The modern warehouse has evolved into a sophisticated ecosystem where artificial intelligence and robotics converge to create unprecedented levels of efficiency, accuracy, and speed in order fulfillment. At the forefront of this technological revolution stand two industry giants, Amazon and Ocado, each pioneering distinct yet revolutionary approaches to automated warehouse operations that have fundamentally transformed the landscape of e-commerce logistics and grocery delivery services.
Explore the latest developments in AI and robotics to understand how cutting-edge technologies are reshaping industries beyond traditional expectations. The convergence of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced robotics has created warehouse environments that operate with precision and efficiency that surpasses human capabilities while maintaining the flexibility to adapt to changing market demands and consumer expectations.
The Evolution of Warehouse Automation
The journey toward fully automated warehouse systems represents decades of technological advancement, beginning with simple conveyor belt systems and evolving into complex networks of interconnected robots, artificial intelligence algorithms, and sophisticated inventory management systems. Amazon and Ocado have each taken distinctly different paths toward achieving operational excellence, with Amazon focusing on scaling existing fulfillment paradigms through robotic enhancement, while Ocado has reimagined the entire fulfillment process from the ground up with robotics as the foundational element.
The transformation from traditional warehouse operations to AI-driven fulfillment centers has required fundamental reimagining of spatial design, workflow optimization, and human-robot collaboration. These changes have not only improved operational metrics but have also redefined the economics of last-mile delivery and consumer expectations for order fulfillment speed and accuracy. The competitive advantage gained through superior warehouse automation has become a critical differentiator in the highly competitive e-commerce and grocery delivery markets.
Amazon’s Robotic Fulfillment Revolution
Amazon’s approach to warehouse robotics represents an evolutionary enhancement of traditional fulfillment center operations, leveraging the company’s massive scale and diverse product catalog to drive innovation in robotic systems. The integration of Kiva robots, now known as Amazon Robotics drive units, has fundamentally transformed how products move through Amazon’s fulfillment centers, creating a symbiotic relationship between human workers and robotic systems that maximizes the strengths of both.
The Amazon robotics ecosystem encompasses multiple generations of autonomous mobile robots that transport entire inventory pods directly to human workers, eliminating the time-consuming process of workers traversing vast warehouse floors to locate individual items. This pod-to-person methodology has dramatically reduced the physical demands on human workers while simultaneously increasing picking accuracy and throughput rates. The system’s intelligence lies not only in the robots themselves but in the sophisticated algorithms that orchestrate the movement of thousands of robots simultaneously, optimizing pathways, managing traffic flow, and predicting inventory needs based on historical data and real-time demand patterns.
Amazon’s robotic systems have evolved to incorporate advanced computer vision, machine learning algorithms for predictive maintenance, and sophisticated coordination protocols that enable seamless operation even as the robot fleet scales to thousands of units within a single facility. The company’s investment in robotic automation extends beyond basic movement and picking operations to include packaging automation, sorting systems, and even experimental drone delivery programs that represent the next frontier in fulfillment automation.
Discover advanced AI capabilities with Claude for analyzing complex logistics optimization problems and developing innovative solutions that can transform operational efficiency across various industries. The integration of advanced AI systems into warehouse operations requires sophisticated analytical capabilities that can process vast amounts of real-time data and make instantaneous decisions that optimize overall system performance.
Ocado’s Grid-Based Innovation Paradigm
Ocado’s approach to warehouse automation represents a fundamental reimagining of fulfillment center design, built around a revolutionary grid-based system that eliminates traditional warehouse aisles and shelving in favor of a three-dimensional cube structure where robots operate on a sophisticated grid network above stacked product containers. This innovative design philosophy has created what is arguably the most advanced automated grocery fulfillment system in the world, capable of processing thousands of orders simultaneously with minimal human intervention.
