The digital landscape has become increasingly complex, with artificial intelligence technologies now permeating every aspect of our online experience while simultaneously raising unprecedented concerns about privacy and data security. In this environment, privacy-focused AI tools have emerged as essential guardians of personal information, offering sophisticated protection mechanisms that leverage artificial intelligence to safeguard user data while maintaining functionality and user experience. Three standout platforms in this privacy revolution are DuckDuckGo, Brave Browser, and Signal, each representing a unique approach to protecting user privacy through innovative AI-powered technologies.
Explore the latest privacy and AI trends to understand how these technologies are evolving to better protect user data while maintaining cutting-edge functionality. The intersection of artificial intelligence and privacy protection represents one of the most critical technological developments of our time, as these tools work tirelessly to ensure that the benefits of AI can be enjoyed without compromising personal privacy or security.
The Evolution of Privacy-Focused AI Technologies
The development of privacy-focused AI tools represents a fundamental shift in how technology companies approach user data protection and artificial intelligence implementation. Traditional AI systems often required extensive data collection and processing to function effectively, creating inherent tensions between functionality and privacy. However, innovative companies like DuckDuckGo, Brave, and Signal have pioneered new approaches that demonstrate how artificial intelligence can enhance privacy protection rather than compromise it.
These privacy-first AI implementations utilize sophisticated techniques such as differential privacy, on-device processing, federated learning, and advanced encryption methods to ensure that user data remains protected while still enabling powerful AI-driven features. The result is a new generation of tools that provide users with the benefits of artificial intelligence without requiring them to sacrifice their privacy or personal data security.
The emergence of these privacy-focused solutions has been driven by growing consumer awareness of data privacy issues, regulatory pressures such as GDPR and CCPA, and a recognition that sustainable technology business models must respect user privacy. This convergence of factors has created a market environment where privacy-focused AI tools are not only viable but increasingly preferred by informed users who understand the value of their personal data.
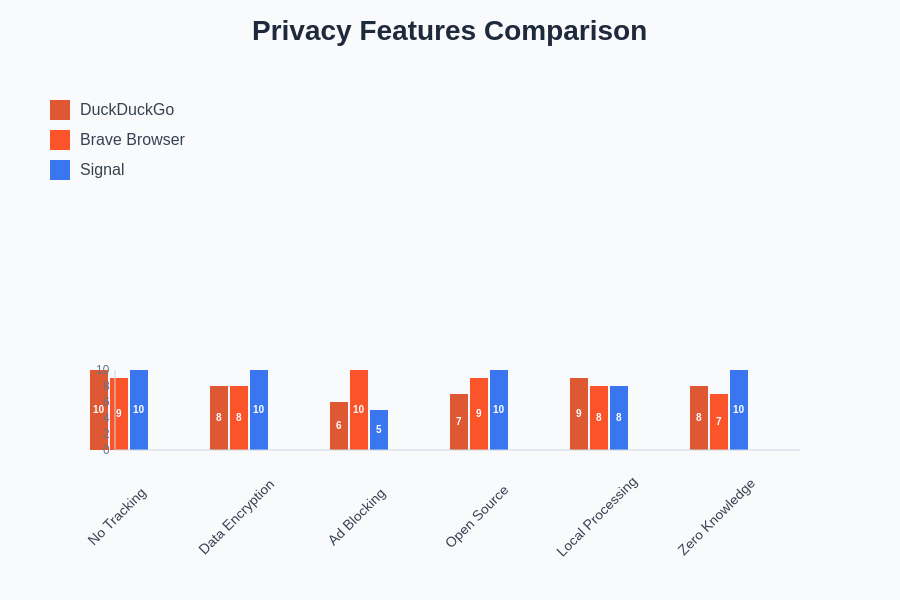
The comparative analysis of privacy features across DuckDuckGo, Brave Browser, and Signal reveals distinct strengths in different areas of privacy protection, demonstrating how specialized tools can provide comprehensive coverage when used together as part of a privacy-focused digital ecosystem.
