The legal profession has experienced a transformative shift with the integration of artificial intelligence into document translation services, fundamentally altering how law firms approach multilingual legal work. As globalization continues to expand the scope of legal practice across international boundaries, the demand for accurate, secure, and efficient translation services has reached unprecedented levels. Modern law firms find themselves navigating complex multilingual legal landscapes where the precision of translation can determine the outcome of critical legal proceedings, contract negotiations, and regulatory compliance matters.
Discover the latest AI translation technologies that are reshaping how legal professionals handle multilingual documentation and cross-border legal work. The evolution of AI-powered translation tools has created new possibilities for legal practitioners while simultaneously introducing challenges related to accuracy, confidentiality, and professional liability that require careful consideration and evaluation.
The emergence of sophisticated translation platforms like DeepL and Google Translate has democratized access to advanced linguistic capabilities that were previously available only through human translators or specialized translation services. However, the unique requirements of legal translation, including precision in terminology, maintenance of legal meaning across languages, and adherence to strict confidentiality standards, necessitate a comprehensive evaluation of these platforms to determine their suitability for professional legal applications.
Understanding Legal Translation Requirements
Legal translation represents one of the most demanding applications of linguistic conversion, requiring not merely the transformation of words from one language to another, but the preservation of legal meaning, intent, and enforceability across different legal systems and cultural contexts. The complexity of legal translation stems from the specialized nature of legal terminology, the precise relationships between concepts, and the potential consequences of mistranslation in legal proceedings or contractual arrangements.
Professional legal translation traditionally demands expertise in both source and target languages, comprehensive understanding of relevant legal systems, familiarity with specialized legal terminology, and awareness of cultural nuances that might affect legal interpretation. The introduction of AI-powered translation tools into this domain represents a significant technological advancement, but also raises important questions about accuracy, reliability, and professional responsibility in legal practice.
The stakes involved in legal translation accuracy cannot be overstated, as mistranslations can result in contract disputes, regulatory violations, litigation complications, and potential malpractice claims. Law firms considering the adoption of AI translation tools must carefully evaluate the capabilities and limitations of available platforms to ensure that their use aligns with professional standards and client expectations for quality and confidentiality.
DeepL: Advanced Neural Networks for Legal Precision
DeepL has established itself as a premium translation platform distinguished by its sophisticated neural network architecture and demonstrated superiority in handling complex, nuanced text translation tasks. The platform’s approach to translation goes beyond simple word substitution, employing advanced machine learning algorithms that analyze contextual relationships, linguistic patterns, and semantic structures to produce translations that maintain the original meaning and tone of source documents.
The technical foundation of DeepL rests on transformer-based neural networks that have been trained on extensive multilingual corpora, enabling the system to understand subtle linguistic nuances and contextual dependencies that are particularly crucial in legal document translation. This advanced architecture allows DeepL to handle complex sentence structures, specialized terminology, and the intricate logical relationships that characterize legal writing across different languages and legal traditions.
For law firms, DeepL’s strengths become particularly apparent when dealing with documents containing specialized legal terminology, complex contractual language, and intricate logical structures that require precise translation to maintain legal validity and enforceability. The platform’s ability to preserve the formal register and technical precision required in legal documents has made it increasingly popular among legal professionals who require higher translation quality than what is typically available through general-purpose translation tools.
Experience enhanced AI translation capabilities with Claude for comprehensive document analysis and translation review tasks that require sophisticated understanding of legal contexts and terminology. The integration of multiple AI tools can provide additional layers of verification and quality assurance for critical legal translation projects.
Google Translate: Accessibility and Integration Advantages
Google Translate represents the most widely accessible AI translation platform, offering extensive language coverage, seamless integration with existing Google Workspace tools, and rapid processing capabilities that can accommodate high-volume translation needs. The platform’s strength lies in its comprehensive language support, covering over 100 languages with varying degrees of accuracy and sophistication, making it particularly valuable for law firms that work with diverse international clients and documents in less common language pairs.
