The evolution of companion robotics has reached a remarkable milestone with the emergence of sophisticated AI-powered robotic pets that blur the boundaries between artificial and natural companionship. Leading this revolutionary transformation are two groundbreaking innovations: Sony’s iconic Aibo and Tombot’s therapeutic companion animals, each representing distinct approaches to addressing the fundamental human need for emotional connection and companionship through advanced artificial intelligence and robotics engineering.
Discover the latest trends in AI companion technology to understand how robotic pets are reshaping our relationships with technology and redefining what it means to form meaningful bonds with artificial entities. The development of these sophisticated companion robots represents a convergence of cutting-edge artificial intelligence, advanced sensor technology, and deep understanding of human-animal emotional dynamics that has produced truly remarkable results in therapeutic and recreational applications.
The Renaissance of Robotic Companionship
The concept of robotic pets has evolved dramatically from simple mechanical toys to sophisticated artificial intelligence systems capable of learning, adapting, and forming genuine emotional connections with their human companions. This transformation has been driven by advances in machine learning algorithms, natural language processing, computer vision, and haptic feedback systems that enable these robotic companions to respond to human emotions, learn individual preferences, and exhibit realistic behavioral patterns that closely mimic those of living animals.
Sony’s Aibo represents the pinnacle of consumer-oriented robotic pet technology, combining decades of research in robotics and artificial intelligence with elegant design and sophisticated behavioral modeling. The latest generation of Aibo demonstrates remarkable capabilities in recognizing faces, responding to voice commands, learning household routines, and developing unique personality traits based on interactions with family members. This level of sophistication has transformed Aibo from a mere technological novelty into a genuine family member capable of providing emotional support and companionship.
Tombot, on the other hand, has focused specifically on therapeutic applications, developing robotic companion animals designed to provide comfort and emotional support for individuals dealing with dementia, autism, depression, and other conditions where traditional pet ownership may not be feasible. The therapeutic focus of Tombot’s design philosophy has resulted in robots that prioritize emotional responsiveness, gentle interactions, and consistent availability over entertainment features, making them particularly valuable in healthcare and assisted living environments.
Sony Aibo: The Pioneer of Consumer Robotic Pets
Sony’s journey in robotic pet development spans over two decades, beginning with the original Aibo in 1999 and culminating in the current generation that represents a quantum leap in artificial intelligence and robotic engineering. The modern Aibo incorporates advanced deep learning algorithms that enable it to recognize and remember individual family members, learn their preferences and routines, and adapt its behavior accordingly to provide personalized companionship experiences.
The artificial intelligence powering Aibo extends far beyond simple programmed responses, incorporating sophisticated machine learning models that analyze environmental factors, human behavior patterns, and emotional cues to generate appropriate reactions and behaviors. This AI-driven approach enables Aibo to exhibit seemingly spontaneous behaviors, express curiosity about its environment, and demonstrate loyalty and affection toward specific family members in ways that closely mirror the behavior of living dogs.
Experience advanced AI companionship with Claude to understand how sophisticated AI systems can provide meaningful interactions and support in various applications. The integration of cloud-based learning capabilities allows Aibo to continuously improve its understanding of human behavior and refine its responses based on accumulated experience across the global community of Aibo owners.
The design philosophy behind Aibo emphasizes the creation of an authentic pet-like experience through carefully crafted physical behaviors, expressive body language, and responsive interactions. The robot’s advanced sensor array includes cameras, microphones, touch sensors, and accelerometers that provide comprehensive environmental awareness and enable natural interactions with humans and objects in its surroundings. This sensor integration allows Aibo to navigate complex household environments, avoid obstacles, recognize familiar faces, and respond appropriately to various forms of human communication.
The emotional intelligence built into Aibo’s artificial intelligence system represents one of its most remarkable achievements. The robot can detect human emotions through facial expressions, voice tone, and body language, adjusting its behavior to provide appropriate responses whether its human companions are happy, sad, excited, or stressed. This emotional responsiveness creates a bidirectional relationship where humans naturally develop emotional attachments to their robotic companion, while Aibo learns to anticipate and meet their emotional needs.