The Ocado Smart Platform operates on principles of vertical integration and modular scalability, where hundreds of robots move simultaneously across a grid measuring hundreds of meters in each direction, accessing products stored in vertical stacks beneath the grid surface. Each robot is equipped with advanced sensors, wireless communication systems, and precision handling mechanisms that enable them to collaborate seamlessly while avoiding collisions and optimizing retrieval sequences based on order priorities and product characteristics.
The sophistication of Ocado’s system extends beyond the physical robotics to encompass advanced machine learning algorithms that continuously optimize robot routing, predict maintenance requirements, and adapt to changing order patterns and seasonal variations in product demand. The system’s artificial intelligence components can process millions of possible robot movements per second, ensuring optimal coordination while maintaining the flexibility to handle unexpected situations such as robot maintenance or system modifications.
Ocado’s innovation extends to the integration of advanced computer vision systems that enable robots to identify and handle products with varying shapes, sizes, and fragility requirements. The system’s ability to process complex grocery orders containing everything from delicate fruits to heavy bottles represents a significant technological achievement that has positioned Ocado as a leader in automated grocery fulfillment technology.
Technological Infrastructure and AI Integration
The technological foundations underlying both Amazon’s and Ocado’s warehouse automation systems represent some of the most sophisticated applications of artificial intelligence and robotics in commercial operations. These systems require seamless integration of hardware and software components operating at unprecedented scales, with real-time coordination of thousands of moving parts while maintaining operational reliability that meets consumer expectations for order accuracy and delivery timing.
Amazon’s technological infrastructure leverages the company’s extensive cloud computing capabilities through Amazon Web Services, creating a integrated ecosystem where warehouse operations benefit from the same technological foundations that power the company’s e-commerce platform. This integration enables sophisticated predictive analytics that can anticipate demand patterns, optimize inventory placement, and coordinate fulfillment operations across multiple facilities to minimize delivery times and transportation costs.
The machine learning algorithms powering Amazon’s robotic systems continuously analyze operational data to identify optimization opportunities, predict equipment maintenance needs, and adapt to changing operational conditions. These systems process millions of data points daily, including robot movement patterns, order fulfillment times, error rates, and energy consumption metrics, using this information to continuously refine operational efficiency and identify areas for further automation.
Ocado’s technological architecture is built around a proprietary software platform that manages every aspect of warehouse operations, from initial order processing through final packaging and dispatch. The system’s artificial intelligence components utilize advanced algorithms for route optimization, load balancing, and predictive maintenance that ensure optimal performance even as operational complexity increases with facility size and order volume.
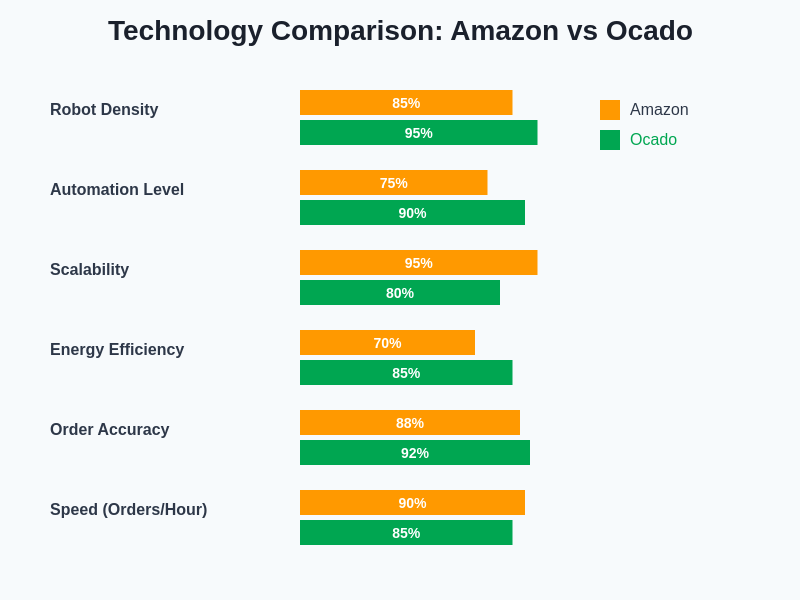
The technological sophistication of modern warehouse robotics systems represents a convergence of multiple advanced technologies working in harmony to achieve operational excellence that exceeds human capabilities while maintaining the flexibility required for complex fulfillment operations.