The integration capabilities of Google Translate extend throughout the Google ecosystem, enabling law firms already utilizing Google Workspace, Gmail, and other Google services to incorporate translation functionality seamlessly into their existing workflows. This integration advantage can significantly reduce the friction associated with implementing translation tools in legal practice, allowing attorneys and support staff to access translation capabilities directly within their familiar work environments.
Google Translate’s continuous improvement through machine learning ensures that the platform benefits from ongoing refinements based on vast amounts of translation data and user feedback. The platform’s ability to handle real-time translation needs, support voice input and output, and provide instant translation capabilities makes it particularly valuable for client communications, preliminary document review, and situations where immediate translation access is more important than absolute precision.
Accuracy Analysis: Precision in Legal Context
The evaluation of translation accuracy in legal contexts requires examination of multiple dimensions including terminological precision, preservation of legal meaning, maintenance of document structure and formatting, and consistency across related documents. Legal translation accuracy encompasses not only linguistic correctness but also legal validity, enforceability, and compliance with relevant legal standards and conventions.
DeepL consistently demonstrates superior performance in maintaining the nuanced meaning and formal register required for legal documents, particularly in European language pairs where the platform’s training data and algorithmic optimization have been most comprehensive. The platform’s ability to handle complex sentence structures, specialized terminology, and the logical relationships inherent in legal writing makes it particularly suitable for contracts, legal opinions, and regulatory documents where precision is paramount.
Google Translate, while offering broader language coverage, sometimes struggles with the specialized terminology and complex syntactic structures that characterize legal writing. However, the platform’s continuous improvement and vast training data enable it to handle many legal translation tasks adequately, particularly for preliminary document review, client communication, and situations where perfect accuracy is less critical than immediate accessibility and broad language support.
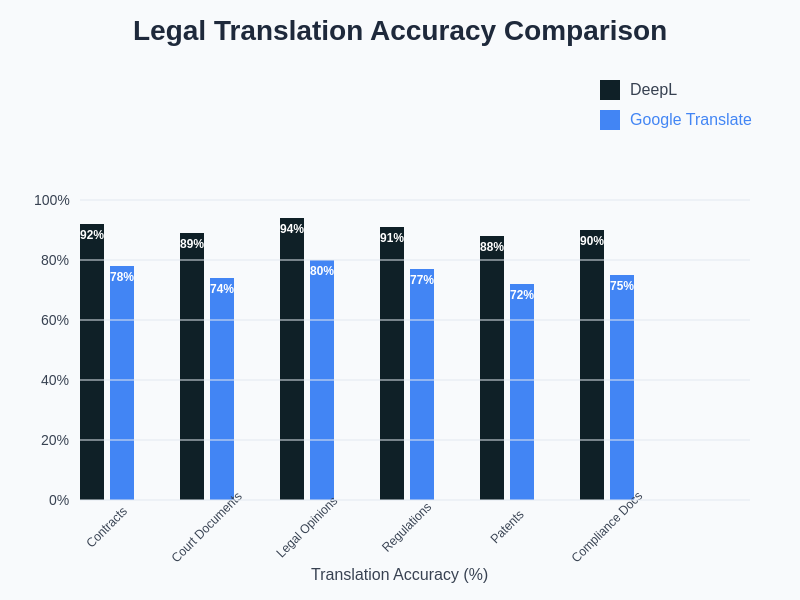
The performance differential between DeepL and Google Translate becomes most apparent in documents containing complex legal reasoning, specialized terminology, and intricate conditional structures that require precise logical relationships to be maintained across languages. Professional legal translation requires not only linguistic accuracy but also preservation of legal meaning and enforceability.
Security and Confidentiality Considerations
Legal translation involves handling highly sensitive and confidential information that requires robust security measures and strict adherence to professional confidentiality standards. Law firms must evaluate translation platforms not only for their linguistic capabilities but also for their security architectures, data handling practices, and compliance with relevant privacy regulations and professional responsibility requirements.
DeepL offers enhanced security features through its DeepL Pro service, including data encryption, no storage of translated content, and compliance with European data protection standards. These security measures align well with the confidentiality requirements of legal practice, providing law firms with greater assurance that client information and sensitive legal documents remain protected during the translation process. The platform’s commitment to data privacy and its European regulatory compliance make it particularly attractive to law firms handling sensitive international legal matters.