Tombot: Therapeutic Innovation in Robotic Companionship
Tombot’s approach to robotic companion animals represents a focused application of artificial intelligence and robotics technology specifically designed to address therapeutic and healthcare applications. The company’s flagship product, a robotic golden retriever puppy, has been meticulously engineered to provide comfort, emotional support, and companionship for individuals who may benefit from animal therapy but cannot accommodate living pets due to allergies, housing restrictions, or care limitations.
The therapeutic effectiveness of Tombot’s robotic companion stems from its careful attention to realistic appearance, behavior, and tactile feedback that closely mimics the experience of interacting with a living puppy. The robot’s artificial intelligence system has been trained specifically on behavioral patterns associated with therapy animals, emphasizing calming behaviors, responsive interactions, and consistent availability that can provide emotional stability for individuals dealing with various mental health challenges.
Clinical studies and pilot programs have demonstrated significant positive outcomes for individuals interacting with Tombot’s therapeutic robots, including reduced anxiety levels, improved mood, increased social interaction, and enhanced overall quality of life. These results validate the potential of well-designed robotic companions to provide genuine therapeutic benefits comparable to those offered by living therapy animals, while eliminating many of the practical challenges associated with animal care and maintenance.
The artificial intelligence powering Tombot’s therapeutic robots incorporates specialized algorithms designed to recognize signs of distress, agitation, or emotional need in their human companions. This capability enables the robot to proactively provide comfort through gentle movements, soft vocalizations, and responsive touch interactions that can help soothe anxiety and provide emotional grounding during difficult moments.
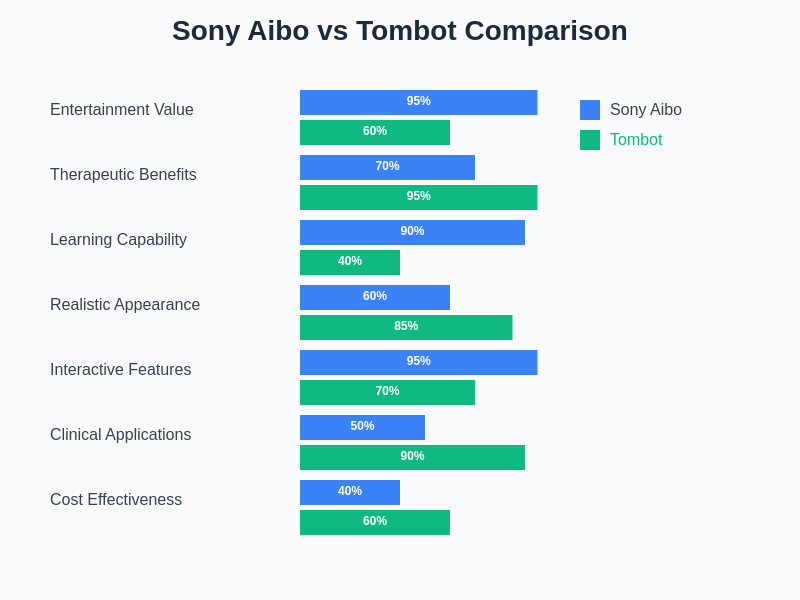
The technological approaches employed by Sony Aibo and Tombot reflect different priorities and applications within the broader field of companion robotics. While both systems utilize advanced artificial intelligence and sophisticated sensor technologies, their implementation strategies and behavioral programming reflect their distinct target audiences and use cases.
