The landscape of educational assessment has been fundamentally transformed by the integration of artificial intelligence technologies, with two industry giants leading this revolutionary change: Educational Testing Service (ETS) and Pearson Education. These organizations have developed sophisticated automated scoring systems that promise to enhance the accuracy, efficiency, and scalability of student evaluations while addressing the growing demands of modern educational institutions worldwide.
Discover the latest AI innovations in education to understand how automated assessment technologies are reshaping traditional evaluation methods and creating new opportunities for personalized learning experiences. The competition between ETS and Pearson in the automated scoring arena represents more than just technological advancement; it embodies a fundamental shift toward data-driven educational decision-making that could redefine how academic achievement is measured and understood.
The Evolution of Automated Assessment Technology
The journey toward automated scoring began decades ago with simple optical mark recognition systems, but the integration of artificial intelligence has elevated these capabilities to unprecedented levels of sophistication. Educational Testing Service, established in 1947, has leveraged its extensive experience in standardized testing to develop cutting-edge AI systems that can evaluate complex written responses with remarkable accuracy. Meanwhile, Pearson, with its global reach and comprehensive educational portfolio, has invested heavily in machine learning algorithms that promise to revolutionize how educational content is delivered and assessed.
The technological foundation of modern automated scoring systems relies on natural language processing, machine learning algorithms, and sophisticated statistical models that can analyze student responses across multiple dimensions simultaneously. These systems evaluate not only factual accuracy but also reasoning processes, writing quality, creativity, and critical thinking skills that were previously assessable only through human evaluation. The advancement of these technologies has created opportunities for more frequent, comprehensive, and consistent assessment practices that can provide immediate feedback to both students and educators.
ETS Automated Scoring: The Pioneer’s Approach
Educational Testing Service has established itself as a pioneer in automated scoring through its development of the e-rater scoring engine, which has been continuously refined over more than two decades of research and implementation. The e-rater system employs sophisticated natural language processing techniques to evaluate written responses across multiple dimensions, including grammar, usage, mechanics, style, organization, development, and vocabulary usage. This comprehensive approach ensures that automated scores align closely with human evaluator assessments while providing consistent and reliable results across large-scale testing programs.
Experience advanced AI capabilities with Claude to understand how sophisticated language models can enhance educational assessment and provide detailed feedback on student performance. The ETS approach emphasizes the importance of construct validity, ensuring that automated scoring systems measure the same underlying skills and knowledge that traditional assessments are designed to evaluate. This focus on maintaining assessment integrity while leveraging technological efficiency has made ETS a trusted partner for major testing programs including the GRE, TOEFL, and Praxis series.
The e-rater system’s architecture incorporates multiple scoring models that work in concert to provide holistic evaluation of student responses. Feature extraction algorithms identify linguistic and structural elements within written texts, while machine learning models trained on thousands of human-scored responses provide scoring predictions that demonstrate high correlation with expert human evaluators. The system’s ability to process responses in real-time while maintaining scoring accuracy has enabled ETS to offer immediate score reporting for many of its assessments, significantly reducing the waiting time that has traditionally been associated with standardized testing.
