The intersection of artificial intelligence and assistive technology has opened unprecedented pathways for individuals with speech impediments to communicate more effectively and participate fully in society. This technological revolution represents a profound shift in how we approach communication challenges, transforming what were once insurmountable barriers into manageable obstacles through innovative AI-powered solutions that understand, interpret, and facilitate human expression in ways previously thought impossible.
Explore the latest AI innovations in assistive technology to stay informed about cutting-edge developments that are reshaping communication accessibility. The evolution of speech impediment AI represents not merely a technological advancement but a fundamental reimagining of how society can better support individuals facing communication challenges through intelligent, adaptive, and personalized technological interventions.
Understanding Speech Impediments and Communication Barriers
Speech impediments encompass a broad spectrum of conditions that affect an individual’s ability to produce clear, fluent, or intelligible speech. These conditions range from developmental disorders such as stuttering and apraxia to acquired conditions resulting from stroke, traumatic brain injury, or neurological diseases like Parkinson’s or ALS. The traditional approach to addressing these challenges has relied heavily on speech therapy, physical interventions, and basic communication aids that often fell short of providing the nuanced, real-time support needed for effective daily communication.
The complexity of speech production involves intricate coordination between respiratory, phonatory, and articulatory systems, making it particularly challenging to develop universal solutions that can accommodate the diverse range of speech impediments. Each individual presents unique patterns of difficulty, whether in articulation clarity, fluency patterns, voice quality, or prosodic features, requiring highly personalized approaches that can adapt to specific needs and preferences while maintaining the natural flow of conversation.
The Revolution of AI-Powered Speech Recognition
Modern artificial intelligence has fundamentally transformed speech recognition capabilities through sophisticated machine learning algorithms that can understand and interpret speech patterns far beyond the capabilities of traditional systems. Advanced neural networks now possess the ability to decode speech signals that may be unclear, interrupted, or characterized by atypical patterns, making communication possible for individuals whose speech was previously incomprehensible to conventional recognition systems.
These AI systems employ deep learning architectures that continuously improve their understanding of individual speech patterns through exposure and training. The technology can learn to recognize the unique characteristics of each user’s speech impediment, whether it involves consonant substitutions, vowel distortions, rhythm irregularities, or prosodic variations. This personalized learning approach enables the system to achieve remarkably high accuracy rates even with severely impaired speech, providing users with reliable communication tools that respond appropriately to their specific speech characteristics.
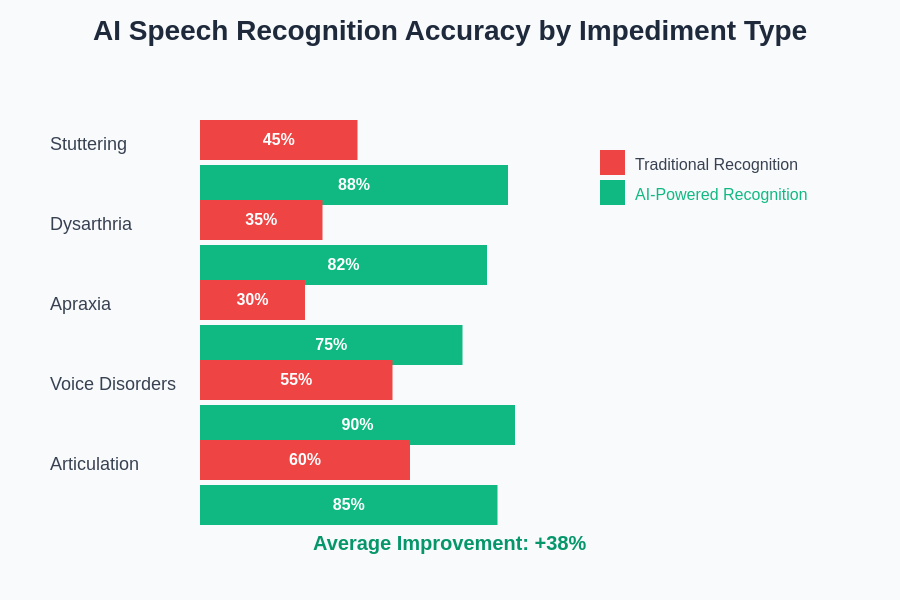
The technological advancement in AI speech recognition has created a dramatic improvement in accuracy and reliability compared to traditional systems. Modern AI-powered solutions demonstrate superior performance across various speech impediment types, enabling more effective communication for users with diverse communication challenges.
