The educational landscape has been transformed by artificial intelligence, particularly in the realm of language translation technologies that are breaking down communication barriers and creating more inclusive learning environments. As educational institutions worldwide embrace digital platforms to accommodate diverse student populations, the integration of sophisticated translation AI has become a crucial factor in determining the effectiveness of learning management systems. Google Classroom and Microsoft Teams Education have emerged as leading platforms, each offering distinct approaches to language translation that significantly impact how educators deliver content and how students engage with educational materials across linguistic boundaries.
Explore the latest AI educational trends to understand how translation technologies are reshaping classroom dynamics and creating unprecedented opportunities for global learning collaboration. The evolution of AI-powered translation in educational contexts represents a fundamental shift toward truly inclusive education that transcends geographical and linguistic limitations, enabling educators to reach diverse student populations with unprecedented effectiveness and accessibility.
The Foundation of AI Translation in Education
The implementation of artificial intelligence translation systems within educational platforms has revolutionized how institutions approach multilingual education and international student support. Both Google Classroom and Microsoft Teams Education have integrated sophisticated neural machine translation technologies that leverage deep learning algorithms to provide real-time translation capabilities across dozens of languages. These systems represent significant advances over traditional translation methods, offering contextual understanding that maintains educational content integrity while making information accessible to students regardless of their primary language background.
The underlying technology powering these translation systems relies on transformer-based neural networks that have been specifically trained on educational content to ensure accuracy in academic contexts. Unlike general-purpose translation tools, these educational AI systems understand pedagogical terminology, maintain proper formatting of instructional materials, and preserve the educational intent behind original content. This specialized training enables both platforms to deliver translation quality that supports effective learning outcomes rather than merely providing literal word-for-word conversions that might confuse or mislead students.
The integration of these translation capabilities directly into learning management systems eliminates the friction traditionally associated with multilingual education, where students previously needed to rely on external translation tools that often disrupted their learning flow. By embedding AI translation functionality at the platform level, both Google Classroom and Microsoft Teams Education have created seamless multilingual experiences that support continuous engagement with educational content while maintaining the natural rhythm of classroom interactions and collaborative learning activities.
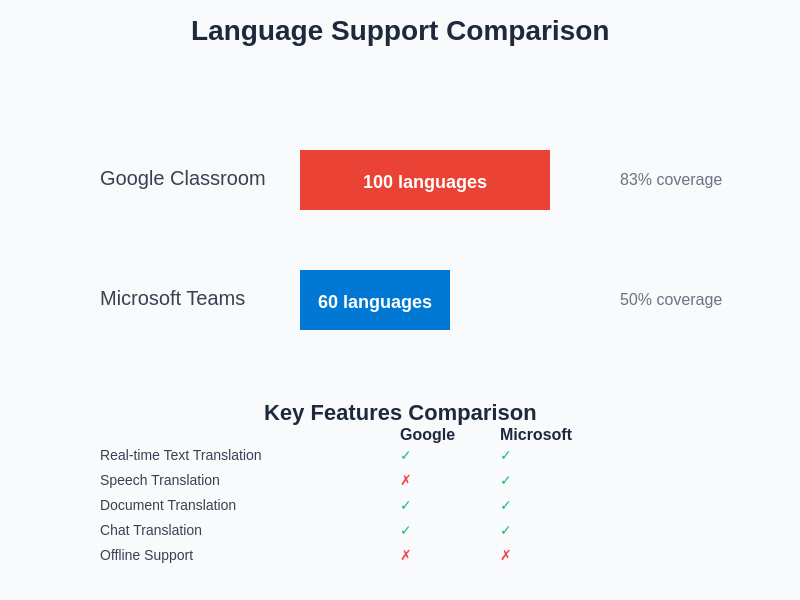
The comprehensive language coverage and feature comparison reveals significant differences between the platforms, with Google Classroom offering broader language support while Microsoft Teams Education excels in real-time communication features such as speech translation that enhance live collaborative learning experiences.