DuckDuckGo: Redefining Private Search with AI Intelligence
DuckDuckGo has revolutionized the search engine landscape by demonstrating that powerful AI-driven search capabilities can be delivered without compromising user privacy. The platform’s approach to artificial intelligence is fundamentally different from traditional search engines, as it implements AI algorithms that enhance search quality and relevance without tracking users or collecting personal information for advertising purposes.
The search engine utilizes sophisticated natural language processing and machine learning algorithms to understand user queries and deliver relevant results, but these AI systems are designed to operate without creating persistent user profiles or storing search histories. This privacy-by-design approach ensures that users can benefit from advanced AI-powered search capabilities while maintaining complete anonymity and privacy protection.
Experience enhanced AI capabilities with Claude for tasks requiring sophisticated reasoning while maintaining privacy standards. The integration of privacy-preserving AI technologies demonstrates that users need not choose between functionality and privacy when selecting their digital tools.
DuckDuckGo’s AI implementation extends beyond basic search functionality to include features such as instant answers, query understanding improvements, and result ranking optimizations. These AI-powered enhancements are achieved through techniques that process queries in real-time without retaining user data, utilizing pre-trained models and anonymized data processing methods that maintain the privacy-first philosophy while delivering exceptional search experiences.
The platform’s commitment to privacy extends to its handling of AI training data and model development. Unlike traditional search engines that use personal user data to train and improve their AI systems, DuckDuckGo relies on privacy-preserving techniques and anonymized datasets that ensure user privacy is never compromised in the pursuit of improved AI functionality.
Brave Browser: AI-Powered Privacy Protection and Content Blocking
Brave Browser represents a comprehensive approach to privacy protection that leverages artificial intelligence to provide users with advanced security features, intelligent content blocking, and personalized experiences without compromising privacy. The browser’s AI systems work continuously in the background to identify and block tracking scripts, malicious content, and privacy-invasive elements while maintaining optimal browsing performance and user experience.
The browser’s AI-powered ad and tracker blocking system utilizes machine learning algorithms to identify and neutralize new tracking techniques and advertising methods in real-time. This dynamic approach to content blocking ensures that users remain protected against evolving privacy threats without requiring manual updates or configuration changes. The AI system continuously learns and adapts to new tracking methods while operating entirely on the user’s device, ensuring that no personal browsing data is transmitted to external servers.
Brave’s implementation of AI extends to its innovative approach to digital advertising through the Brave Rewards system. This privacy-preserving advertising model uses AI to match users with relevant advertisements based on local device processing rather than invasive tracking and profiling. The system demonstrates how artificial intelligence can create value for both users and advertisers while maintaining strict privacy standards and user control over personal data.
The browser’s AI capabilities also include intelligent HTTPS upgrading, malicious site detection, and phishing protection systems that operate through local processing and privacy-preserving techniques. These features provide users with comprehensive security protection powered by advanced AI algorithms without requiring the transmission of personal browsing data to external analysis systems.
Signal: Secure Messaging with AI-Enhanced Privacy Features
Signal has established itself as the gold standard for private messaging by implementing AI-powered features that enhance user experience and security while maintaining end-to-end encryption and zero-knowledge architecture. The platform’s approach to artificial intelligence demonstrates how advanced AI capabilities can be integrated into privacy-focused applications without compromising the fundamental security principles that make the platform trustworthy.
The messaging platform utilizes AI algorithms for various functionality enhancements, including message delivery optimization, spam detection, and user interface improvements, all while ensuring that message content remains completely private and inaccessible to the platform operators. These AI systems operate through techniques that analyze metadata and usage patterns without accessing actual message content, maintaining the platform’s commitment to user privacy.
Signal’s AI implementation includes sophisticated spam and abuse detection systems that protect users from malicious content and unwanted communications without compromising message privacy. These systems utilize machine learning algorithms that can identify suspicious patterns and behaviors without accessing message content, demonstrating the possibility of effective content moderation while maintaining end-to-end encryption.