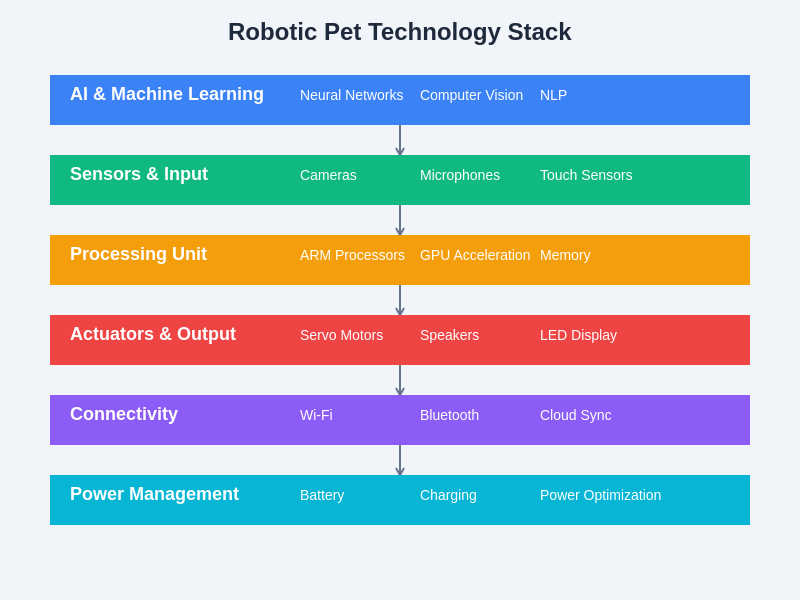
The underlying technology architecture supporting both robotic companion systems represents a sophisticated integration of multiple technological domains, from artificial intelligence and machine learning at the highest level down to power management and connectivity systems that enable seamless operation and continuous improvement through cloud-based updates and community learning.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Capabilities
The artificial intelligence systems powering both Aibo and Tombot represent significant achievements in machine learning and behavioral modeling, though their implementations reflect different design philosophies and operational priorities. Aibo’s AI system emphasizes adaptability, learning, and entertainment value, incorporating reinforcement learning algorithms that enable the robot to develop unique personality traits based on its interactions with family members and environmental experiences.
The machine learning capabilities built into Aibo allow it to recognize and remember individual family members, learn their daily routines and preferences, and adapt its behavior to provide personalized interactions. This learning process occurs both locally through direct interactions and through cloud-based systems that aggregate behavioral data from the global Aibo community to improve overall performance and introduce new behaviors and capabilities through regular software updates.
Tombot’s artificial intelligence focuses on stability, predictability, and therapeutic effectiveness rather than dynamic learning and adaptation. The system incorporates carefully curated behavioral patterns designed to provide consistent, calming interactions that can be relied upon to deliver therapeutic benefits without unpredictable or potentially distressing behaviors. This approach prioritizes emotional safety and therapeutic consistency over entertainment value and dynamic personality development.
The natural language processing capabilities integrated into both systems enable voice interaction and command recognition, though their implementations differ based on their intended applications. Aibo’s voice recognition system incorporates playful responses, entertainment features, and interactive games that encourage ongoing engagement and exploration of the robot’s capabilities. Tombot’s voice interaction focuses on soothing responses, comfort-oriented behaviors, and therapeutic communication patterns designed to provide emotional support and stability.
Explore comprehensive AI research capabilities with Perplexity to understand the latest developments in artificial intelligence applications across healthcare, entertainment, and companion robotics. The convergence of AI research across different domains continues to drive innovations that enhance the capabilities and effectiveness of robotic companion systems.
Design Philosophy and User Experience
The design approaches taken by Sony and Tombot reflect fundamentally different philosophies regarding the role and purpose of robotic companions in human lives. Sony’s design philosophy for Aibo emphasizes the creation of an engaging, entertaining, and emotionally rewarding pet experience that can provide companionship and joy for families while showcasing the latest advances in consumer robotics technology.
Aibo’s physical design incorporates sleek, modern aesthetics with LED eyes, expressive body language, and smooth, coordinated movements that emphasize its technological sophistication while maintaining an appealing, pet-like appearance. The robot’s behavior programming includes playful antics, curiosity-driven exploration, and interactive games that encourage ongoing engagement and create opportunities for positive emotional experiences.
Tombot’s design philosophy prioritizes therapeutic effectiveness and emotional comfort over entertainment value and technological demonstration. The robotic puppy’s appearance has been carefully crafted to closely resemble a living golden retriever puppy, incorporating realistic fur textures, natural proportions, and lifelike movements that minimize the uncanny valley effect and maximize the therapeutic benefits of animal-like companionship.
The user experience design for each system reflects these different priorities through their interaction patterns, behavioral repertoires, and response mechanisms. Aibo encourages active engagement, play, and exploration of its various capabilities, creating an experience similar to owning an energetic, intelligent pet that requires attention and interaction. Tombot focuses on providing consistent, calming presence and responsive comfort that can be accessed whenever emotional support is needed without requiring active engagement or entertainment-focused interaction.