Experience advanced AI communication tools through Claude which offers sophisticated language processing capabilities that can support various communication needs and accessibility requirements. The integration of such advanced AI systems into assistive technology represents a significant leap forward in making technology more inclusive and responsive to individual needs.
Real-Time Speech Translation and Enhancement
One of the most transformative applications of AI in speech impediment assistance involves real-time speech translation and enhancement systems that can interpret unclear or fragmented speech and convert it into clear, fluent output. These systems work by analyzing the acoustic patterns, contextual clues, and linguistic structures within impaired speech to reconstruct the intended message with remarkable accuracy and natural fluency.
The technology employs sophisticated natural language processing algorithms that can fill in missing phonemes, correct mispronunciations, and smooth out disfluencies while preserving the speaker’s intended meaning and emotional tone. This capability is particularly valuable for individuals with conditions like dysarthria, where speech may be slow, slurred, or difficult to understand, but the underlying language comprehension and formulation remain intact.
Advanced systems can also provide multiple output modalities, allowing users to communicate through synthesized speech, text display, or even sign language interpretation depending on the communication context and recipient preferences. This flexibility ensures that individuals with speech impediments can participate effectively in various social, educational, and professional environments without being limited by their specific communication challenges.
Predictive Text and Communication Assistance
AI-powered predictive text systems have evolved far beyond simple word completion to become sophisticated communication partners that can anticipate and facilitate complex thought expression. These systems analyze patterns in individual communication styles, vocabulary preferences, and contextual usage to provide intelligent suggestions that align with the user’s intended message while reducing the physical and cognitive effort required for communication.
For individuals with conditions that affect speech planning or execution, such as apraxia or severe stuttering, predictive text can serve as a bridge between thought and expression. The AI can suggest complete phrases, provide alternative expressions for difficult-to-articulate concepts, and even adapt to emotional or contextual nuances that affect communication needs. This technology is particularly valuable in time-sensitive communication situations where traditional speech therapy techniques may be insufficient.
The most advanced predictive systems incorporate emotional intelligence capabilities that can recognize frustration, urgency, or other emotional states that may affect communication attempts. By understanding these contextual factors, the AI can adjust its assistance level, suggestion types, and response timing to provide optimal support without interfering with the natural flow of conversation or the user’s sense of autonomy in communication.
Personalized Speech Therapy and Training
Artificial intelligence has revolutionized speech therapy by enabling highly personalized, data-driven treatment approaches that can adapt in real-time to individual progress and needs. AI-powered therapy systems can analyze speech patterns with precision that far exceeds human perception, identifying subtle improvements or emerging challenges that might be missed in traditional therapy sessions.
These systems provide continuous assessment and feedback, allowing users to practice speech exercises with immediate, objective evaluation of their performance. The AI can detect minute changes in articulation accuracy, fluency patterns, or voice quality, providing detailed feedback that helps users understand their progress and adjust their techniques accordingly. This constant monitoring and adjustment capability accelerates the therapy process while ensuring that treatment remains targeted and effective.
Advanced therapy systems can also generate personalized exercise regimens based on individual speech characteristics, learning preferences, and progress patterns. The AI analyzes which types of exercises produce the best results for each user and automatically adjusts difficulty levels, practice frequency, and focus areas to optimize therapeutic outcomes. This personalized approach ensures that therapy time is used most efficiently while maintaining user engagement and motivation.
Discover comprehensive AI research capabilities with Perplexity for accessing the latest research and developments in speech therapy and assistive technology. The continuous evolution of AI-powered therapy systems represents a significant advancement in making high-quality speech therapy more accessible and effective for individuals worldwide.