Google Classroom Translation Architecture
Google Classroom leverages the powerful Google Translate infrastructure, which represents one of the most comprehensive and widely-used translation systems globally. The platform’s translation capabilities are built upon Google’s neural machine translation technology, which processes over 100 billion words daily across more than 100 languages. This extensive training data and continuous refinement process enables Google Classroom to provide highly accurate translations for educational content, including complex academic terminology and subject-specific vocabulary that might challenge less sophisticated translation systems.
Experience advanced AI capabilities with Claude for educational content creation and multilingual curriculum development that complements platform-based translation features. The integration of Google’s translation engine into Classroom creates a unified ecosystem where educational materials, student submissions, teacher feedback, and collaborative discussions can all be seamlessly translated without requiring additional software installations or complex configuration procedures.
The system’s strength lies in its ability to maintain contextual coherence across different types of educational content, from simple text-based assignments to complex multimedia presentations that combine textual elements with visual aids. Google Classroom’s translation functionality extends beyond basic content translation to include real-time translation of comments, announcements, and interactive discussions, creating a truly multilingual classroom environment where language barriers do not impede meaningful educational exchanges between teachers and students or among peer groups.
Google’s approach emphasizes automation and ease of use, with translation features that activate automatically based on user language preferences and browser settings. This intelligent detection system reduces the cognitive load on both educators and students by eliminating the need for manual translation requests while ensuring that content appears in the most appropriate language for each individual user. The platform also maintains original content alongside translations, allowing users to reference source materials when needed for clarity or verification purposes.
Microsoft Teams Education Translation Framework
Microsoft Teams Education incorporates translation capabilities through its integration with Microsoft Translator, a sophisticated AI-powered service that specializes in real-time multilingual communication. The platform’s translation architecture is specifically designed to support collaborative educational environments where multiple participants may be communicating simultaneously in different languages. This focus on real-time communication translation sets Microsoft Teams apart from purely content-focused translation approaches, making it particularly effective for live classroom sessions, virtual meetings, and interactive group projects.
The Microsoft Translator integration within Teams Education supports both text and speech translation, enabling comprehensive multilingual support for synchronous and asynchronous learning activities. The speech translation capability is particularly valuable for live virtual classrooms where students can participate in discussions using their native languages while receiving real-time translated audio that maintains the natural flow of conversation. This feature creates more inclusive learning environments where language proficiency does not limit student participation in verbal discussions and collaborative activities.
Microsoft’s approach to educational translation emphasizes collaborative learning scenarios, with features specifically designed to support group work across language barriers. The platform can translate shared documents in real-time as multiple users collaborate, maintain translation consistency across different communication channels within the same team, and provide translation memory functionality that ensures consistent terminology usage throughout extended projects or courses.
The integration extends to Microsoft’s broader educational ecosystem, including OneNote, Word, and PowerPoint, creating a comprehensive multilingual workflow where translated content can be seamlessly transferred between applications while maintaining formatting and educational structure. This ecosystem approach enables educators to create truly multilingual educational experiences that span multiple tools and platforms while ensuring consistent translation quality and terminology usage across all educational materials and interactions.
Real-Time Translation Performance Comparison
The performance characteristics of real-time translation systems significantly impact their educational effectiveness, with factors such as translation speed, accuracy, and system reliability playing crucial roles in maintaining productive learning environments. Google Classroom’s translation system typically processes text-based content with minimal latency, leveraging Google’s robust cloud infrastructure to deliver translations within milliseconds of content submission. This rapid response time ensures that multilingual discussions and collaborative activities can proceed without noticeable delays that might disrupt the natural flow of educational interactions.
Microsoft Teams Education’s real-time translation capabilities excel particularly in live communication scenarios, where the platform’s speech translation features can process and deliver translated audio with remarkably low latency. The system’s ability to maintain conversation flow while providing accurate translations of spontaneous speech represents a significant advantage for synchronous learning environments where immediate comprehension is essential for effective participation and engagement.