Google Translate’s security model reflects Google’s broader approach to data handling and privacy protection, with standard encryption and security measures that are appropriate for many business applications. However, law firms must carefully consider whether Google’s data handling practices align with their specific confidentiality requirements and professional responsibility obligations. The platform’s integration with broader Google services may raise concerns for firms with strict data isolation requirements or specific regulatory compliance needs.
The choice between platforms often depends on the sensitivity level of translated documents, applicable regulatory requirements, and the specific security policies and procedures maintained by individual law firms. Many firms adopt tiered approaches where highly sensitive documents are handled through more secure translation methods while less sensitive materials can utilize more accessible platforms.
Cost-Effectiveness and Scalability
The economic considerations surrounding AI translation adoption in law firms encompass not only direct translation costs but also factors such as time savings, productivity improvements, integration expenses, and the potential costs associated with translation errors or security breaches. Law firms must evaluate translation platforms within the context of their overall operational efficiency and client service delivery models.
DeepL’s pricing structure reflects its positioning as a premium translation service, with higher per-character costs offset by superior translation quality and enhanced security features. For law firms handling complex legal documents where accuracy is paramount, the additional cost of DeepL may be justified by reduced editing requirements, decreased risk of mistranslation, and improved client satisfaction with translation quality.
Google Translate offers more accessible pricing and extensive free usage tiers that can accommodate the needs of smaller law firms or those with limited translation budgets. The platform’s integration with existing Google services can reduce implementation costs and training requirements, making it an attractive option for firms seeking to incorporate translation capabilities without significant upfront investments or workflow disruptions.
The scalability considerations for both platforms involve their ability to handle varying volumes of translation work, accommodate growth in international practice areas, and maintain consistent performance as usage increases. Law firms experiencing rapid growth in international work may find Google Translate’s extensive language coverage and integration capabilities more suitable for their evolving needs.
Explore comprehensive AI research capabilities with Perplexity to conduct thorough analysis of translation accuracy, cost-effectiveness, and security features across different platforms and use cases. Advanced research tools can help law firms make informed decisions about translation platform adoption and implementation strategies.
Integration with Legal Technology Ecosystems
The successful implementation of AI translation tools in law firm environments requires seamless integration with existing legal technology ecosystems, including document management systems, case management platforms, billing systems, and client communication tools. The ease of integration and compatibility with established workflows can significantly impact the adoption success and overall value derived from translation platform implementation.
DeepL’s integration capabilities focus primarily on API-based connections and specialized integrations with professional translation and content management systems. The platform’s emphasis on quality and security aligns well with enterprise legal technology requirements, though implementation may require more technical expertise and customization to achieve optimal workflow integration.
Google Translate’s extensive integration ecosystem spans numerous third-party applications, document management systems, and productivity tools commonly used in legal practice. The platform’s compatibility with Google Workspace, Microsoft Office applications, and various cloud-based legal technology solutions can simplify implementation and reduce the technical barriers to adoption.
The integration evaluation process should consider factors such as single sign-on compatibility, document format preservation, batch processing capabilities, and the ability to maintain audit trails and version control throughout the translation process. Law firms with complex technology environments may require customized integration solutions that maintain security standards while optimizing workflow efficiency.
Specialized Legal Language Handling
Legal language presents unique challenges for AI translation systems due to its specialized terminology, complex syntactic structures, and the critical importance of maintaining precise meaning across different legal traditions and cultural contexts. The evaluation of translation platforms must consider their ability to handle various types of legal documents, from contracts and agreements to court filings and regulatory submissions.
DeepL demonstrates particular strength in handling formal legal register and maintaining the logical relationships that characterize legal writing. The platform’s neural network architecture appears better suited to preserving the complex conditional structures, defined terms, and cross-references that are essential elements of legal documents. This capability makes DeepL particularly valuable for translating contracts, legal opinions, and other documents where precision in legal logic is paramount.