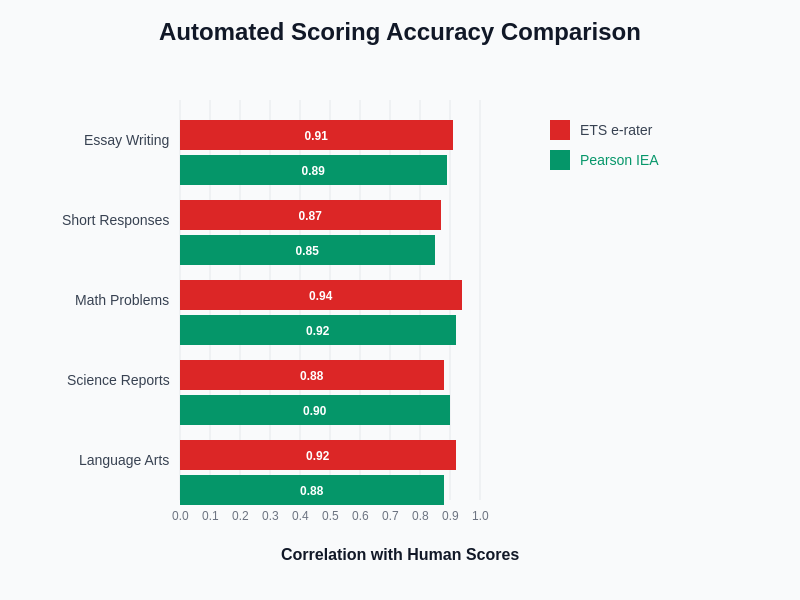
The empirical evidence demonstrates that both ETS and Pearson automated scoring systems achieve remarkable accuracy levels across different assessment types, with correlation coefficients consistently exceeding 0.85 when compared to expert human evaluators. These performance metrics validate the reliability of automated scoring technologies for high-stakes educational assessments.
Pearson’s Intelligent Essay Assessor: Innovation in Action
Pearson Education has developed the Intelligent Essay Assessor (IEA), a sophisticated automated scoring system that leverages latent semantic analysis and machine learning techniques to evaluate written content. The IEA system focuses on content analysis, examining the semantic meaning and conceptual understanding demonstrated in student responses rather than relying solely on surface-level linguistic features. This approach enables the system to assess deeper learning outcomes and provide more nuanced feedback about student comprehension and analytical thinking abilities.
The technological foundation of Pearson’s automated scoring system incorporates advanced algorithms that can identify patterns in student writing that correlate with specific learning objectives and performance standards. The system’s ability to analyze content across multiple subject areas and grade levels makes it particularly valuable for educational institutions seeking comprehensive assessment solutions that can adapt to diverse curricular requirements. Pearson’s extensive database of scored responses provides the training data necessary for machine learning models to achieve high levels of accuracy and reliability across different assessment contexts.
Pearson’s approach to automated scoring emphasizes the integration of assessment data with broader educational analytics platforms, enabling educators to gain deeper insights into student learning patterns and instructional effectiveness. The system’s capacity to provide detailed diagnostic feedback helps teachers identify specific areas where students may need additional support while also highlighting strengths that can be further developed. This data-driven approach to educational assessment aligns with contemporary trends toward personalized learning and evidence-based instructional decision-making.
Comparative Analysis of Scoring Accuracy and Reliability
Both ETS and Pearson have invested extensively in validating their automated scoring systems through rigorous research studies that compare machine-generated scores with expert human evaluations. ETS reports correlation coefficients between e-rater scores and human scores ranging from 0.87 to 0.94 across different assessment types, indicating strong agreement between automated and human evaluation methods. These correlation levels demonstrate that automated scoring can provide reliable assessments that maintain the validity and integrity expected from high-stakes testing programs.
Pearson’s Intelligent Essay Assessor has demonstrated similar levels of accuracy, with correlation coefficients typically ranging from 0.85 to 0.92 when compared to trained human raters. The consistency of these results across different subject areas and student populations suggests that both systems have achieved sufficient reliability for practical implementation in educational settings. However, the specific strengths of each system may vary depending on the type of assessment content and the particular skills being evaluated.
Enhance your research capabilities with Perplexity to access comprehensive data about educational assessment technologies and their comparative performance across different implementation contexts. The reliability of automated scoring systems extends beyond simple correlation with human scores to include considerations of consistency across different testing occasions, fairness across diverse student populations, and resistance to gaming or manipulation strategies that students might employ to artificially inflate their scores.
Implementation Strategies and Scalability Considerations
The practical implementation of automated scoring systems requires careful consideration of technical infrastructure, staff training, security protocols, and integration with existing educational technology systems. ETS has developed comprehensive implementation frameworks that support large-scale testing programs while maintaining the security and integrity necessary for high-stakes assessments. The organization’s experience with major testing programs has provided valuable insights into the operational requirements for successful automated scoring deployment.