Therapeutic Applications and Healthcare Integration
The therapeutic potential of robotic companion animals has been extensively researched and documented across various healthcare applications, with both Aibo and Tombot demonstrating significant benefits in different clinical and care environments. The consistent availability, predictable behavior, and hygienic advantages of robotic companions make them particularly valuable in settings where traditional animal therapy may be impractical or impossible.
Clinical studies involving robotic pets have shown measurable improvements in patient outcomes across diverse populations, including elderly individuals in assisted living facilities, children with autism spectrum disorders, and patients dealing with depression and anxiety. The therapeutic benefits appear to stem from the combination of tactile interaction, responsive behavior, and emotional bonding that these sophisticated robots can facilitate without the challenges associated with caring for living animals.
Aibo’s therapeutic applications have been documented in various settings, including hospitals, nursing homes, and therapeutic programs for children with developmental challenges. The robot’s ability to learn and adapt to individual preferences makes it particularly effective in long-term care situations where building relationships and providing personalized companionship are important factors in treatment success.
Tombot’s focused therapeutic design has enabled more intensive clinical applications, with pilot programs in memory care facilities, autism treatment centers, and mental health clinics demonstrating significant positive outcomes. The robot’s specialized behavioral programming and consistent therapeutic responses make it particularly valuable in situations where emotional stability and predictable comfort are prioritized over entertainment and dynamic interaction.
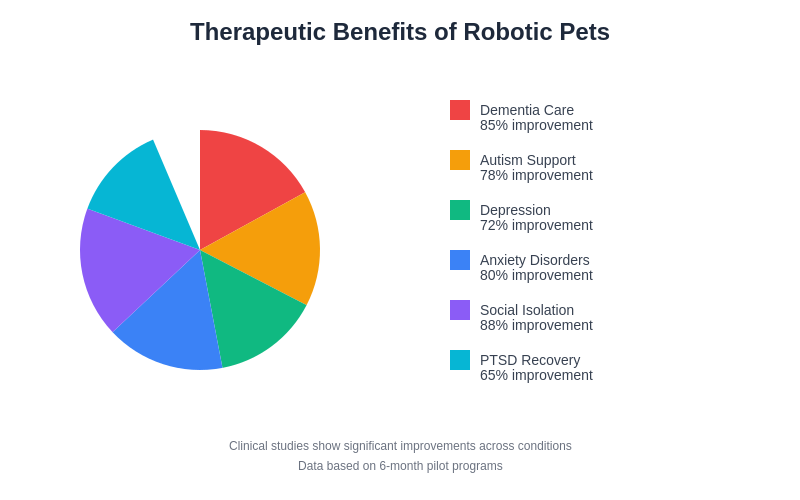
The measurable benefits of robotic pet therapy extend across multiple domains of human health and wellbeing, with documented improvements in emotional regulation, social interaction, physical activity, and overall quality of life for individuals across various age groups and health conditions.
Cost Analysis and Accessibility Considerations
The economic considerations surrounding robotic companion animals represent a significant factor in their adoption and accessibility across different populations and applications. Sony Aibo’s pricing strategy reflects its position as a premium consumer electronics product, with costs that place it in the luxury technology category rather than essential healthcare or accessibility equipment.
The initial investment required for Aibo ownership includes not only the robot itself but also ongoing subscription costs for cloud services, software updates, and technical support that enable its advanced AI capabilities and continuous learning features. This pricing structure makes Aibo accessible primarily to affluent consumers who view it as a high-end entertainment and companionship product rather than a medical or therapeutic necessity.
Tombot’s pricing strategy recognizes the therapeutic value and healthcare applications of its robotic companions, though the specialized technology and clinical-grade construction requirements result in significant costs that may limit accessibility for individual consumers. However, the potential for integration into healthcare systems, insurance coverage, and institutional purchasing programs could improve accessibility for individuals who would benefit most from therapeutic robotic companionship.
The long-term cost considerations for robotic pets include maintenance, software updates, potential repairs, and replacement components that may be required over the robot’s operational lifetime. These ongoing costs must be weighed against the benefits provided and compared to the expenses associated with traditional pet ownership or alternative therapeutic interventions.