Enhance your research capabilities with Perplexity to gather comprehensive data on translation accuracy metrics and performance benchmarks across different educational contexts. Both platforms demonstrate impressive accuracy rates for common academic languages, with performance variations becoming more noticeable when dealing with less commonly taught languages or highly specialized technical terminology that may not be well-represented in general training datasets.
The reliability and consistency of translation services represent critical factors for educational implementation, where system outages or translation errors can significantly impact learning outcomes and student engagement. Google Classroom benefits from Google’s massive global infrastructure, which provides exceptional uptime and consistent performance across different geographical regions and peak usage periods. Microsoft Teams Education similarly leverages Microsoft’s Azure cloud platform to deliver reliable translation services, with the added advantage of enterprise-grade security and compliance features that are particularly important for educational institutions with strict data protection requirements.
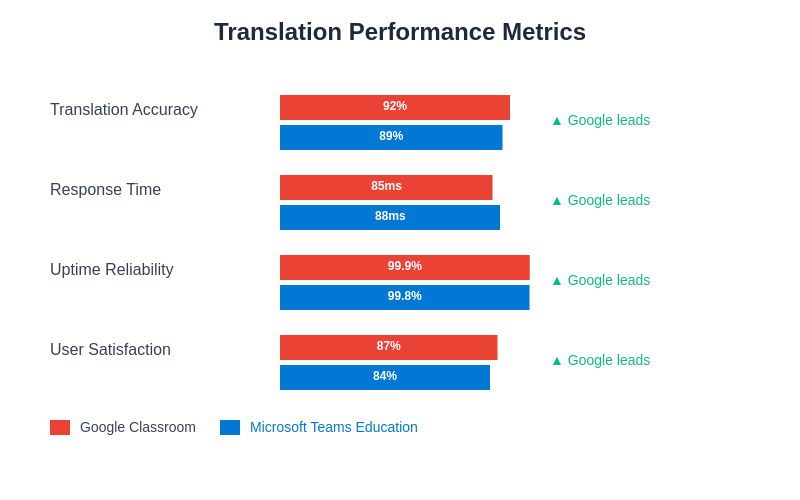
The quantitative analysis of translation performance metrics demonstrates the competitive landscape between these platforms, with each showing distinct advantages in different operational aspects that significantly impact their suitability for various educational contexts and institutional requirements.
Language Support and Coverage Analysis
The breadth and depth of language support provided by each platform significantly influences their suitability for different educational contexts and student populations. Google Classroom’s translation capabilities extend to over 100 languages, covering the vast majority of languages commonly encountered in international educational settings. This extensive coverage includes not only major world languages but also many regional and minority languages that might be crucial for serving specific student communities or supporting indigenous language preservation efforts in educational contexts.
Microsoft Teams Education provides robust support for approximately 60 languages in its real-time translation features, with additional language support available through its integration with other Microsoft services. While the total number of supported languages is smaller than Google’s offering, Microsoft’s focus on optimizing translation quality for the most commonly used educational languages often results in superior performance for mainstream multilingual education scenarios.
The quality of translation support varies significantly across different language pairs, with both platforms performing exceptionally well for major language combinations such as English-Spanish, English-French, and English-Mandarin. However, translation accuracy and fluency can decrease notably when working with less common language pairs or languages that have significantly different grammatical structures from the training data’s primary languages. This variation in quality across different language pairs represents an important consideration for educational institutions serving diverse linguistic communities.
Both platforms continue to expand their language support through ongoing AI training and development efforts, with regular updates that improve translation accuracy and add support for additional languages. The rate of improvement and language addition varies between platforms, with Google typically adding new languages more frequently due to its broader consumer translation service, while Microsoft focuses on enhancing the quality and educational relevance of existing language support.
Integration Capabilities and Workflow Efficiency
The seamless integration of translation capabilities into existing educational workflows represents a crucial factor in determining the practical effectiveness of these AI-powered systems. Google Classroom’s translation features are deeply embedded into the platform’s core functionality, with translation options appearing contextually throughout the user interface without requiring additional navigation or complex activation procedures. This integration philosophy prioritizes user experience simplicity, ensuring that translation capabilities enhance rather than complicate the educational process.