Operational Efficiency and Performance Metrics
The measurement of operational efficiency in automated warehouse systems encompasses multiple dimensions of performance, including order processing speed, accuracy rates, energy consumption, maintenance requirements, and scalability characteristics. Both Amazon and Ocado have achieved remarkable improvements in these metrics compared to traditional warehouse operations, though their different approaches have resulted in distinct performance profiles that reflect their unique operational philosophies and target markets.
Amazon’s robotic fulfillment centers have demonstrated significant improvements in picking productivity, with robots enabling human workers to process orders at rates that substantially exceed traditional warehouse operations. The company’s systems have achieved impressive accuracy rates while handling the complexity of fulfilling orders containing diverse product types, sizes, and packaging requirements. The integration of robotics has also improved workplace safety by reducing the physical demands on human workers and minimizing the risk of injuries associated with traditional warehouse operations.
The scalability of Amazon’s robotic systems has been demonstrated through deployment across hundreds of fulfillment centers worldwide, with the flexibility to adapt to different facility sizes, product categories, and operational requirements. This scalability has enabled Amazon to maintain consistent service levels while expanding into new geographic markets and product categories, demonstrating the robustness and adaptability of their technological approach.
Ocado’s performance metrics reflect the company’s focus on grocery fulfillment, where operational requirements include careful handling of perishable products, temperature-controlled storage, and complex order assembly that may include hundreds of individual items with varying storage and handling requirements. The company’s automated systems have achieved industry-leading accuracy rates while processing orders with remarkable speed and consistency.
The energy efficiency of Ocado’s grid-based system represents a significant advantage over traditional warehouse operations, with the company’s robots designed for optimal energy consumption and the grid structure eliminating the need for traditional warehouse lighting and climate control systems in robot-operated areas. This efficiency contributes to the system’s overall environmental sustainability while reducing operational costs.
Enhance your research capabilities with Perplexity to access comprehensive information about emerging technologies and industry trends that are shaping the future of automated logistics and supply chain management. The rapidly evolving landscape of warehouse automation requires continuous monitoring of technological developments and competitive innovations.
Human-Robot Collaboration Models
The integration of robotics into warehouse operations has not eliminated the need for human workers but has instead transformed their roles and created new models of human-robot collaboration that leverage the unique strengths of both humans and machines. Amazon and Ocado have developed distinct approaches to this collaboration, reflecting their different operational philosophies and the specific requirements of their respective markets and product categories.
Amazon’s fulfillment centers exemplify a collaborative model where robots handle the physically demanding tasks of transporting inventory while humans focus on activities requiring dexterity, decision-making, and quality control. This division of labor has improved job satisfaction by eliminating the most physically demanding aspects of warehouse work while creating opportunities for workers to develop technical skills related to robotic system operation and maintenance.
The training and development programs implemented by Amazon recognize that successful human-robot collaboration requires workers who understand the capabilities and limitations of robotic systems while possessing the flexibility to adapt to evolving technological capabilities. The company has invested significantly in workforce development programs that prepare employees for the changing nature of warehouse work and create career advancement opportunities within the automated fulfillment environment.
Ocado’s approach to human-robot collaboration reflects the company’s highly automated operational model, where human workers primarily focus on exception handling, quality assurance, and system monitoring activities. The reduced need for human intervention in routine operations has enabled Ocado to maintain high operational efficiency while providing employees with opportunities to develop expertise in advanced technological systems.
The evolution of human-robot collaboration in warehouse environments continues to advance as artificial intelligence systems become more sophisticated and robotic capabilities expand. Both companies are exploring applications of artificial intelligence that could further enhance the effectiveness of human-robot teams while maintaining the human oversight and decision-making capabilities that remain essential for complex operational environments.