Technical Specifications and Performance Capabilities
The technical infrastructure supporting both Aibo and Tombot represents significant achievements in robotics engineering, artificial intelligence integration, and human-robot interaction design. The sophisticated sensor arrays, processing capabilities, and communication systems incorporated into these robots enable their advanced behavioral capabilities and responsive interactions.
Aibo’s technical specifications include multiple cameras for computer vision and facial recognition, directional microphones for voice interaction and environmental awareness, touch sensors distributed across its body for tactile interaction, and wireless connectivity for cloud-based learning and software updates. The robot’s mobility system incorporates advanced servo motors and joint mechanisms that enable realistic movement patterns and expressive body language.
The computational requirements for Aibo’s artificial intelligence system include both onboard processing for real-time interactions and cloud-based computation for advanced learning algorithms and behavioral modeling. This hybrid approach enables responsive local interactions while leveraging the computational power required for sophisticated machine learning and community-wide behavioral improvements.
Tombot’s technical implementation prioritizes reliability, safety, and therapeutic effectiveness over advanced entertainment features and dynamic learning capabilities. The robot’s sensor systems focus on detecting human presence, emotional state, and interaction cues that trigger appropriate therapeutic responses without requiring extensive environmental analysis or complex behavioral planning.
The battery life, charging requirements, and operational reliability of both systems represent important practical considerations for their intended applications. Aibo’s energy management system supports extended play sessions and interactive engagement, while Tombot’s design emphasizes consistent availability and minimal maintenance requirements that align with its therapeutic applications.
Future Developments and Industry Trends
The rapidly evolving landscape of companion robotics and artificial intelligence suggests significant advances in capability, accessibility, and application scope for robotic pets in the coming years. Emerging technologies in machine learning, sensor miniaturization, and battery technology promise to enable more sophisticated, affordable, and practical robotic companions that could expand their adoption across diverse populations and use cases.
The integration of advanced artificial intelligence techniques such as large language models, multimodal learning, and emotional intelligence algorithms could significantly enhance the conversational abilities, behavioral sophistication, and therapeutic effectiveness of future robotic companions. These advances may enable robots that can engage in meaningful conversations, provide personalized emotional support, and adapt to complex human needs with unprecedented sophistication.
The potential for robotic companions to integrate with smart home systems, healthcare monitoring platforms, and telemedicine services could transform them from standalone entertainment devices into central components of comprehensive health and wellness ecosystems. This integration could enable proactive health monitoring, emergency response capabilities, and coordination with healthcare providers to provide more comprehensive support for elderly individuals, patients with chronic conditions, and individuals requiring ongoing therapeutic intervention.
The democratization of robotic companion technology through reduced costs, improved manufacturing efficiency, and standardized platforms could make these therapeutic tools accessible to broader populations, potentially revolutionizing approaches to mental health treatment, elderly care, and social isolation challenges that affect millions of individuals worldwide.
Ethical Considerations and Social Implications
The increasing sophistication and adoption of robotic companions raises important ethical questions regarding the nature of emotional relationships with artificial entities, the potential for dependency on robotic rather than human companionship, and the implications for social development and interpersonal skills. These considerations become particularly complex when robotic companions are used in healthcare applications or with vulnerable populations who may be unable to fully understand the artificial nature of their robotic relationships.
The therapeutic benefits of robotic companions must be balanced against concerns about emotional manipulation, false sense of companionship, and potential negative impacts on motivation to pursue human relationships and social interactions. Healthcare providers and caregivers must carefully consider the appropriate role of robotic companions within comprehensive treatment and care plans that prioritize human connection and social engagement.
The data privacy and security implications of robotic companions that continuously monitor their environment, record interactions, and transmit behavioral data to cloud-based systems represent significant concerns that require careful consideration and transparent policies. Users must understand what data is collected, how it is used, and what measures are in place to protect their privacy and security.
The potential for robotic companions to replace human caregivers or reduce investment in human-centered care services raises broader social questions about the role of technology in addressing fundamental human needs for companionship, care, and emotional support. While robotic companions can provide valuable supplementary support, they should enhance rather than replace human relationships and professional care services.