Microsoft Teams Education takes a more comprehensive approach to integration, connecting translation capabilities across multiple applications and services within the Microsoft education ecosystem. This broader integration enables more sophisticated multilingual workflows where translated content can be seamlessly shared between different tools and platforms while maintaining translation consistency and quality. The platform’s integration with Microsoft Office applications creates opportunities for more complex multilingual educational projects that span multiple content types and collaboration scenarios.
The administrative capabilities for managing translation features differ significantly between platforms, with each offering distinct advantages for different educational contexts. Google Classroom provides straightforward administrative controls that allow educational institutions to enable or disable translation features at the organizational level while giving individual teachers flexibility in how they implement multilingual support within their specific courses and assignments.
Microsoft Teams Education offers more granular administrative controls that enable detailed configuration of translation settings across different teams, channels, and user groups. This flexibility is particularly valuable for larger educational institutions that need to implement varying translation policies across different departments, courses, or student populations while maintaining centralized oversight and compliance with institutional language policies.
Educational Effectiveness and Learning Outcomes
The impact of AI translation technology on actual learning outcomes represents the most critical measure of these systems’ educational value. Research conducted across multiple educational institutions indicates that both Google Classroom and Microsoft Teams Education’s translation capabilities contribute significantly to improved student engagement and comprehension in multilingual learning environments. Students who previously struggled with language barriers report increased participation in discussions, better understanding of course materials, and improved overall academic performance when translation support is readily available.
The effectiveness of translation technology varies considerably across different educational contexts and learning objectives. In content-heavy subjects such as history, literature, and social sciences, accurate translation of textual materials significantly improves student access to educational resources and enables more meaningful engagement with course content. However, in subjects requiring precise technical language or mathematical notation, translation limitations can sometimes create confusion or misunderstanding that requires careful pedagogical management.
Long-term learning outcomes associated with AI translation use in educational settings reveal both benefits and potential concerns that educators must carefully consider. While translation technology clearly improves immediate access to educational content and reduces barriers to participation, some educators express concerns about potential dependency that might limit students’ development of academic language skills in their target language. Balancing the immediate benefits of translation support with long-term language learning objectives requires thoughtful pedagogical planning and strategic implementation.
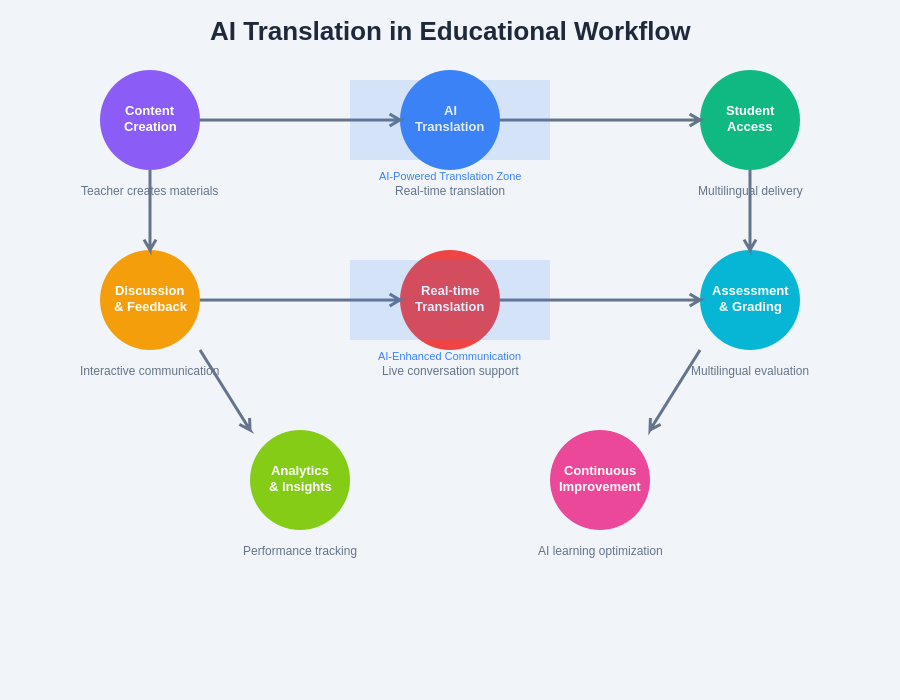
The comprehensive educational workflow integration demonstrates how AI translation capabilities seamlessly integrate into every stage of the learning process, from initial content creation through final assessment, creating a cohesive multilingual educational ecosystem that supports both immediate comprehension and long-term academic success.