Economic Impact and Cost Optimization
The economic implications of advanced warehouse robotics extend far beyond the immediate operational improvements achieved through automation, encompassing fundamental changes in the economics of e-commerce fulfillment, employment patterns, and competitive dynamics within the retail and logistics industries. The substantial capital investments required for robotic warehouse systems must be evaluated against long-term operational benefits, scalability advantages, and competitive positioning considerations.
Amazon’s massive scale has enabled the company to amortize the costs of robotic system development and deployment across hundreds of facilities, creating economic advantages that may be difficult for smaller competitors to replicate. The operational cost savings achieved through robotics have contributed to Amazon’s ability to offer competitive shipping options while maintaining profitability, creating a virtuous cycle where improved operational efficiency enables further investment in technological advancement.
The labor cost implications of warehouse robotics are complex, with automation reducing the number of workers required for traditional picking and packing operations while creating new roles in robot maintenance, system monitoring, and exception handling. The net economic impact varies by geographic location, labor market conditions, and the specific implementation approach chosen by each company.
Ocado’s business model demonstrates how advanced warehouse automation can create new revenue opportunities through technology licensing and consulting services. The company’s Ocado Smart Platform has been licensed to retailers worldwide, creating a technology business that leverages the innovations developed for Ocado’s own operations while generating additional revenue streams that help justify the substantial research and development investments required for continued innovation.
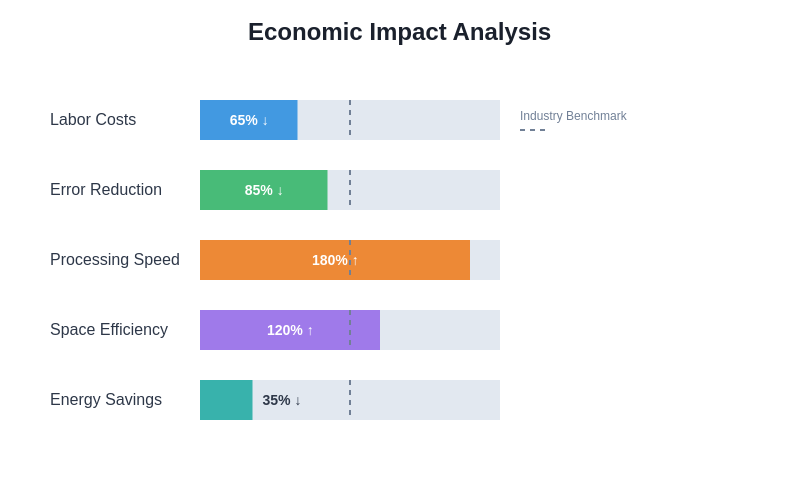
The long-term economic benefits of warehouse robotics include improved inventory management, reduced error rates, enhanced customer satisfaction, and the ability to operate facilities in locations where traditional warehouse operations might not be economically viable due to labor availability or cost considerations.
Supply Chain Integration and Optimization
The effectiveness of warehouse robotics systems is significantly enhanced when they are integrated into broader supply chain optimization strategies that encompass everything from supplier relationships and inventory management to transportation networks and customer delivery options. Both Amazon and Ocado have developed comprehensive approaches to supply chain integration that maximize the benefits of their robotic fulfillment capabilities while creating competitive advantages that extend beyond warehouse operations.
Amazon’s supply chain integration strategy leverages the company’s vast logistics network to optimize inventory placement, reduce transportation costs, and minimize delivery times through strategic positioning of products within the robotic fulfillment network. The predictive analytics capabilities of Amazon’s systems enable sophisticated demand forecasting that ensures optimal inventory levels while minimizing storage costs and reducing the risk of stockouts or excess inventory.
The integration of Amazon’s warehouse robotics with the company’s transportation and delivery networks has created a seamless flow of products from suppliers through fulfillment centers to customers, with robotic systems providing the reliability and predictability required for advanced logistics optimization. This integration has enabled Amazon to offer increasingly aggressive delivery commitments while maintaining operational efficiency and cost control.