Pearson’s implementation approach emphasizes flexibility and customization, enabling educational institutions to adapt automated scoring systems to their specific assessment needs and curricular requirements. The company’s global presence and diverse educational partnerships have informed the development of implementation strategies that can accommodate different educational contexts, regulatory environments, and technological capabilities. This adaptability has made Pearson’s automated scoring solutions attractive to institutions seeking tailored assessment approaches.
The scalability advantages of automated scoring systems become particularly evident when considering the volume of assessments processed by modern educational institutions. Both ETS and Pearson systems can process thousands of responses simultaneously while maintaining consistent scoring quality, enabling educational organizations to conduct more frequent assessments without proportional increases in human resource requirements. This scalability potential has significant implications for the future of educational assessment and the ability of institutions to provide timely feedback to students and educators.
Technical Architecture and Machine Learning Approaches
The underlying technical architectures of ETS and Pearson automated scoring systems reflect different philosophical approaches to artificial intelligence implementation in educational assessment. ETS employs a hybrid approach that combines rule-based linguistic analysis with machine learning algorithms, enabling the system to leverage both expert knowledge about language structure and data-driven insights about scoring patterns. This combination provides robustness and interpretability that are crucial for maintaining stakeholder confidence in automated assessment results.
Pearson’s technical approach emphasizes deep learning and neural network architectures that can automatically discover relevant features within student responses without requiring extensive manual feature engineering. This approach enables the system to adapt more readily to new assessment contexts and potentially identify subtle patterns that might not be apparent through traditional analytical methods. The trade-off between interpretability and adaptive capability represents a fundamental consideration in automated scoring system design.
Both organizations continue to invest in research and development aimed at improving the accuracy, efficiency, and fairness of their automated scoring systems. Recent advances in transformer-based language models, attention mechanisms, and multi-modal analysis techniques offer new opportunities for enhancing automated assessment capabilities while addressing persistent challenges related to bias detection, construct validity, and student privacy protection.
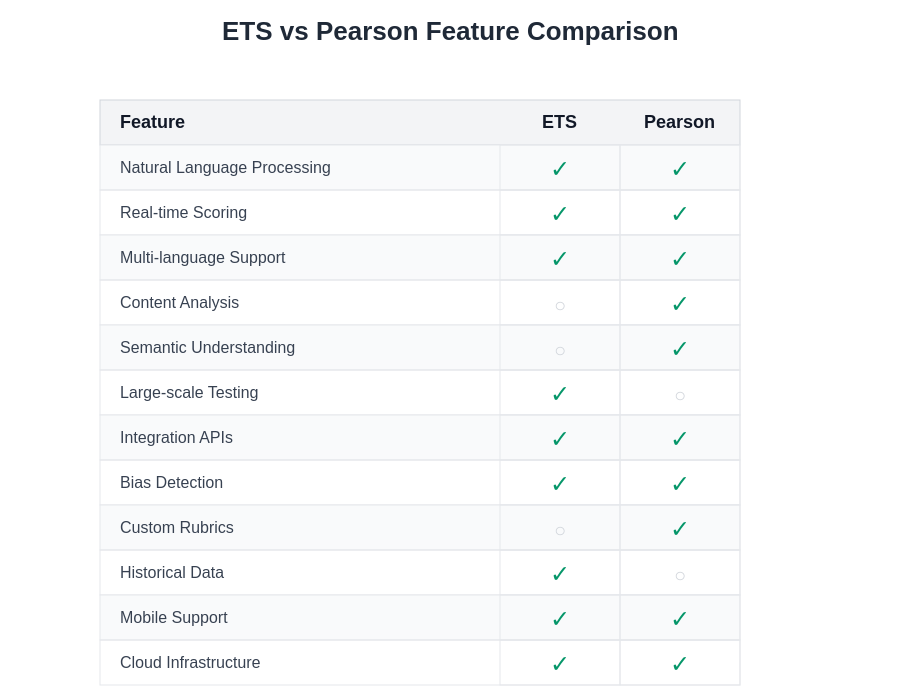
The comprehensive feature analysis reveals distinct strengths and focus areas for each platform, with ETS demonstrating particular excellence in large-scale testing infrastructure and historical data management, while Pearson shows superior capabilities in content analysis and semantic understanding technologies.