Google Translate’s approach to legal language reflects its broader training on diverse text types, which can sometimes result in more natural-sounding translations at the expense of technical precision. While the platform handles many legal translation tasks adequately, complex legal reasoning and specialized terminology may require additional review and editing to ensure accuracy and legal validity.
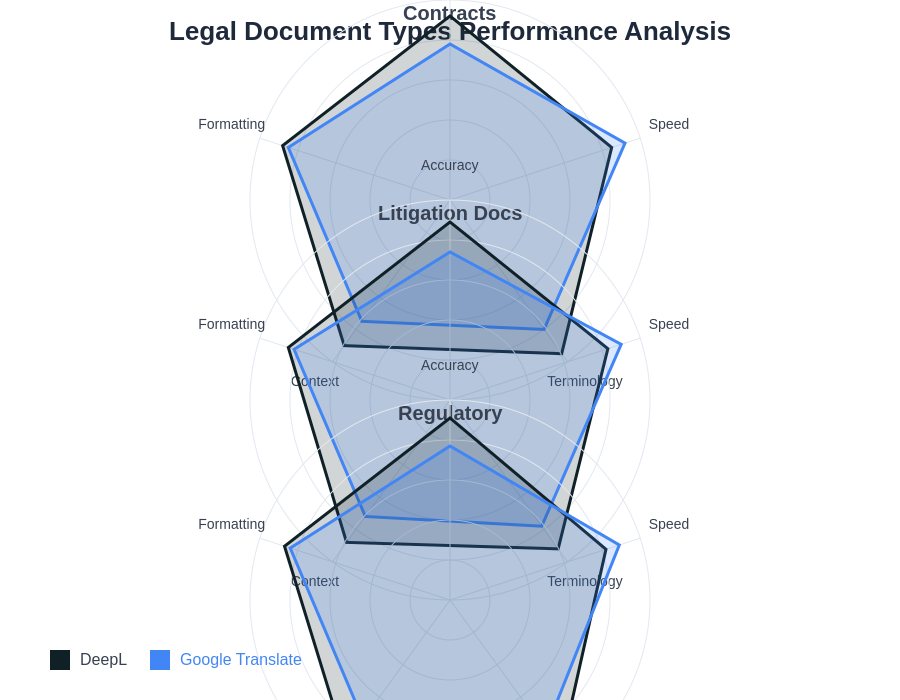
The performance variations across different legal document types highlight the importance of matching translation platform capabilities to specific document requirements and use cases within legal practice.
Professional Liability and Risk Management
The adoption of AI translation tools in legal practice introduces new considerations for professional liability and risk management that law firms must carefully evaluate and address through appropriate policies and procedures. The potential consequences of translation errors in legal contexts require comprehensive risk assessment and mitigation strategies that account for both technological limitations and professional responsibility requirements.
Professional liability considerations include the potential for mistranslation to affect contract interpretation, regulatory compliance, litigation strategy, and client representation quality. Law firms must establish clear protocols for AI translation use, including appropriate supervision, quality control measures, and circumstances where human translation or additional verification may be required.
Risk management strategies should encompass documentation of translation processes, maintenance of audit trails, implementation of quality assurance procedures, and clear communication with clients about the use of AI translation tools in their matters. Many firms adopt policies that require attorney review of AI-generated translations for critical documents while allowing more flexible use for preliminary review and internal communication purposes.
The insurance implications of AI translation adoption may require consultation with professional liability carriers to ensure adequate coverage for potential translation-related claims. Some firms choose to maintain relationships with human translators for critical documents while utilizing AI tools for efficiency gains in appropriate contexts.
Implementation Best Practices for Law Firms
Successful implementation of AI translation tools in legal practice requires careful planning, appropriate training, and establishment of clear policies and procedures that balance efficiency gains with professional responsibility requirements. Law firms should develop comprehensive implementation strategies that address technical, legal, and operational considerations while ensuring compliance with applicable professional standards.