Discover comprehensive AI research capabilities with Perplexity while maintaining focus on privacy-preserving technologies and research methodologies. The balance between functionality and privacy in AI systems represents a crucial area of ongoing technological development.
The platform’s commitment to privacy extends to its AI development practices, which emphasize open-source development, transparent algorithms, and community-driven improvements. This approach ensures that AI enhancements to the platform can be independently verified and audited, maintaining the trust and transparency that are essential for privacy-focused communication tools.
Comparative Analysis: Privacy Approaches and AI Implementation
When examining DuckDuckGo, Brave Browser, and Signal collectively, several important patterns emerge in how privacy-focused organizations approach AI implementation. Each platform demonstrates unique strategies for balancing AI functionality with privacy protection, offering valuable insights into the future of privacy-preserving artificial intelligence technologies.
DuckDuckGo’s approach emphasizes server-side AI processing with strict data anonymization and no user tracking, proving that sophisticated search AI can operate without personal data collection. Brave Browser focuses on client-side AI processing that keeps user data local while providing intelligent protection and personalization features. Signal demonstrates how AI can enhance secure communications through metadata analysis and pattern recognition without compromising message content privacy.
These different approaches highlight the versatility of privacy-preserving AI techniques and demonstrate that there are multiple viable paths for implementing artificial intelligence while maintaining user privacy. The success of these platforms has influenced broader industry trends toward privacy-by-design AI development and has shown that privacy protection can be a competitive advantage rather than a limitation.
The technical innovations developed by these platforms have contributed to the broader field of privacy-preserving AI, including advances in differential privacy, federated learning, homomorphic encryption, and on-device machine learning. These contributions benefit the entire technology ecosystem by providing proven methods for implementing AI functionality while protecting user privacy.
Privacy-Preserving AI Techniques and Technologies
The implementation of AI in privacy-focused tools relies on several key technologies and methodologies that enable sophisticated functionality while maintaining strict privacy standards. Differential privacy ensures that AI systems can learn from user data without revealing individual user information, while federated learning allows AI models to improve through distributed learning without centralizing personal data.
On-device processing represents another crucial technique employed by privacy-focused AI tools, enabling sophisticated AI functionality to operate locally on user devices without transmitting personal data to external servers. This approach provides users with advanced AI capabilities while maintaining complete control over their personal information and ensuring that sensitive data never leaves their devices.
Homomorphic encryption and secure multi-party computation represent advanced cryptographic techniques that enable AI computations to be performed on encrypted data without decrypting it, ensuring that personal information remains protected even during AI processing. These technologies are becoming increasingly important as AI systems become more sophisticated and require more complex data processing capabilities.
Zero-knowledge architectures ensure that service providers can offer AI-powered functionality without gaining knowledge of user data or behavior patterns. This approach is exemplified by Signal’s implementation, where the platform can provide intelligent features without accessing message content or user communications patterns.
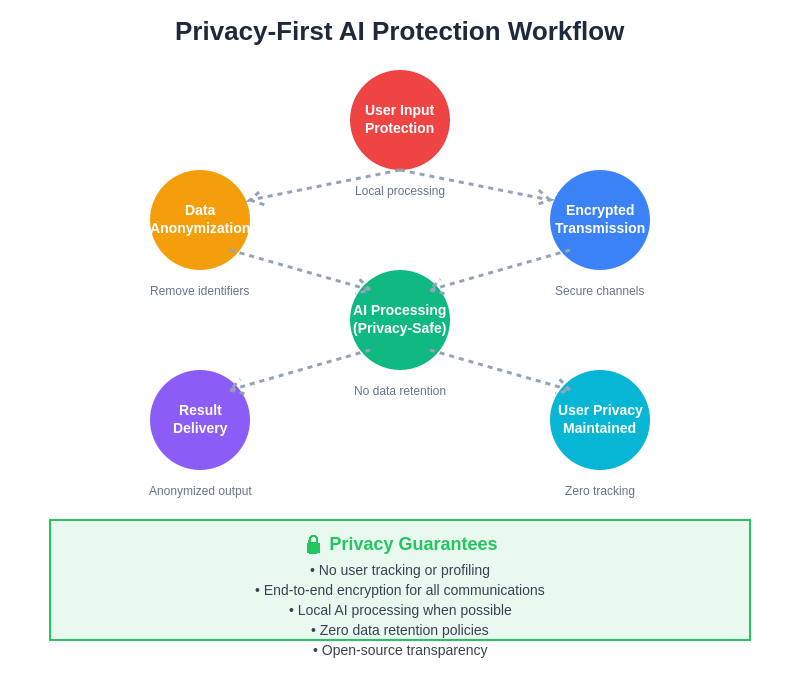
The privacy-first AI protection workflow demonstrates how user data can be processed and analyzed while maintaining complete anonymity and privacy protection throughout the entire process, from initial input through final result delivery.