Addressing Bias and Fairness in Automated Scoring
The implementation of automated scoring systems in educational contexts raises important questions about fairness and potential bias that could disproportionately affect certain student populations. Both ETS and Pearson have developed comprehensive approaches to bias detection and mitigation that involve ongoing monitoring of scoring patterns across different demographic groups and assessment contexts. These efforts are essential for maintaining the credibility and ethical acceptability of automated assessment technologies.
ETS has established detailed protocols for evaluating potential bias in e-rater scores through statistical analysis of scoring differences across various student subgroups. The organization’s research has focused on identifying and addressing factors that might contribute to unfair scoring outcomes while maintaining the validity and reliability of assessment results. This ongoing commitment to fairness evaluation has become a model for responsible AI implementation in educational assessment.
Pearson’s approach to bias mitigation incorporates proactive measures designed to identify and correct potential sources of unfairness during the system development process rather than relying solely on post-implementation monitoring. The company’s research initiatives have explored the intersection of automated scoring technology with broader questions of educational equity and access, contributing to a growing body of knowledge about responsible AI implementation in educational contexts.
Integration with Learning Management Systems
The practical value of automated scoring systems depends significantly on their ability to integrate seamlessly with existing educational technology infrastructure, particularly learning management systems and student information systems. ETS has developed application programming interfaces and integration tools that facilitate the incorporation of automated scoring capabilities into various educational platforms while maintaining data security and privacy protections required for student information.
Pearson’s integration approach emphasizes interoperability and standards compliance, enabling automated scoring systems to work effectively within diverse technological environments. The company’s experience with comprehensive educational technology solutions has informed the development of integration frameworks that can accommodate different institutional requirements and technical constraints while providing consistent functionality and user experiences.
The integration of automated scoring with learning analytics platforms creates opportunities for more sophisticated analysis of student learning patterns and instructional effectiveness. Both ETS and Pearson systems can provide detailed data about student performance that can be combined with other educational metrics to support evidence-based decision-making at individual, classroom, and institutional levels.
Cost-Benefit Analysis and Return on Investment
Educational institutions considering the implementation of automated scoring systems must carefully evaluate the financial implications and potential return on investment associated with these technologies. The initial costs of automated scoring implementation include licensing fees, technical infrastructure, staff training, and system integration expenses that can represent significant financial commitments for educational organizations with limited budgets.
ETS pricing models typically reflect the organization’s focus on large-scale testing programs and institutional partnerships, with cost structures that can provide economies of scale for organizations processing large volumes of assessments. The company’s established reputation and extensive validation research may justify premium pricing for institutions that prioritize reliability and credibility in their assessment programs.
Pearson’s pricing approach emphasizes flexibility and customization options that can accommodate different institutional needs and budget constraints. The company’s comprehensive educational technology portfolio enables bundled solutions that may provide cost advantages for institutions seeking integrated educational technology platforms rather than standalone automated scoring capabilities.
The long-term financial benefits of automated scoring systems include reduced human resource requirements for assessment processing, faster turnaround times for score reporting, increased assessment frequency capabilities, and improved consistency in evaluation standards. These benefits must be weighed against ongoing licensing costs, technical maintenance requirements, and the need for continued staff training and system updates.