Voice Banking and Synthetic Speech Generation
Voice banking technology represents one of the most emotionally significant applications of AI in speech impediment assistance, allowing individuals to preserve their natural voice before progressive conditions lead to complete speech loss. Advanced AI systems can now create highly realistic synthetic voices from relatively small speech samples, enabling individuals to maintain their vocal identity even as their natural speech capabilities decline.
The process involves sophisticated machine learning algorithms that analyze the unique characteristics of an individual’s voice, including pitch patterns, resonance qualities, pronunciation tendencies, and prosodic features. This analysis enables the creation of synthetic speech that captures not just the sound of the person’s voice but also their natural speaking patterns and emotional expressiveness. For individuals facing conditions like ALS or Parkinson’s disease, this technology provides a way to maintain their communicative identity and emotional connection with family and friends.
Modern voice banking systems can work with limited speech samples and can even extrapolate from partially impaired speech to reconstruct the individual’s original voice characteristics. The AI can compensate for existing speech difficulties to create a clear, natural-sounding synthetic voice that represents the person’s true vocal identity. This capability is particularly valuable for individuals whose speech has already begun to deteriorate, as it allows them to bank their voice even after onset of their condition.
Augmentative and Alternative Communication Enhancement
AI has transformed traditional augmentative and alternative communication devices from simple picture-based systems into sophisticated, context-aware communication platforms that can understand and adapt to complex communication needs. Modern AAC devices powered by AI can learn individual communication patterns, predict likely message content based on context, and provide intelligent organization of vocabulary and phrases to facilitate faster, more natural communication.
These enhanced systems can analyze communication contexts to automatically adjust available vocabulary, suggest relevant phrases, and even modify interface layouts to match specific communication situations. For example, the system might present different vocabulary sets and communication options when the user is in a medical setting compared to a social environment, ensuring that the most relevant communication tools are readily accessible.
Advanced AAC systems also incorporate natural language generation capabilities that can help users express complex ideas more effectively. Rather than requiring users to construct messages word by word, the AI can help transform simple inputs into more sophisticated, grammatically correct, and contextually appropriate expressions. This capability is particularly valuable for individuals with cognitive-communication disorders who may struggle with language formulation but retain clear thinking and intention.
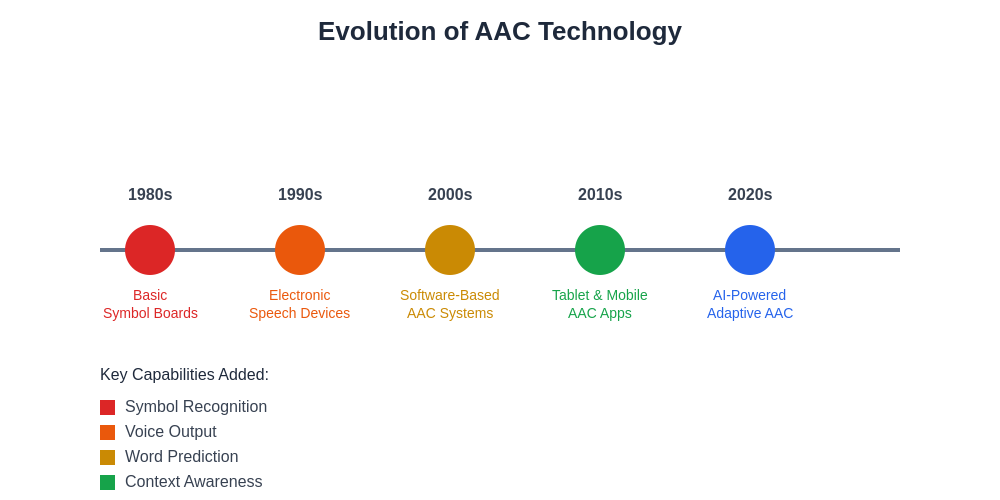
The evolution of augmentative and alternative communication technology demonstrates significant advancement from basic symbol-based systems to sophisticated AI-powered platforms. Modern AAC devices offer unprecedented capabilities for personalized, context-aware communication support that adapts to individual needs and preferences.