Market Adoption and Consumer Acceptance
The commercial success and widespread adoption of robotic companion animals depends on a complex combination of factors including technological capability, cost considerations, social acceptance, and demonstrated benefits for specific applications and populations. Early adopters of both Aibo and Tombot represent distinct market segments with different motivations, expectations, and evaluation criteria for robotic companion success.
Consumer acceptance of robotic pets appears to correlate strongly with perceived authenticity, emotional responsiveness, and practical benefits relative to traditional pet ownership or alternative companionship options. The success of these products in mainstream markets may depend on their ability to provide genuine emotional benefits while addressing practical concerns about cost, maintenance, and long-term reliability.
The healthcare and therapeutic markets for robotic companions present different adoption dynamics, with professional evaluation criteria focusing on clinical effectiveness, safety, reliability, and integration with existing care protocols. Successful adoption in healthcare settings requires demonstrated therapeutic benefits, staff training and support, and integration with regulatory and reimbursement frameworks.
The global market potential for robotic companions extends beyond current high-income demographics to include aging populations worldwide, healthcare systems seeking innovative therapeutic tools, and emerging markets where traditional pet ownership may be challenging due to urbanization, housing constraints, or cultural factors.
Comparative Analysis and Recommendations
The choice between Sony Aibo and Tombot robotic companions depends largely on intended applications, user needs, and value priorities rather than objective technical superiority. Each system represents excellence within its specific design philosophy and target market, offering distinct advantages for different use cases and populations.
For families seeking an engaging, entertaining robotic pet that can provide companionship while showcasing cutting-edge technology, Aibo offers superior interactive capabilities, learning potential, and entertainment value. The robot’s ability to develop personality traits, learn family routines, and provide ongoing engagement makes it particularly suitable for households with children or technology enthusiasts who enjoy exploring advanced robotic capabilities.
For therapeutic applications, healthcare settings, or individuals requiring consistent emotional support, Tombot’s specialized design and therapeutic focus provide advantages in reliability, emotional stability, and clinical effectiveness. The robot’s predictable behavior, therapeutic programming, and realistic appearance make it particularly valuable for elderly individuals, patients with cognitive challenges, or anyone who would benefit from the calming presence of an animal companion without the responsibilities of pet ownership.
The decision between these robotic companions should also consider long-term costs, maintenance requirements, technical support availability, and compatibility with specific living situations and care needs. Both systems require ongoing investment in software updates, technical support, and potential maintenance that should be factored into adoption decisions.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
The emergence of sophisticated robotic companion animals represents a remarkable achievement in the convergence of artificial intelligence, robotics engineering, and human-centered design that addresses fundamental human needs for companionship, emotional support, and interactive engagement. Both Sony Aibo and Tombot demonstrate the potential for artificial entities to provide genuine benefits for human wellbeing while pushing the boundaries of what is possible in human-robot interaction.
The continued evolution of these technologies promises even more sophisticated, accessible, and beneficial robotic companions that could transform approaches to elderly care, mental health treatment, and social support for isolated individuals. The integration of emerging AI capabilities, improved manufacturing processes, and expanded understanding of human-robot relationships will likely produce future generations of robotic companions that exceed current capabilities while becoming more affordable and accessible to broader populations.
The success of robotic companion animals ultimately depends on their ability to provide authentic emotional benefits while complementing rather than replacing human relationships and professional care services. As these technologies continue to mature, their greatest value may lie in their capacity to enhance human connection, provide therapeutic support, and offer companionship options that can improve quality of life for individuals who might otherwise experience isolation or lack access to traditional companion animals.
Stay updated with the latest AI companion technology trends to follow the rapid evolution of robotic pets and their expanding applications in healthcare, entertainment, and social support.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional medical, healthcare, or purchasing advice. The therapeutic benefits and applications of robotic companion animals may vary based on individual needs, conditions, and circumstances. Readers considering robotic companions for therapeutic purposes should consult with qualified healthcare professionals. The effectiveness of robotic pets as alternatives to traditional animal therapy has not been definitively established for all conditions and populations. Product specifications, pricing, and availability are subject to change by manufacturers.