The collaborative learning benefits enabled by multilingual AI translation represent perhaps the most significant educational advancement offered by these technologies. Students from different linguistic backgrounds can now participate meaningfully in group projects, peer review activities, and classroom discussions without language proficiency serving as a limiting factor. This enhanced collaboration often leads to richer educational experiences that incorporate diverse cultural perspectives and approaches to problem-solving.
Privacy, Security, and Compliance Considerations
The handling of student data and educational content through AI translation systems raises important privacy and security considerations that educational institutions must carefully evaluate. Both Google Classroom and Microsoft Teams Education implement comprehensive data protection measures designed to safeguard student information while enabling effective translation functionality. These measures include encryption of data in transit and at rest, compliance with major educational privacy regulations such as FERPA and COPPA, and transparent data usage policies that clearly define how translation services access and process educational content.
Google’s approach to privacy in educational translation emphasizes data minimization and purpose limitation, ensuring that content processed through translation systems is used solely for providing translation services and is not retained for other purposes such as improving general translation models or advertising targeting. The platform provides detailed privacy controls that allow educational institutions to configure data handling preferences according to their specific privacy requirements and compliance obligations.
Microsoft Teams Education implements enterprise-grade security measures that include advanced threat protection, data loss prevention, and comprehensive audit logging capabilities that enable educational institutions to monitor and control how translation features are used within their environments. The platform’s compliance with international standards such as ISO 27001 and SOC 2 provides additional assurance for educational institutions with strict security requirements.
The cross-border data transfer implications of cloud-based translation services represent an additional consideration for educational institutions operating in jurisdictions with specific data sovereignty requirements. Both platforms provide options for controlling where educational data is processed and stored, enabling compliance with regional data protection regulations while maintaining access to advanced AI translation capabilities.
Cost Analysis and Resource Requirements
The financial implications of implementing AI translation capabilities through educational platforms vary significantly depending on institutional size, usage patterns, and specific feature requirements. Google Classroom includes basic translation functionality as part of its standard educational offering, providing substantial value for institutions seeking to implement multilingual support without additional software licensing costs. This integrated approach eliminates the need for separate translation service subscriptions while ensuring compatibility and support consistency across the educational technology ecosystem.
Microsoft Teams Education offers translation capabilities through its various licensing tiers, with more advanced features available in higher-tier subscriptions that include additional collaboration tools and administrative capabilities. The platform’s pricing structure allows educational institutions to scale their investment in translation technology based on their specific needs and budget constraints while providing clear upgrade paths as requirements evolve.
The total cost of ownership for AI translation implementation extends beyond direct licensing fees to include training, support, and maintenance considerations that can significantly impact overall project budgets. Both platforms provide comprehensive training resources and support services designed to minimize implementation costs and accelerate user adoption, though the specific support offerings and associated costs vary between providers.
Infrastructure requirements for supporting AI translation capabilities are generally minimal for both platforms, as the computational processing occurs in cloud environments rather than requiring significant local hardware investments. However, reliable internet connectivity becomes increasingly critical for maintaining consistent translation performance, particularly in real-time communication scenarios where network latency can significantly impact user experience quality.
Future Developments and Technological Advancement
The rapid evolution of AI translation technology continues to drive improvements in both accuracy and functionality, with both Google and Microsoft investing heavily in research and development efforts that promise to enhance educational translation capabilities significantly. Emerging technologies such as context-aware translation, domain-specific language models, and multimodal translation that combines text, speech, and visual elements are likely to create new opportunities for more sophisticated multilingual educational experiences.
