain strong relationships with major industrial customers who require the highest levels of capability and performance from their automation investments.
The artificial intelligence capabilities being developed by both companies represent potential game-changing advantages that could significantly alter the competitive landscape in industrial robotics. The company that most effectively integrates AI capabilities into practical, reliable, and cost-effective robotic solutions may gain substantial competitive advantages in future market competitions.
Integration Challenges and Solutions
The practical implementation of ABB and KUKA robotic systems in real-world manufacturing environments presents distinct challenges and opportunities that manufacturers must carefully consider. ABB’s collaborative approach often simplifies integration by reducing safety barrier requirements, simplifying programming procedures, and enabling gradual implementation strategies that minimize operational disruption. However, achieving optimal performance from ABB systems may require significant attention to application design, workflow optimization, and operator training to fully realize the benefits of their AI-powered capabilities.
KUKA’s high-performance systems typically require more comprehensive integration planning, including detailed analysis of production requirements, precise mechanical design, and sophisticated programming to achieve optimal results. The complexity of KUKA implementations often necessitates specialized expertise and careful project management, but the results can justify these investments through superior performance and capabilities.
The artificial intelligence features in both companies’ systems provide valuable assistance during integration and optimization phases, offering automated configuration suggestions, performance optimization recommendations, and troubleshooting support that can significantly reduce implementation complexity and time requirements.
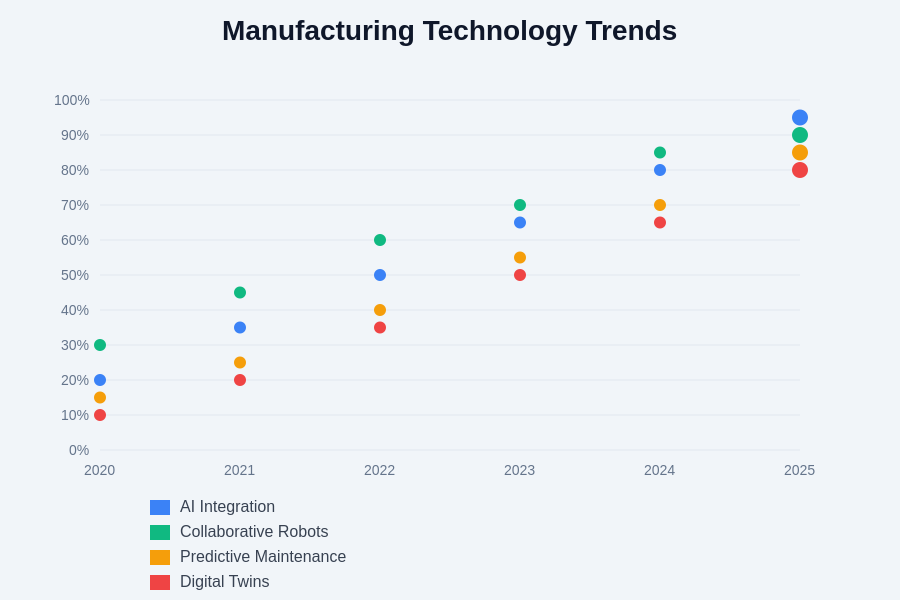
The evolution of manufacturing technology continues to create new opportunities and challenges for industrial robotics implementation. Understanding these trends and their implications for automation strategy is crucial for manufacturers seeking to maximize the value of their technology investments and maintain competitive advantages in rapidly changing markets.
Strategic Decision Framework for Manufacturers
Manufacturers evaluating ABB versus KUKA robotic systems must consider multiple factors that extend beyond technical specifications to encompass strategic business objectives, operational requirements, and long-term growth plans. The decision framework should include careful analysis of production volume requirements, product complexity, quality specifications, flexibility needs, and available expertise within the organization.
Companies with diverse product lines, frequent changeovers, or limited automation experience may find ABB’s collaborative approach and AI-powered ease of use features provide optimal solutions for their requirements. The ability to quickly adapt to new products, modify processes, and integrate human workers into automated operations can provide significant advantages in dynamic manufacturing environments.
Organizations with high-volume, standardized production requirements may achieve superior results with KUKA’s high-performance systems, particularly when precision, speed, and reliability are critical success factors. The AI-powered optimization capabilities in KUKA systems can deliver substantial productivity improvements and quality enhancements that justify higher implementation investments.
The artificial intelligence capabilities being integrated into both companies’ systems represent important considerations for future-proofing automation investments. Manufacturers should evaluate not only current capabilities but also the potential for future enhancements and upgrades that could extend the useful life and value of their robotic systems.
Conclusion and Industry Impact
The competition between ABB and KUKA in AI-powered industrial robotics represents more than a simple vendor comparison; it embodies fundamental questions about the future direction of manufacturing automation and the role of artificial intelligence in industrial operations. Both companies have developed sophisticated solutions that address different aspects of the manufacturing automation challenge, and their continued innovation promises to deliver even more capable and intelligent systems in the future.
The success of both ABB and KUKA in integrating artificial intelligence into practical, reliable robotic systems has demonstrated the tremendous potential for AI to transform manufacturing operations. Their achievements have paved the way for broader adoption of intelligent automation technologies and have established new standards for what manufacturers can expect from their automation investments.
The ongoing evolution of AI-powered industrial robotics promises to continue reshaping manufacturing operations, creating new opportunities for efficiency improvements, quality enhancements, and operational flexibility that will help manufacturers compete more effectively in global markets. The choices manufacturers make today regarding their automation strategies and technology partners will have lasting impacts on their future competitiveness and success.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional advice. The views expressed are based on publicly available information and industry analysis. Readers should conduct their own research and consider their specific requirements when evaluating industrial robotics solutions. Performance characteristics and capabilities may vary depending on specific applications, configurations, and operational conditions. Manufacturers should consult with qualified automation specialists and conduct thorough evaluations before making investment decisions.