Ocado’s approach to supply chain integration reflects the company’s focus on grocery fulfillment, where supply chain optimization must account for product perishability, temperature requirements, and the complex logistics of coordinating deliveries from multiple suppliers. The company’s robotic systems are integrated with sophisticated inventory management algorithms that optimize product rotation, minimize waste, and ensure optimal freshness for delivered products.
The predictive capabilities of Ocado’s systems enable advanced demand planning that helps suppliers optimize their own operations while ensuring that the automated fulfillment centers maintain optimal inventory levels across thousands of product categories. This collaborative approach to supply chain management has created efficiencies that benefit all participants in the grocery supply chain while improving service levels for end customers.
Innovation Trajectories and Future Development
The rapid pace of innovation in warehouse robotics and artificial intelligence suggests that the current generation of automated fulfillment systems represents only the beginning of a transformation that will continue to evolve and expand in scope and sophistication. Both Amazon and Ocado are actively developing next-generation technologies that promise to further enhance the capabilities and efficiency of automated warehouse operations while exploring new applications for robotic and AI technologies.
Amazon’s research and development efforts encompass multiple areas of innovation, including advanced manipulation robotics that could automate additional aspects of order fulfillment, machine learning algorithms that further optimize operational efficiency, and integration with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and advanced sensors. The company’s acquisition strategy has consistently focused on companies developing complementary technologies that could enhance warehouse automation capabilities.
The development of Amazon’s drone delivery program represents an extension of warehouse automation concepts into the last-mile delivery challenge, potentially creating an integrated system where robotic fulfillment centers directly interface with autonomous delivery systems. This integration could fundamentally transform the economics and speed of e-commerce delivery while creating new competitive advantages for companies capable of implementing such sophisticated technological systems.
Ocado’s innovation roadmap includes continued refinement of the grid-based fulfillment system, development of more sophisticated robotic handling capabilities, and expansion of artificial intelligence applications throughout the fulfillment process. The company’s focus on creating a technology platform that can be licensed to other retailers has driven innovation that addresses a broad range of fulfillment challenges while maintaining the flexibility required for different market conditions and operational requirements.
The convergence of warehouse robotics with emerging technologies such as augmented reality, advanced sensors, and next-generation artificial intelligence promises to create fulfillment capabilities that exceed current expectations for speed, accuracy, and cost efficiency. Both companies are well-positioned to capitalize on these technological developments while continuing to push the boundaries of what is possible in automated fulfillment operations.
Competitive Landscape and Market Impact
The advanced warehouse robotics capabilities developed by Amazon and Ocado have created significant competitive advantages that extend beyond operational efficiency to encompass customer experience, market expansion opportunities, and the ability to enter new geographic markets with reduced infrastructure requirements. These advantages have reshaped competitive dynamics within the e-commerce and grocery retail industries while creating pressure for other companies to develop or acquire similar technological capabilities.
Amazon’s warehouse robotics advantage has contributed to the company’s ability to offer increasingly aggressive shipping options, including same-day and next-day delivery services that would be economically unfeasible without the operational efficiencies provided by robotic fulfillment systems. This capability has forced competitors to invest in their own fulfillment technologies or partner with companies that possess advanced warehouse automation capabilities.
The scalability of Amazon’s robotic systems has enabled rapid expansion into new markets and product categories while maintaining consistent service levels and operational efficiency. This scalability advantage has proven particularly valuable in international expansion efforts where the ability to quickly establish efficient fulfillment capabilities provides significant competitive advantages over local competitors with traditional warehouse operations.
Ocado’s technology licensing strategy has created a unique competitive position where the company generates revenue from competitors while establishing its robotic fulfillment technology as an industry standard. This approach has enabled Ocado to expand its influence in the grocery retail industry beyond its direct operations while generating the resources required for continued technological innovation.