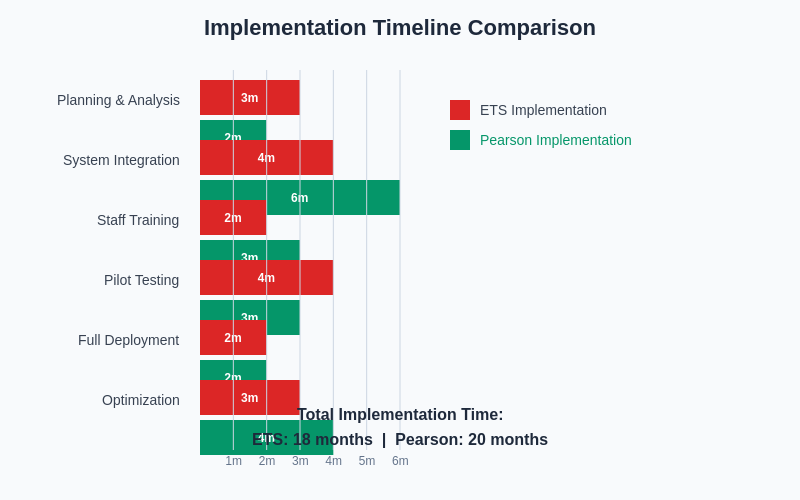
The implementation timeline analysis demonstrates significant differences in deployment strategies, with ETS focusing on streamlined integration processes while Pearson emphasizes comprehensive customization and optimization phases that may require longer initial investment periods but offer greater long-term flexibility.
Quality Assurance and Validation Processes
Both ETS and Pearson have established comprehensive quality assurance frameworks that ensure automated scoring systems maintain high standards of accuracy and reliability over time. These processes involve continuous monitoring of system performance, regular validation studies comparing automated scores with human evaluations, and ongoing refinement of scoring algorithms based on new data and research insights.
ETS quality assurance protocols include detailed statistical analysis of scoring patterns, outlier detection procedures, and regular recalibration of scoring models to maintain consistency with established performance standards. The organization’s extensive experience with high-stakes testing has informed the development of quality assurance procedures that can identify and address potential issues before they affect assessment outcomes.
Pearson’s quality assurance approach incorporates automated monitoring systems that can detect anomalies in scoring patterns and alert administrators to potential issues requiring investigation. The company’s global operations and diverse client base have necessitated the development of quality assurance procedures that can accommodate different regulatory requirements and performance expectations across various educational contexts.
Future Developments and Emerging Technologies
The future of automated scoring in educational assessment will likely be shaped by continued advances in artificial intelligence technology, including improvements in natural language processing, multimodal analysis capabilities, and adaptive learning algorithms. Both ETS and Pearson are actively investing in research and development initiatives aimed at expanding the capabilities and applications of automated scoring systems.
Emerging technologies such as speech recognition and analysis offer new opportunities for automated assessment of oral communication skills, presentation abilities, and language proficiency that have traditionally required human evaluation. The integration of these capabilities with existing automated scoring systems could provide more comprehensive assessment solutions that address a broader range of learning objectives and skill areas.
The development of more sophisticated AI models also raises questions about the balance between automation and human judgment in educational assessment. Future automated scoring systems may incorporate hybrid approaches that leverage both artificial intelligence capabilities and human expertise to provide more nuanced and contextually appropriate evaluation of student performance while maintaining the efficiency and scalability advantages of automated systems.
Implications for Educational Practice and Policy
The widespread adoption of automated scoring systems has significant implications for educational practice and policy development at institutional, regional, and national levels. The availability of more frequent and detailed assessment data creates opportunities for more responsive instructional practices and data-driven educational decision-making, but also raises questions about the appropriate role of assessment in educational systems and the potential for over-reliance on quantitative measures of student achievement.
Educational policymakers must consider how automated scoring technologies align with broader educational goals and values while ensuring that these systems support rather than constrain innovative teaching and learning practices. The implementation of automated scoring systems also requires consideration of teacher training needs, student privacy protections, and the maintenance of educational equity across diverse student populations.
The competitive landscape between ETS and Pearson in automated scoring reflects broader trends in educational technology toward data-driven solutions and artificial intelligence implementation. The continued evolution of these technologies will require ongoing dialogue between technology developers, educational practitioners, and policy makers to ensure that automated assessment systems serve the best interests of students and educational institutions while maintaining the integrity and validity that are essential for effective educational evaluation.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional advice. The information presented is based on publicly available data and research about automated scoring systems. Educational institutions should conduct their own thorough evaluation of automated scoring technologies and consult with appropriate experts before making implementation decisions. The effectiveness and suitability of automated scoring systems may vary depending on specific institutional needs, student populations, and assessment contexts.