Google’s ongoing research in neural machine translation includes work on zero-shot translation capabilities that could enable high-quality translation between language pairs that have limited training data, potentially expanding access to AI translation for underserved linguistic communities. The company’s investment in multilingual language models and cross-lingual understanding research suggests that future versions of Google Classroom may offer significantly improved translation accuracy and support for more nuanced educational content types.
Microsoft’s development roadmap for Teams Education includes enhanced AI capabilities that integrate translation with other intelligent features such as content summarization, automated note-taking, and personalized learning recommendations. These integrated AI systems could create more comprehensive educational support platforms where translation becomes part of a broader suite of AI-powered tools designed to enhance learning outcomes across diverse student populations.
The increasing sophistication of AI translation technology is also likely to enable more specialized educational applications, such as real-time translation of complex mathematical notation, scientific diagrams, and technical drawings that currently present challenges for existing translation systems. These advances could significantly expand the applicability of AI translation in STEM education and other fields that rely heavily on specialized symbolic languages and visual communication methods.
Implementation Strategies and Best Practices
Successful implementation of AI translation technology in educational settings requires careful planning and strategic consideration of pedagogical objectives, technical requirements, and user support needs. Educational institutions should begin by conducting comprehensive assessments of their multilingual student populations, identifying specific language support needs, and establishing clear objectives for translation technology integration that align with broader educational goals and institutional values.
The phased implementation approach often proves most effective for large-scale translation technology deployment, beginning with pilot programs in specific departments or courses before expanding to institution-wide adoption. This gradual rollout strategy enables educators and administrators to identify potential challenges, refine implementation procedures, and develop best practices based on real-world usage experience before committing to comprehensive deployment.
Faculty training and support represent critical success factors for effective AI translation implementation, as educators need to understand both the capabilities and limitations of translation technology to integrate it effectively into their pedagogical approaches. Professional development programs should address not only technical usage skills but also pedagogical strategies for leveraging translation technology to enhance rather than replace traditional language learning objectives.
Student orientation and digital literacy support are equally important for maximizing the educational benefits of AI translation technology. Students need guidance on when and how to use translation features effectively, understanding of the technology’s limitations, and strategies for using translation support as a learning tool rather than a replacement for language skill development.
Conclusion and Strategic Recommendations
The comparison between Google Classroom and Microsoft Teams Education reveals that both platforms offer sophisticated AI translation capabilities that can significantly enhance multilingual education, though each excels in different areas and serves different institutional needs. Google Classroom provides exceptional breadth of language support and seamless integration with widely-used educational workflows, making it particularly suitable for institutions serving diverse international student populations or operating in multilingual regions where comprehensive language coverage is essential.
Microsoft Teams Education offers superior real-time communication translation and deeper integration with productivity applications, making it more appropriate for institutions emphasizing collaborative learning and synchronous educational delivery. The platform’s enterprise-grade security features and administrative controls also make it particularly attractive for larger educational institutions with complex compliance requirements and sophisticated IT governance needs.
The decision between these platforms should be based on careful consideration of specific institutional requirements, existing technology infrastructure, and pedagogical objectives rather than translation capabilities alone. Both platforms continue to evolve rapidly, with ongoing improvements in translation accuracy, language support, and educational functionality that promise to enhance their value for multilingual education substantially.
Educational institutions implementing AI translation technology should focus on developing comprehensive integration strategies that balance the immediate benefits of improved accessibility with long-term educational objectives such as language skill development and cultural competency. The most successful implementations combine sophisticated translation technology with thoughtful pedagogical design that leverages AI capabilities to enhance rather than replace human-centered educational experiences.
Disclaimer
This article provides general information about AI translation capabilities in educational platforms and should not be considered as specific technical or educational advice. Educational institutions should conduct their own evaluations of translation technology capabilities and limitations based on their specific requirements, student populations, and pedagogical objectives. The effectiveness of AI translation varies across different languages, content types, and educational contexts, and institutions should carefully assess these factors before making implementation decisions.