User Experience and Functionality Balance
One of the most significant achievements of privacy-focused AI tools is their ability to maintain high-quality user experiences while implementing strict privacy protections. Traditional assumptions suggested that privacy protection would necessarily compromise functionality or user experience, but DuckDuckGo, Brave Browser, and Signal have demonstrated that this trade-off is not inevitable.
These platforms have achieved exceptional user experiences through thoughtful design, efficient AI implementation, and innovative approaches to functionality that work within privacy constraints. The result is a new paradigm where privacy protection enhances rather than diminishes the user experience by eliminating intrusive tracking, reducing unwanted content, and providing users with greater control over their digital interactions.
The success of these platforms in maintaining functionality while protecting privacy has influenced user expectations and industry standards, demonstrating that privacy protection is not only compatible with high-quality user experiences but can actually enhance them. This shift has encouraged other technology companies to reconsider their approaches to data collection and AI implementation.
Security and Trust in AI-Powered Privacy Tools
Trust represents a fundamental component of privacy-focused AI tools, as users must have confidence that these platforms will protect their data and maintain their privacy commitments over time. DuckDuckGo, Brave Browser, and Signal have built trust through transparent practices, open-source development where possible, independent security audits, and consistent demonstration of their privacy commitments.
The security implementations of these platforms extend beyond basic privacy protection to include comprehensive security measures that protect users from various threats including malware, phishing, man-in-the-middle attacks, and other security vulnerabilities. These security features are often powered by AI systems that can identify and respond to emerging threats in real-time.
The trust-building efforts of these platforms include regular transparency reports, clear privacy policies, open-source code where feasible, and active engagement with the privacy and security research communities. These practices help users understand exactly how their data is being protected and provide mechanisms for independent verification of privacy claims.
Impact on the Broader Technology Industry
The success of privacy-focused AI tools has had significant impact on the broader technology industry, influencing how other companies approach privacy and AI development. Major technology companies have begun implementing privacy-preserving AI techniques and emphasizing privacy protection in their product development processes, partly in response to the competitive pressure created by privacy-focused alternatives.
Regulatory developments such as GDPR, CCPA, and other privacy legislation have been influenced by the existence of viable privacy-preserving alternatives that demonstrate the technical feasibility of protecting user privacy while maintaining functionality. These tools serve as proof-of-concept implementations that inform policy discussions and regulatory requirements.
The technical innovations developed by privacy-focused AI tools have contributed to the broader field of privacy-preserving technologies, including advances in cryptography, distributed computing, and AI algorithm development. These contributions benefit the entire technology ecosystem by providing proven methods and technologies that other developers can implement.

The threat protection matrix illustrates how different privacy-focused AI tools excel in protecting against various types of digital threats, with each tool providing specialized defenses that complement the others in creating comprehensive privacy protection coverage.
Challenges and Limitations of Privacy-First AI
Despite their successes, privacy-focused AI tools face several challenges and limitations that impact their development and adoption. Technical constraints imposed by privacy requirements can limit the sophistication of AI features compared to platforms that utilize extensive user data collection. Resource requirements for on-device processing and privacy-preserving computations can impact performance and battery life on mobile devices.