The success of both companies’ warehouse robotics initiatives has attracted significant attention from investors, technology companies, and potential competitors, leading to increased investment in warehouse automation technologies across the industry. This competition is driving continued innovation while creating opportunities for technology suppliers and reducing the barriers to entry for companies seeking to implement advanced fulfillment capabilities.
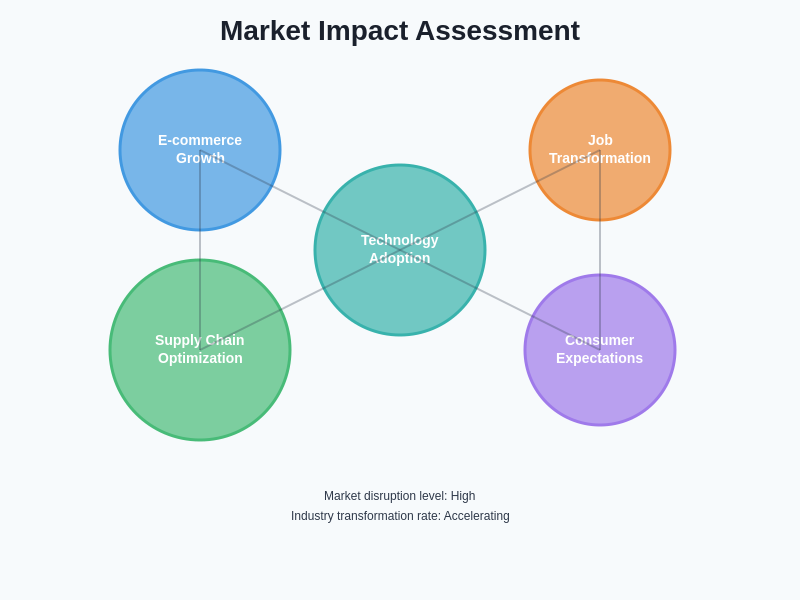
The long-term market impact of advanced warehouse robotics extends beyond immediate competitive advantages to include fundamental changes in consumer expectations, supply chain economics, and the geographic distribution of fulfillment capabilities that could reshape entire industries and economic regions.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
The environmental impact of warehouse operations has become an increasingly important consideration as companies face growing pressure to reduce their carbon footprint and adopt sustainable business practices. The advanced robotics systems implemented by Amazon and Ocado have created opportunities for significant environmental improvements while addressing the operational challenges associated with sustainable logistics and fulfillment operations.
Amazon’s robotic fulfillment centers have achieved substantial energy efficiency improvements compared to traditional warehouse operations, with robots designed for optimal energy consumption and warehouse layouts that reduce the need for extensive climate control systems. The company’s commitment to renewable energy for its operations extends to its fulfillment centers, where the predictable energy consumption patterns of robotic systems facilitate the integration of solar and other renewable energy sources.
The optimization algorithms used in Amazon’s robotic systems contribute to sustainability by minimizing unnecessary robot movements, optimizing inventory placement to reduce transportation requirements, and enabling more efficient packaging processes that reduce material waste. These operational improvements create environmental benefits while simultaneously reducing operational costs and improving service levels.
Ocado’s grid-based fulfillment system offers significant environmental advantages through its energy-efficient design, reduced space requirements compared to traditional warehouse operations, and the ability to operate with minimal lighting and climate control in robot-operated areas. The company’s focus on grocery fulfillment has also driven innovations in sustainable packaging and food waste reduction that contribute to overall environmental sustainability.
The predictive capabilities of Ocado’s systems enable better inventory management that reduces food waste while optimizing delivery routes to minimize transportation-related emissions. The company’s investment in electric delivery vehicles and sustainable packaging materials demonstrates how warehouse automation can be integrated with broader sustainability initiatives to create comprehensive environmental benefits.
The continued development of warehouse robotics technologies presents opportunities for further environmental improvements, including integration with renewable energy systems, development of more energy-efficient robotic systems, and optimization algorithms that consider environmental impact alongside operational efficiency in their decision-making processes.