Training and education programs should ensure that attorneys and staff understand both the capabilities and limitations of chosen translation platforms, appropriate use cases for AI translation, and necessary quality control measures. Implementation should begin with low-risk applications and gradually expand as users develop expertise and confidence in the technology.
Quality assurance procedures should include regular accuracy assessments, comparison testing between platforms, and establishment of benchmark standards for acceptable translation quality in different contexts. Many firms implement tiered quality control systems with varying levels of review based on document sensitivity and potential consequences of translation errors.
Documentation and audit trail requirements should ensure that translation processes can be tracked and verified for professional responsibility and client billing purposes. Clear policies regarding data handling, client consent, and security measures help ensure compliance with confidentiality requirements and professional standards.
Future Developments and Industry Trends
The evolution of AI translation technology continues to accelerate, with ongoing developments in neural network architectures, specialized legal language models, and integration capabilities that promise to further enhance the value and applicability of AI translation tools in legal practice. Law firms should monitor these developments to ensure their technology strategies remain current and competitive.
Emerging trends include the development of specialized legal translation models trained specifically on legal corpora, enhanced security features designed for professional services applications, and improved integration capabilities with legal technology ecosystems. These developments may significantly alter the competitive landscape and optimal platform choices for law firms.
The integration of AI translation with other legal technology tools, including document review platforms, contract analysis systems, and legal research tools, represents a significant opportunity for enhanced workflow efficiency and improved client service delivery. Future implementations may feature seamless integration across multiple AI-powered legal tools.
Regulatory developments and professional responsibility guidance regarding AI tool usage in legal practice continue to evolve, with potential implications for translation platform selection, implementation requirements, and professional liability considerations. Law firms should stay informed about these developments to ensure ongoing compliance and optimal risk management.
Strategic Recommendations for Law Firm Decision-Making
The selection of AI translation platforms requires careful consideration of multiple factors including accuracy requirements, security needs, integration capabilities, cost considerations, and risk tolerance levels that vary significantly across different law firms and practice areas. Successful platform selection requires alignment between technological capabilities and specific firm requirements and objectives.
Law firms with high-volume international practices and sophisticated technology infrastructure may benefit from implementing multiple translation platforms, utilizing each for its specific strengths and optimal use cases. This approach allows firms to leverage DeepL’s accuracy advantages for critical documents while utilizing Google Translate’s accessibility and integration benefits for broader applications.
Smaller firms or those with limited international practice may find single-platform implementations more practical, with platform selection based primarily on cost-effectiveness, ease of use, and integration with existing systems. These firms should prioritize platforms that offer the best balance of capability and accessibility for their specific needs and constraints.
The implementation approach should emphasize gradual adoption with comprehensive training, clear policies, and robust quality control measures that ensure professional standards are maintained while capturing efficiency benefits. Regular evaluation and adjustment of translation strategies help ensure continued alignment with evolving firm needs and technological capabilities.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
The integration of AI translation tools into legal practice represents a significant technological advancement that offers substantial benefits in terms of efficiency, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness while requiring careful consideration of accuracy, security, and professional responsibility requirements. Both DeepL and Google Translate offer valuable capabilities that can enhance law firm operations when implemented appropriately and with proper safeguards.
The choice between platforms ultimately depends on specific firm requirements, risk tolerance, and strategic objectives, with many firms finding value in hybrid approaches that leverage the strengths of multiple platforms for different applications. The continued evolution of AI translation technology promises further improvements in accuracy, security, and integration capabilities that will enhance the value proposition for legal practice applications.
Law firms that approach AI translation adoption strategically, with appropriate training, policies, and quality control measures, can realize significant benefits in terms of operational efficiency and client service enhancement while maintaining professional standards and managing associated risks. The future of legal translation lies in the intelligent integration of AI capabilities with human expertise to create more efficient and effective legal service delivery models.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal or professional advice. The evaluation of AI translation tools for legal practice should consider specific firm requirements, applicable professional responsibility standards, and relevant regulatory requirements. Law firms should consult with appropriate technology and legal professionals when implementing AI translation solutions. The effectiveness and appropriateness of AI translation tools may vary based on specific use cases, document types, and jurisdictional requirements.