Market competition from well-funded platforms that offer more comprehensive feature sets through extensive data collection creates ongoing challenges for privacy-focused alternatives. User education and awareness represent additional challenges, as many users may not fully understand the privacy implications of their technology choices or the benefits of privacy-focused alternatives.
Development costs for privacy-preserving AI can be higher than traditional approaches due to the additional complexity required to implement sophisticated functionality while maintaining privacy protection. This cost differential can impact the ability of privacy-focused platforms to compete with larger, better-funded alternatives that do not prioritize privacy protection.
Future Developments and Emerging Technologies
The future of privacy-focused AI tools looks promising, with ongoing developments in privacy-preserving technologies, increased user awareness of privacy issues, and regulatory support for privacy protection. Emerging technologies such as advanced homomorphic encryption, improved federated learning techniques, and more efficient on-device processing capabilities will enable even more sophisticated privacy-preserving AI implementations.
The integration of blockchain technologies and decentralized computing approaches may provide new models for privacy-preserving AI that eliminate the need for centralized data processing while maintaining sophisticated AI capabilities. These developments could enable new forms of privacy-focused AI tools that operate through distributed networks rather than traditional client-server architectures.
Advances in AI efficiency and optimization will make privacy-preserving implementations more viable by reducing the computational overhead required for privacy protection. These improvements will enable privacy-focused tools to offer feature parity with traditional platforms while maintaining their privacy advantages.
Practical Implementation and User Adoption Strategies
For users considering the adoption of privacy-focused AI tools, practical implementation strategies can help maximize the benefits while minimizing potential disruptions to existing workflows. Gradual migration approaches allow users to test privacy-focused alternatives while maintaining access to familiar tools during the transition period.
Education and training resources help users understand the features and capabilities of privacy-focused tools, enabling them to take full advantage of available functionality. Community support and documentation provide additional resources for users who encounter challenges or need guidance during the adoption process.
Integration with existing workflows and tools represents an important consideration for users evaluating privacy-focused alternatives. The best privacy-focused AI tools provide compatibility with existing systems and workflows while offering migration tools and support to ease the transition process.
The adoption of privacy-focused AI tools often requires some adjustment of user expectations and workflows, but the long-term benefits of enhanced privacy protection and reduced exposure to tracking and data collection typically justify these initial adaptation requirements. Users who make the transition often report improved peace of mind and greater control over their digital experiences.
Conclusion: The Future of Privacy-Preserving AI
DuckDuckGo, Brave Browser, and Signal represent pioneering examples of how artificial intelligence can be implemented in ways that enhance rather than compromise user privacy. These platforms demonstrate that the choice between AI functionality and privacy protection is a false dichotomy, showing that sophisticated AI capabilities can be delivered while maintaining strict privacy standards and user control over personal data.
The success of these privacy-focused AI tools has broader implications for the technology industry, proving that privacy protection can be a competitive advantage and that users value platforms that respect their privacy and data rights. As awareness of privacy issues continues to grow and regulatory frameworks evolve to better protect user privacy, privacy-focused AI tools are likely to become increasingly important and influential.
The technical innovations and approaches developed by these platforms contribute to the broader field of privacy-preserving technologies, providing proven methods and technologies that benefit the entire technology ecosystem. The future of AI development will likely be increasingly influenced by privacy considerations, with privacy-by-design becoming a standard approach rather than an exceptional practice.
The continued evolution of privacy-focused AI tools promises to deliver even more sophisticated capabilities while maintaining the privacy protections that make these platforms trustworthy and valuable. Users who prioritize privacy and data protection will benefit from continued improvements in functionality, performance, and user experience as these tools mature and expand their capabilities.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional advice regarding privacy tools or cybersecurity practices. The views expressed are based on current understanding of privacy technologies and their implementations. Readers should conduct their own research and consider their specific privacy requirements when selecting and implementing privacy-focused AI tools. The effectiveness of privacy protection may vary depending on specific use cases, implementation details, and evolving technology landscapes.