Environmental Adaptation and Context Awareness
Modern AI-powered communication aids possess sophisticated environmental awareness capabilities that can automatically adjust to different acoustic environments, social contexts, and communication demands. These systems can recognize background noise patterns, adjust sensitivity levels, and modify processing algorithms to maintain optimal performance across diverse settings from quiet therapy rooms to bustling restaurants or outdoor environments.
Context awareness extends beyond acoustic considerations to include social and situational factors that affect communication needs. The AI can recognize different types of communication partners, adjust communication style and complexity accordingly, and even provide suggestions for appropriate social communication behaviors. This capability is particularly valuable for individuals with autism spectrum disorders or social communication challenges who may benefit from contextual guidance and support.
Advanced systems can also learn from user feedback and environmental cues to continuously improve their contextual understanding and response appropriateness. The AI develops increasingly sophisticated models of when and how to provide assistance, ensuring that support is available when needed while respecting user autonomy and natural communication preferences.
Integration with Smart Home and IoT Technologies
The integration of speech impediment AI with smart home technologies and Internet of Things devices has created new possibilities for independent living and environmental control. Individuals with speech difficulties can now control their living environments through AI systems that understand their specific speech patterns and can interpret even unclear or fragmented commands to operate lights, temperature controls, security systems, and entertainment devices.
These integrated systems learn to recognize the user’s specific way of pronouncing device names, commands, and preferences, enabling reliable voice control even when traditional voice assistants fail to understand impaired speech. The AI can also provide alternative input methods such as gesture recognition, eye tracking, or switch activation while maintaining the convenience and naturalness of voice interaction when possible.
Advanced integration extends to emergency communication systems that can recognize distress signals, unusual speech patterns, or communication attempts that indicate urgent needs. These systems can automatically contact emergency services, family members, or caregivers while providing clear information about the individual’s communication challenges and specific needs.
Emotional Expression and Prosodic Enhancement
One of the most sophisticated developments in speech impediment AI involves the recognition and enhancement of emotional expression and prosodic features in communication. Advanced systems can detect emotional content in speech attempts and ensure that synthetic or enhanced output maintains the speaker’s intended emotional tone, preserving the richness and authenticity of human communication.
The AI analyzes various acoustic features including pitch variation, rhythm patterns, stress placement, and vocal quality to understand the emotional and prosodic intentions behind speech attempts. This analysis enables the system to generate output that reflects not just the semantic content of the message but also its emotional significance and communicative intent. For individuals whose speech impediments affect prosodic features, this capability ensures that their full communicative expression is preserved and conveyed to listeners.
Emotional intelligence in these systems extends to recognizing frustration, fatigue, or other states that may affect communication attempts. The AI can adjust its assistance level and interaction style to provide appropriate support without overwhelming the user or interfering with their natural communication rhythms. This sensitivity to emotional states helps maintain user engagement and reduces the stress often associated with communication difficulties.
Privacy, Security, and Ethical Considerations
The development and deployment of AI-powered speech impediment assistance technology raises important considerations regarding privacy, security, and ethical use of highly personal communication data. These systems necessarily collect and analyze intimate details of an individual’s speech patterns, communication attempts, and often personal conversation content, requiring robust protection measures and transparent data handling practices.
Advanced privacy protection measures include local processing capabilities that minimize data transmission, encryption of all communication data, and user-controlled data retention and deletion policies. Many systems now offer edge computing solutions that perform AI processing directly on user devices, ensuring that sensitive speech data never leaves the individual’s control while still providing sophisticated AI assistance.
Ethical considerations extend to ensuring that AI assistance enhances rather than replaces human communication skills and that users maintain agency and choice in how they communicate. The technology should empower individuals to communicate more effectively while respecting their preferences for natural speech development and therapeutic goals. This balance requires careful design and implementation that prioritizes user autonomy and individual communication preferences.
Future Developments and Emerging Technologies
The future of speech impediment AI holds promise for even more sophisticated and seamlessly integrated communication support through emerging technologies including brain-computer interfaces, advanced sensor integration, and quantum computing applications. Brain-computer interface technology may eventually enable direct neural communication that bypasses damaged speech production systems entirely while maintaining the user’s natural thought-to-communication flow.