Global Expansion and Technology Transfer
The success of advanced warehouse robotics systems developed by Amazon and Ocado has created opportunities for global expansion and technology transfer that extend the impact of these innovations beyond their original markets and applications. The scalability and adaptability of robotic fulfillment systems enable deployment in diverse geographic and cultural contexts while maintaining the operational advantages that drive their initial success.
Amazon’s global expansion strategy leverages the company’s warehouse robotics capabilities to establish efficient fulfillment operations in new markets without requiring the extensive local logistics infrastructure that might otherwise limit expansion opportunities. The standardization of robotic systems across geographic regions enables consistent operational practices while allowing for local adaptation based on market-specific requirements and regulatory considerations.
The transfer of Amazon’s warehouse robotics technology across international operations has demonstrated the adaptability of automated fulfillment systems to different labor markets, regulatory environments, and consumer expectations. This flexibility has enabled Amazon to maintain competitive advantages in diverse markets while contributing to the global diffusion of advanced warehouse automation technologies.
Ocado’s technology licensing strategy represents a unique approach to global expansion that enables rapid market entry through partnerships with established retailers while generating revenue from technology transfer and ongoing support services. This model has enabled Ocado to expand its influence in global grocery retail while providing local retailers with access to world-class fulfillment technology that might otherwise require years of development and substantial capital investment.
The international licensing of Ocado’s Smart Platform has created opportunities for technology adaptation and local innovation that enhance the system’s capabilities while addressing market-specific requirements. This collaborative approach to technology development has accelerated innovation while creating a global network of retailers utilizing advanced warehouse automation technologies.
The continued global expansion of warehouse robotics technologies promises to create new opportunities for innovation and efficiency improvements while contributing to the development of more sophisticated and capable automated fulfillment systems that benefit retailers, consumers, and the broader logistics industry worldwide.
Future Implications and Industry Transformation
The warehouse robotics innovations pioneered by Amazon and Ocado represent the foundation for a broader transformation of logistics and fulfillment operations that will continue to evolve and expand in scope and sophistication. The success of these systems has demonstrated the viability of large-scale warehouse automation while creating competitive pressures that are driving innovation throughout the industry and related sectors.
The continued advancement of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotics technologies promises to enable even more sophisticated warehouse automation systems that could further reduce human involvement in routine operations while enhancing the capabilities available for complex decision-making and exception handling. These developments could create fulfillment systems that approach complete automation while maintaining the flexibility required for diverse product categories and operational requirements.
The integration of warehouse robotics with emerging technologies such as autonomous vehicles, advanced sensors, and next-generation artificial intelligence could create end-to-end automated supply chain systems that transform the economics and capabilities of logistics operations. These integrated systems could enable new business models and service offerings while creating competitive advantages that reshape entire industries.
The democratization of warehouse automation technologies through improved accessibility and reduced implementation costs could enable smaller retailers and logistics companies to access advanced fulfillment capabilities that are currently available only to large-scale operators. This democratization could create more competitive market conditions while accelerating the adoption of automated fulfillment technologies across diverse market segments.
The long-term implications of warehouse robotics extend beyond operational improvements to encompass fundamental changes in employment patterns, urban planning, and the geographic distribution of economic activity. The ability to operate efficient fulfillment centers with reduced labor requirements could enable warehouse operations in locations that might not otherwise be viable while creating new opportunities for economic development and job creation in technology-related roles.
The continued evolution of warehouse robotics and artificial intelligence promises to unlock new levels of efficiency, accuracy, and capability that will benefit consumers, retailers, and the broader economy while creating opportunities for innovation and growth that extend far beyond the logistics industry itself.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional advice. The information presented is based on publicly available data and industry analysis regarding warehouse robotics and automation technologies. Readers should conduct their own research and consult with qualified professionals when making decisions related to warehouse automation investments or implementations. The effectiveness and suitability of robotic fulfillment systems may vary depending on specific operational requirements, market conditions, and organizational capabilities.