Advanced sensor integration will likely include more sophisticated biometric monitoring that can predict communication difficulties before they occur, enabling proactive assistance and support. Wearable devices equipped with AI processing capabilities will provide continuous communication support that adapts seamlessly to changing needs throughout the day while remaining unobtrusive and socially acceptable.
The convergence of multiple AI technologies including computer vision, natural language processing, and robotic assistance will create comprehensive communication ecosystems that support all aspects of human interaction. These integrated systems will understand not just speech attempts but also gesture, facial expression, and contextual cues to provide holistic communication support that enhances every aspect of human expression and connection.
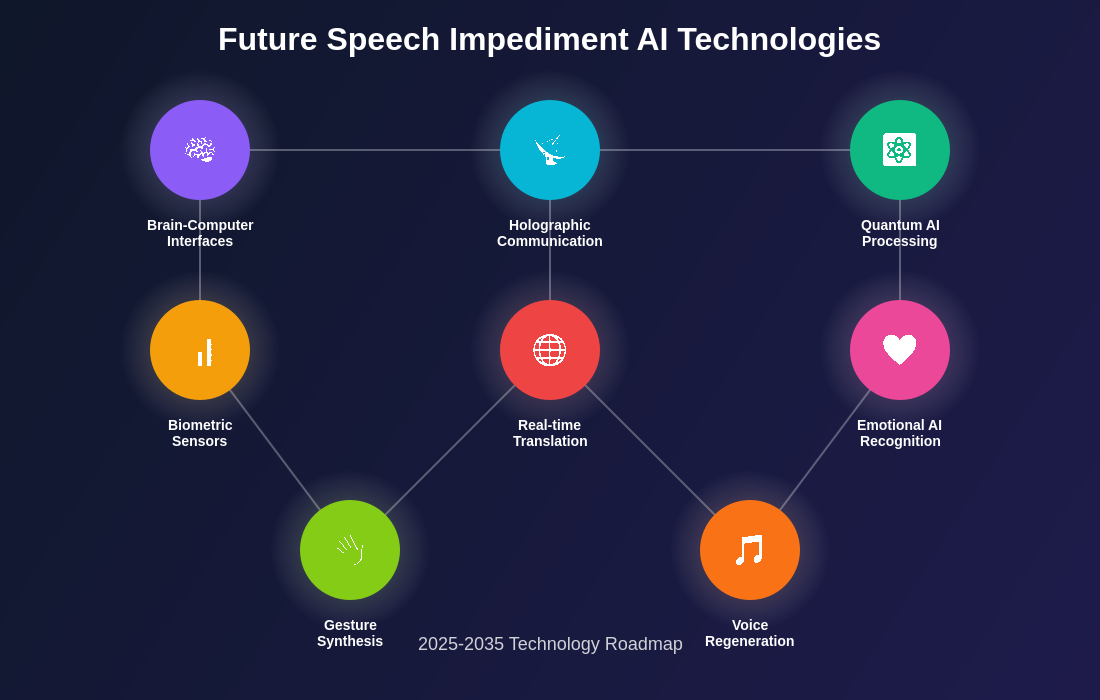
The roadmap for future speech impediment AI technologies shows promising developments across multiple technological domains. From brain-computer interfaces to holographic communication aids, emerging technologies will provide unprecedented support for individuals with communication challenges while maintaining natural human expression and interaction.
The continued advancement of AI-powered assistive technology represents a fundamental shift toward a more inclusive society where communication barriers become opportunities for technological innovation and human connection. As these technologies continue to evolve, they promise to unlock new possibilities for human expression, social participation, and personal fulfillment for individuals with speech impediments while contributing to our broader understanding of communication, accessibility, and human potential.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. The information presented is based on current understanding of AI technologies and their applications in assistive communication. Individuals considering AI-powered assistive technology should consult with qualified speech-language pathologists, medical professionals, and assistive technology specialists to determine appropriate solutions for their specific needs. The effectiveness of AI assistance may vary depending on individual conditions, severity of speech impediments, and personal communication goals.
